Embed presentation
Download to read offline





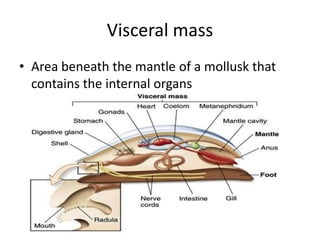








This document defines and describes several key anatomical features and concepts related to mollusks, including the trochophore larval stage, foot, mantle, shell, visceral mass, radula, siphon, and open circular blood system. It also outlines the basic body plans of mollusks in general, as well as the distinguishing characteristics of gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods.













