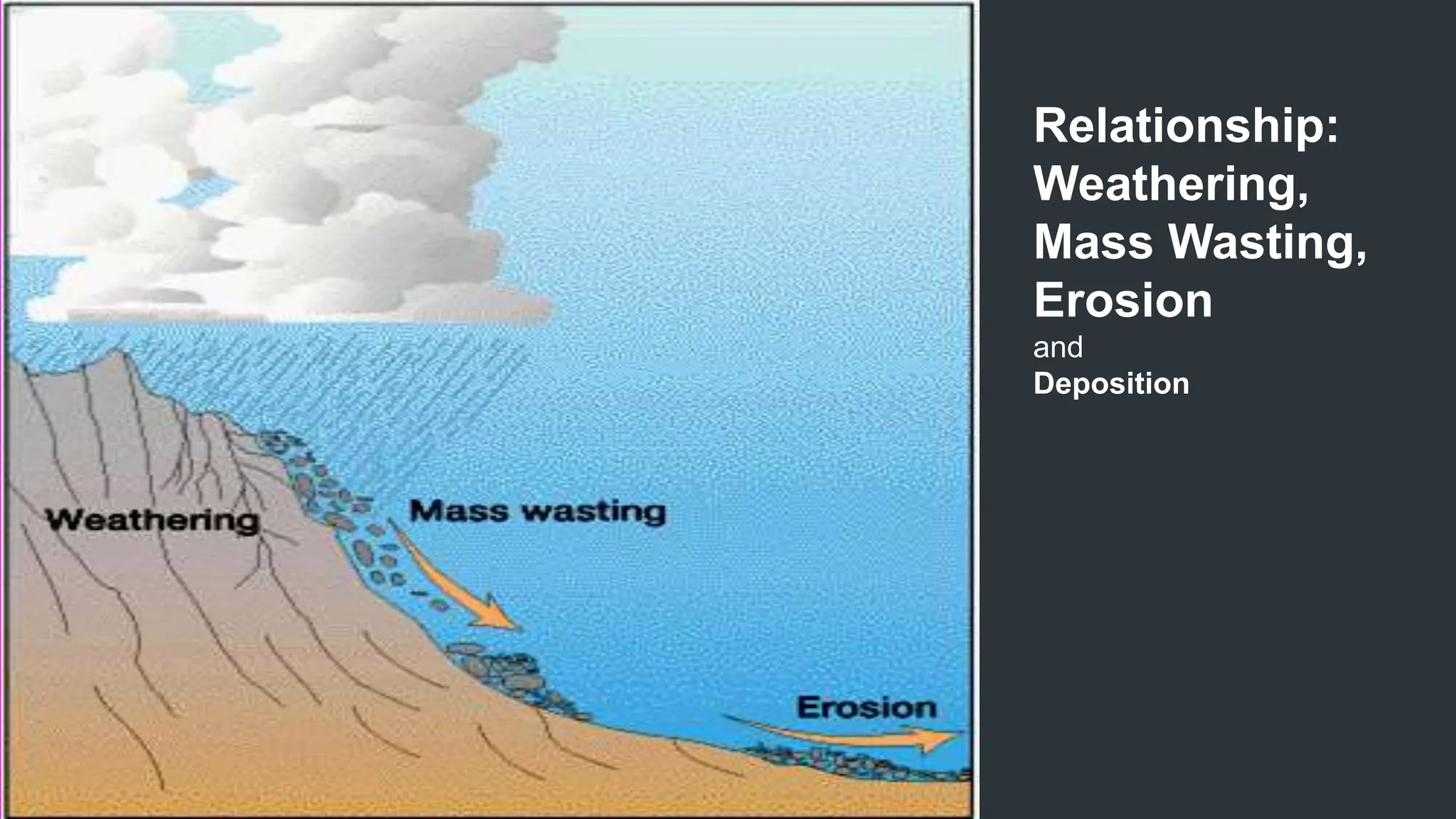
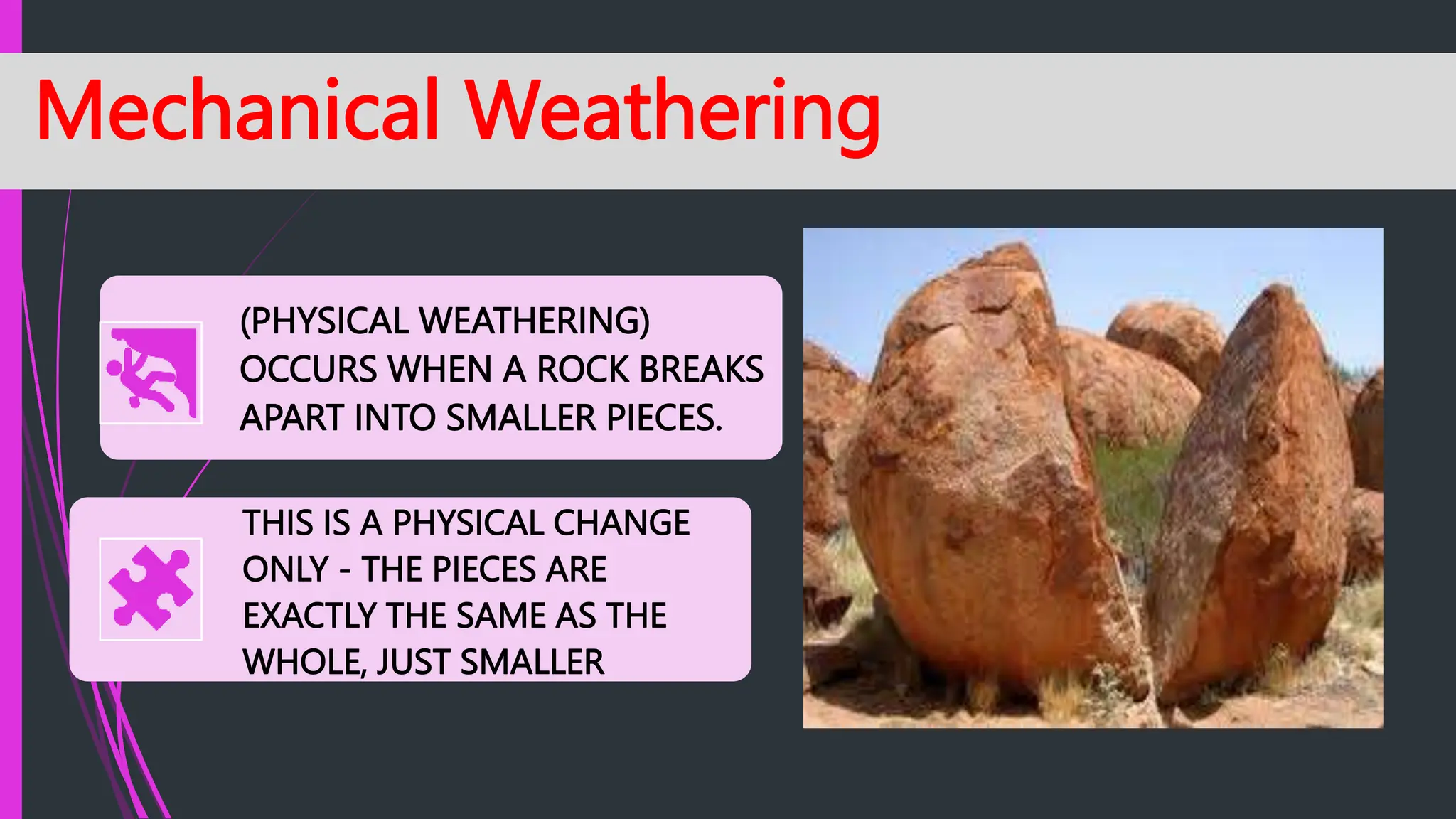
