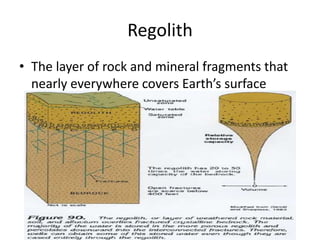
Soil is formed from weathered rock and organic matter and varies in composition with depth, forming distinct horizons. It consists of minerals, organic matter, water, and air. The type of soil depends on the parent material and climate, with pedalfer soils found in humid regions, pedocal soils in drier areas, and laterite soils in the tropics. However, human activities like agriculture and construction can accelerate erosion and damage soil formation.