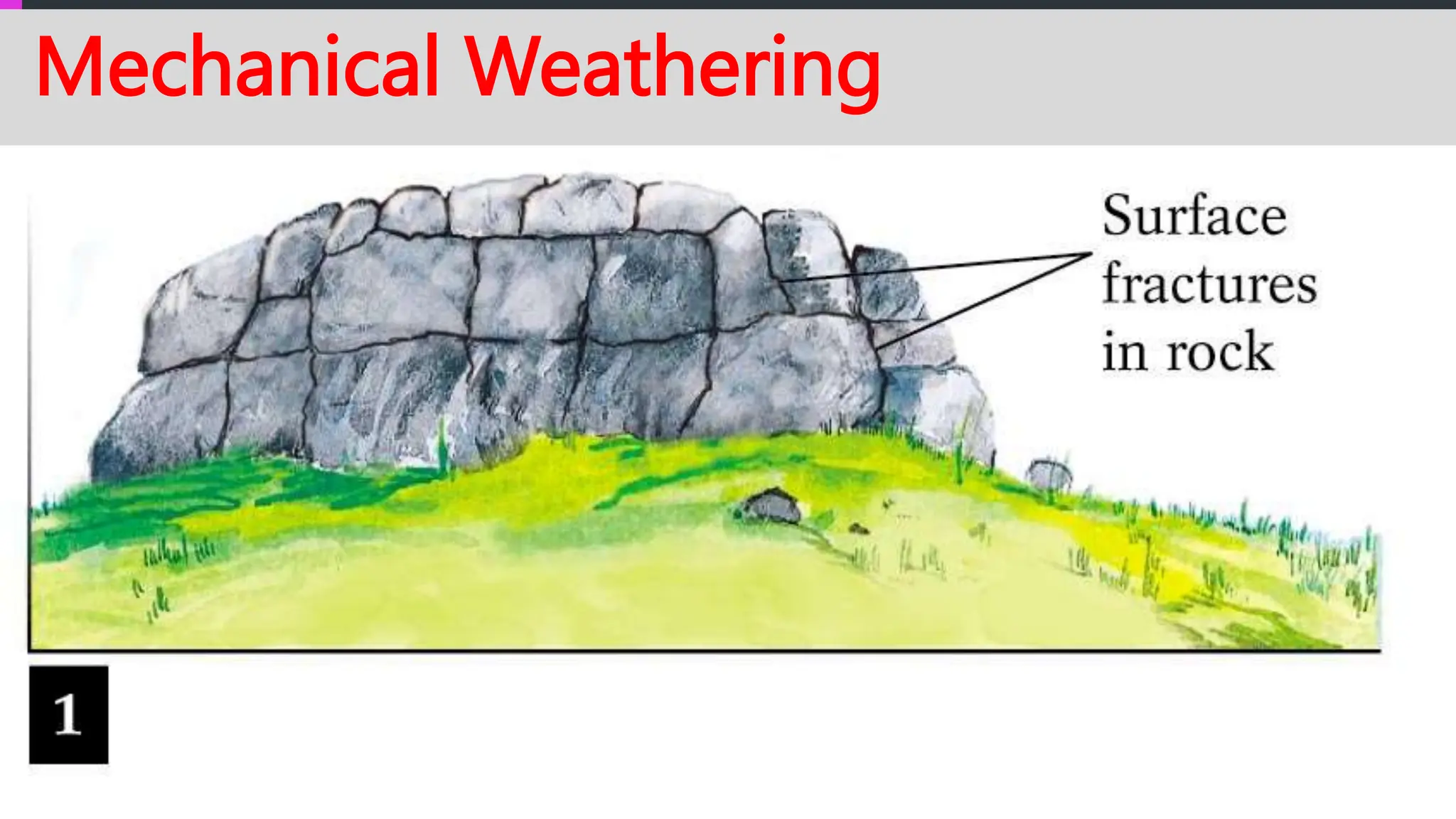
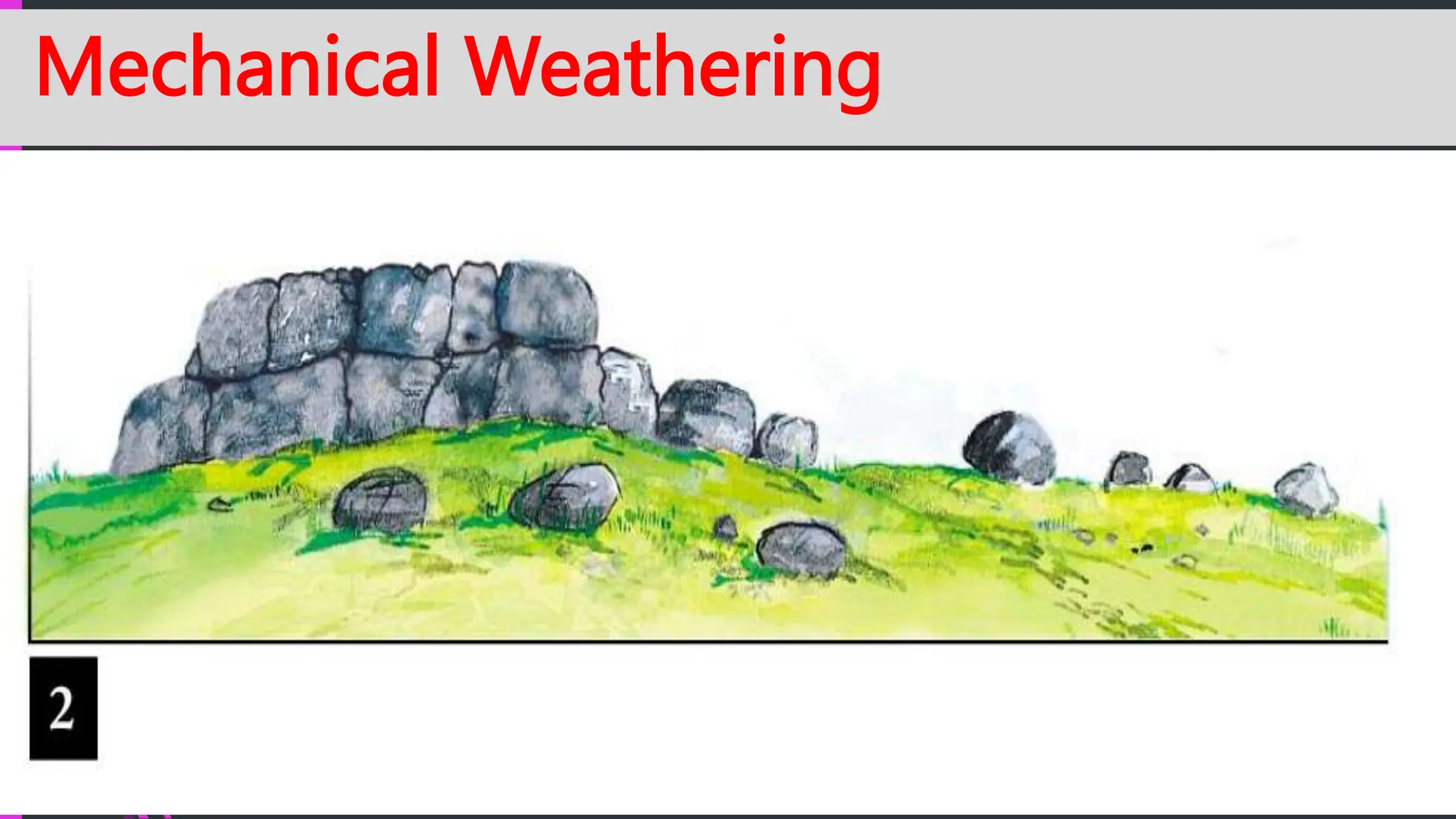
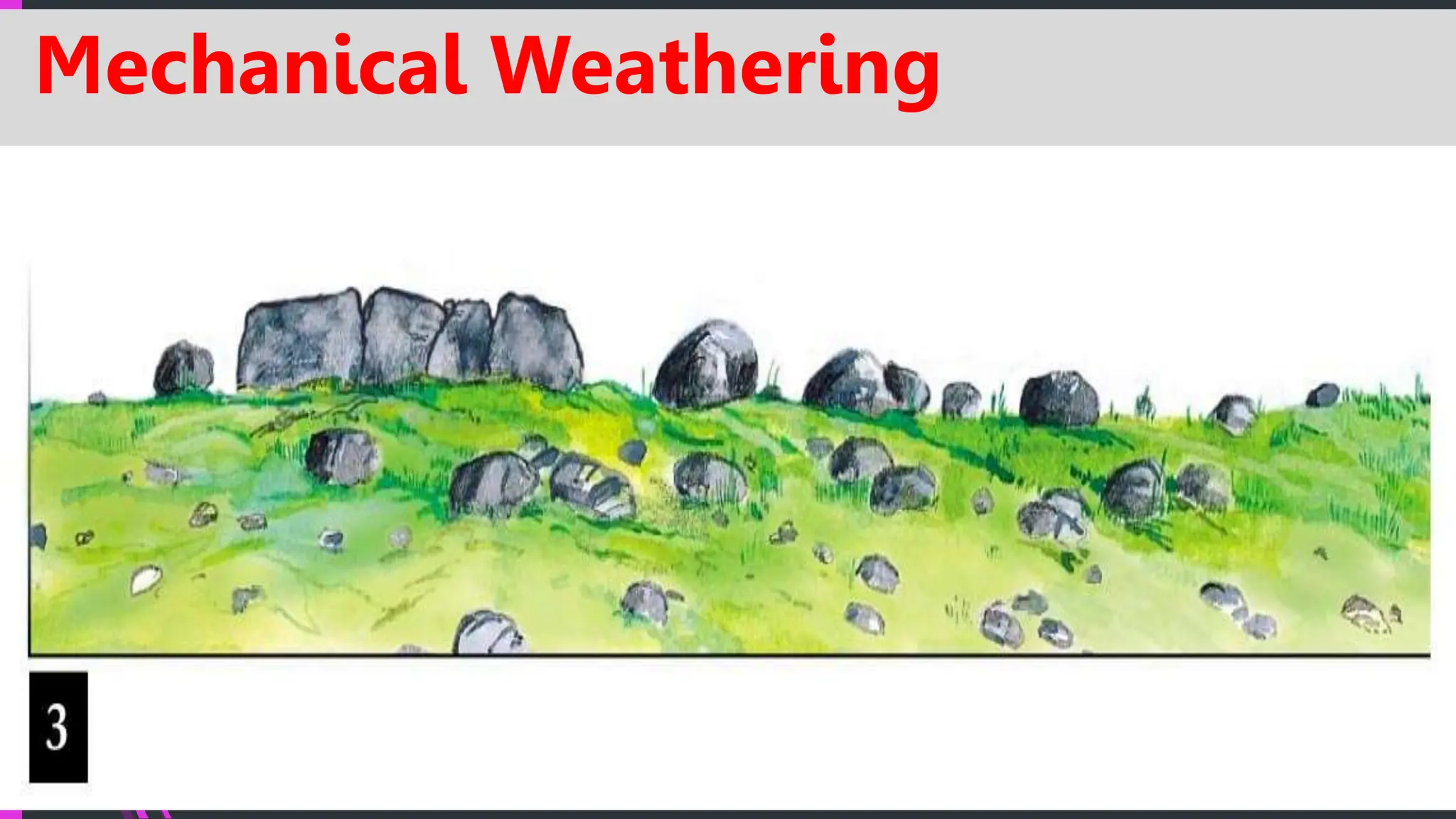
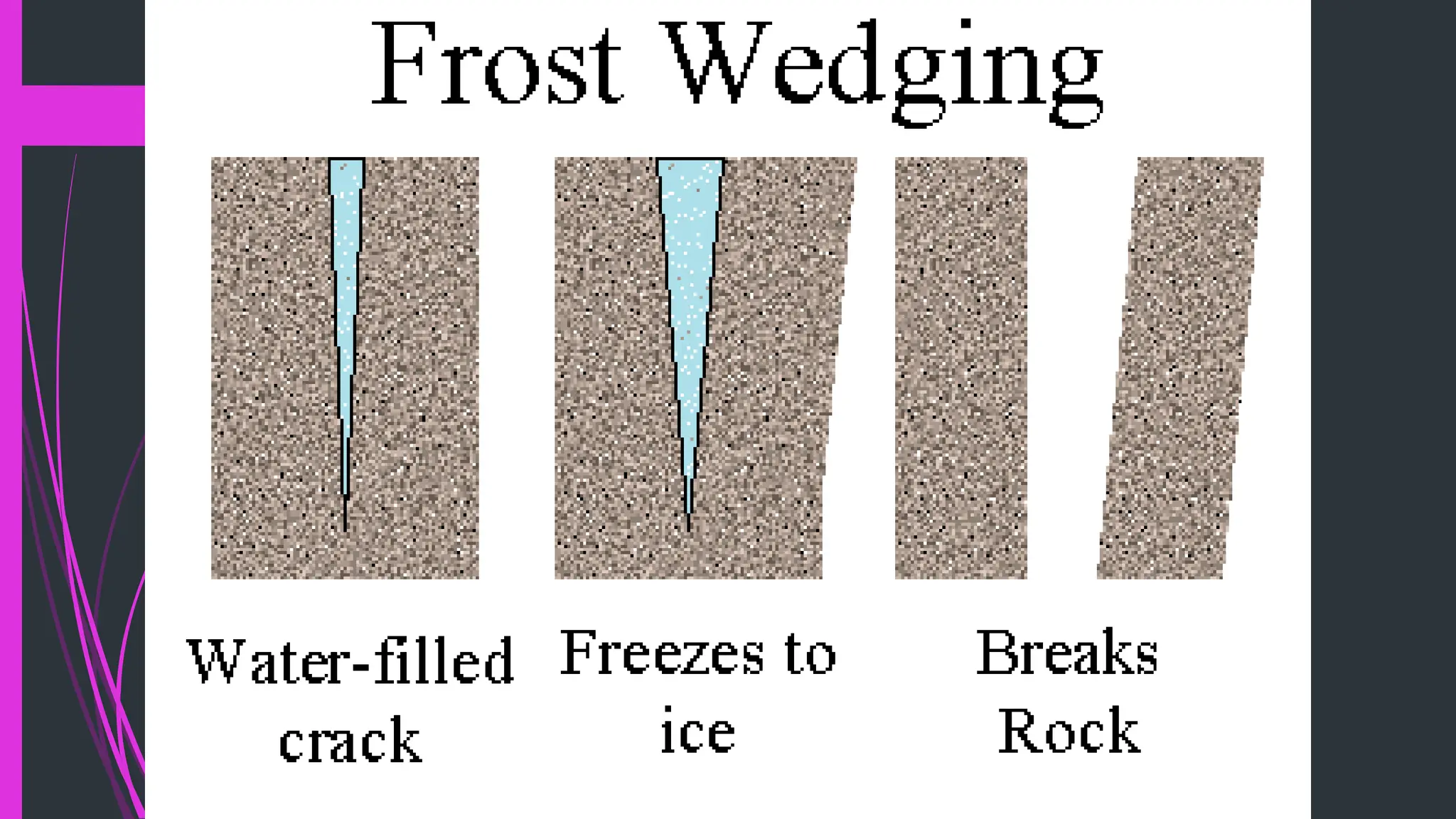
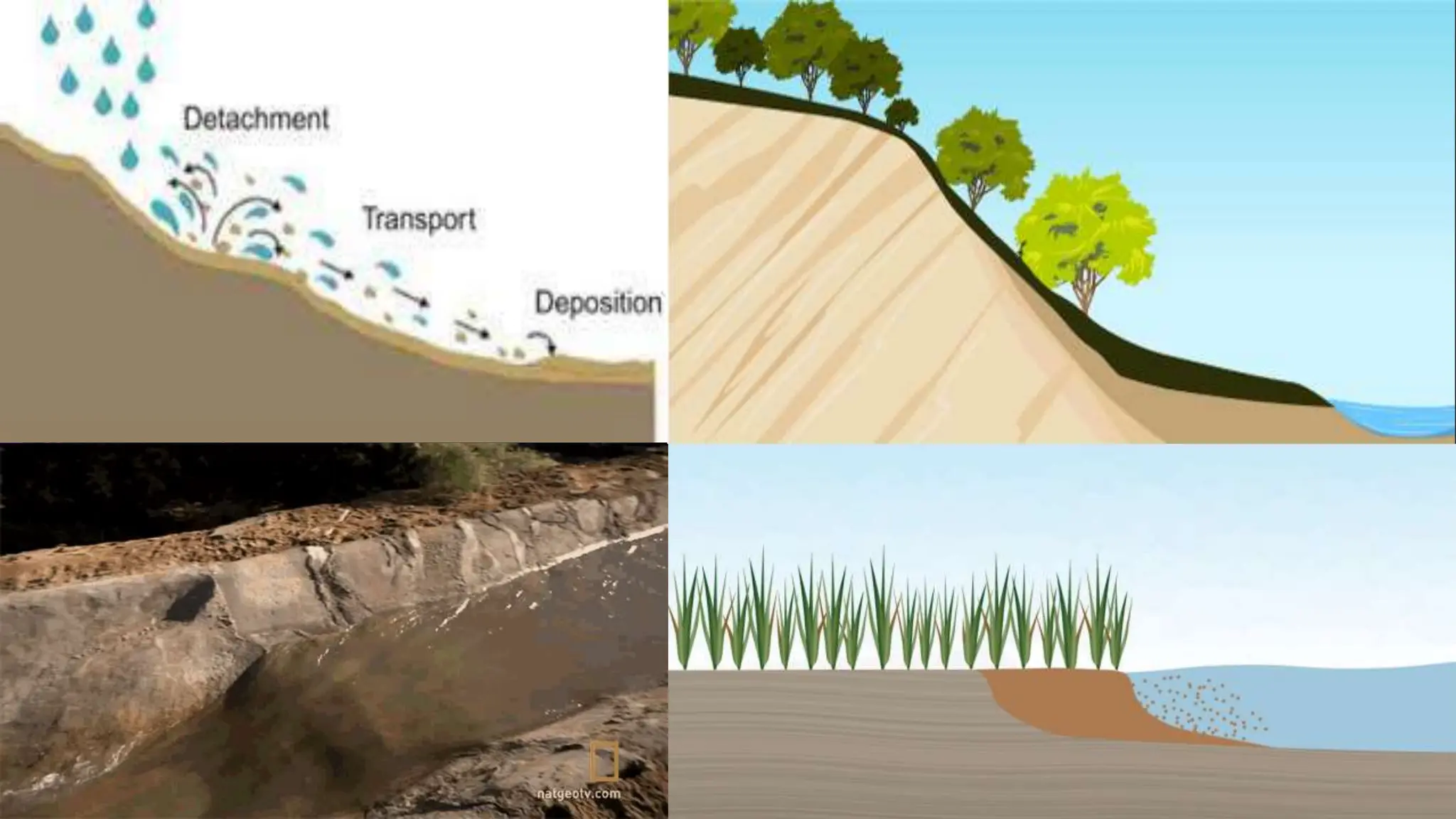
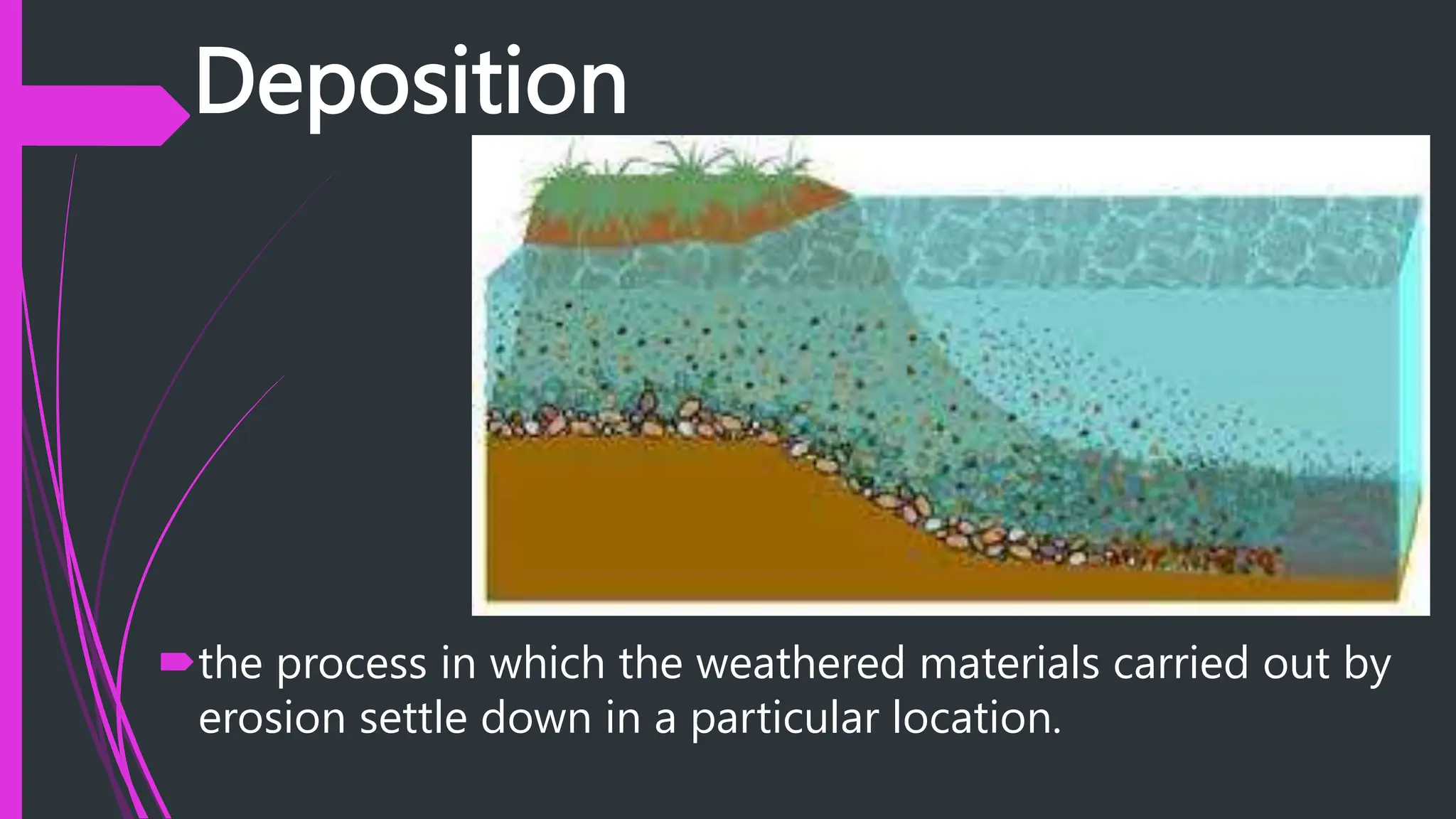
The document explains how rocks break down through weathering, erosion, and deposition, categorizing weathering into mechanical and chemical types. Key processes include mechanical actions like frost wedging and biological weathering, as well as chemical changes caused by hydrolysis and oxidation. Erosion involves the transportation of weathered materials, influenced by natural agents, while mass wasting describes the downslope movement of sediments due to gravity.