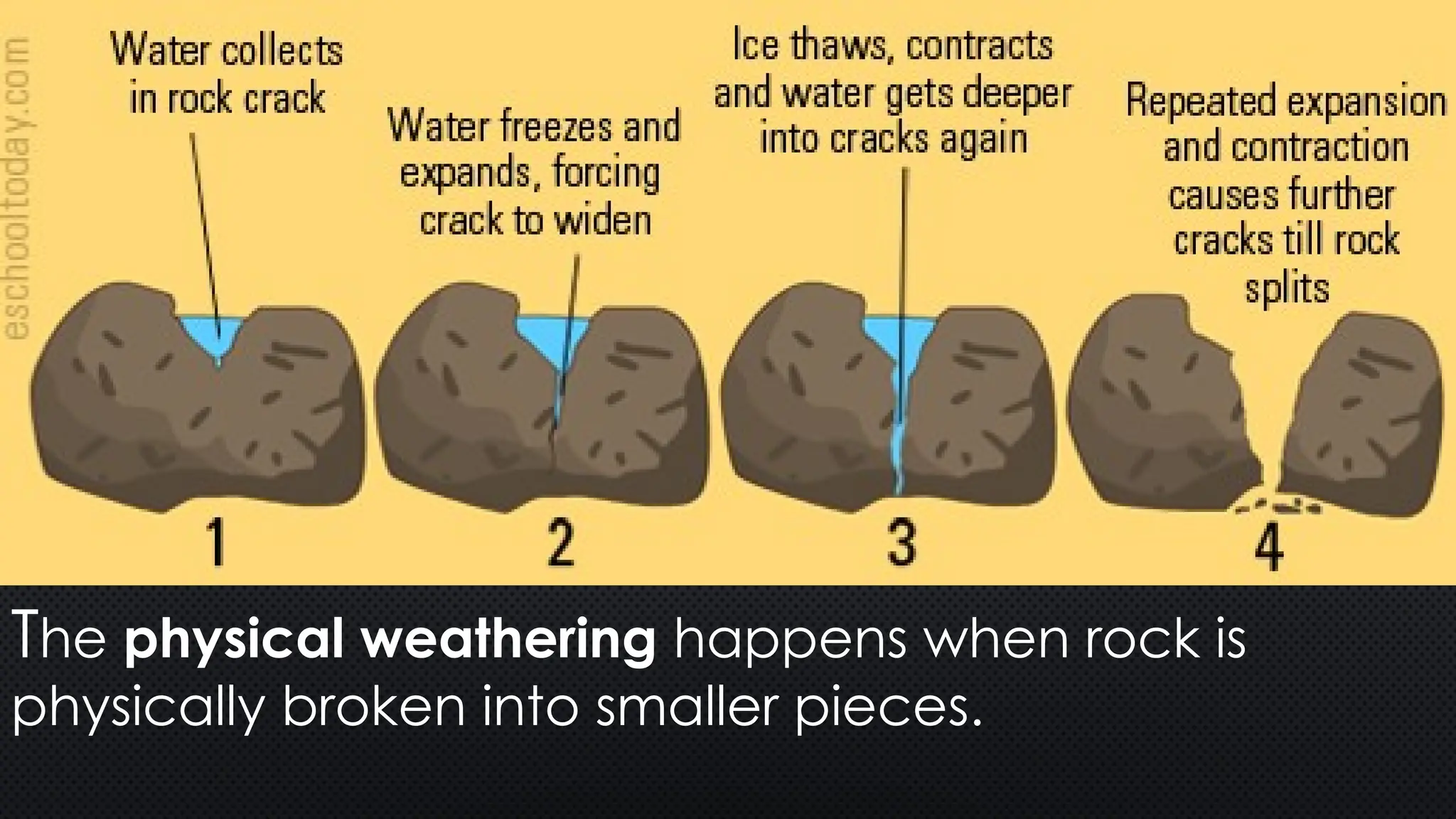
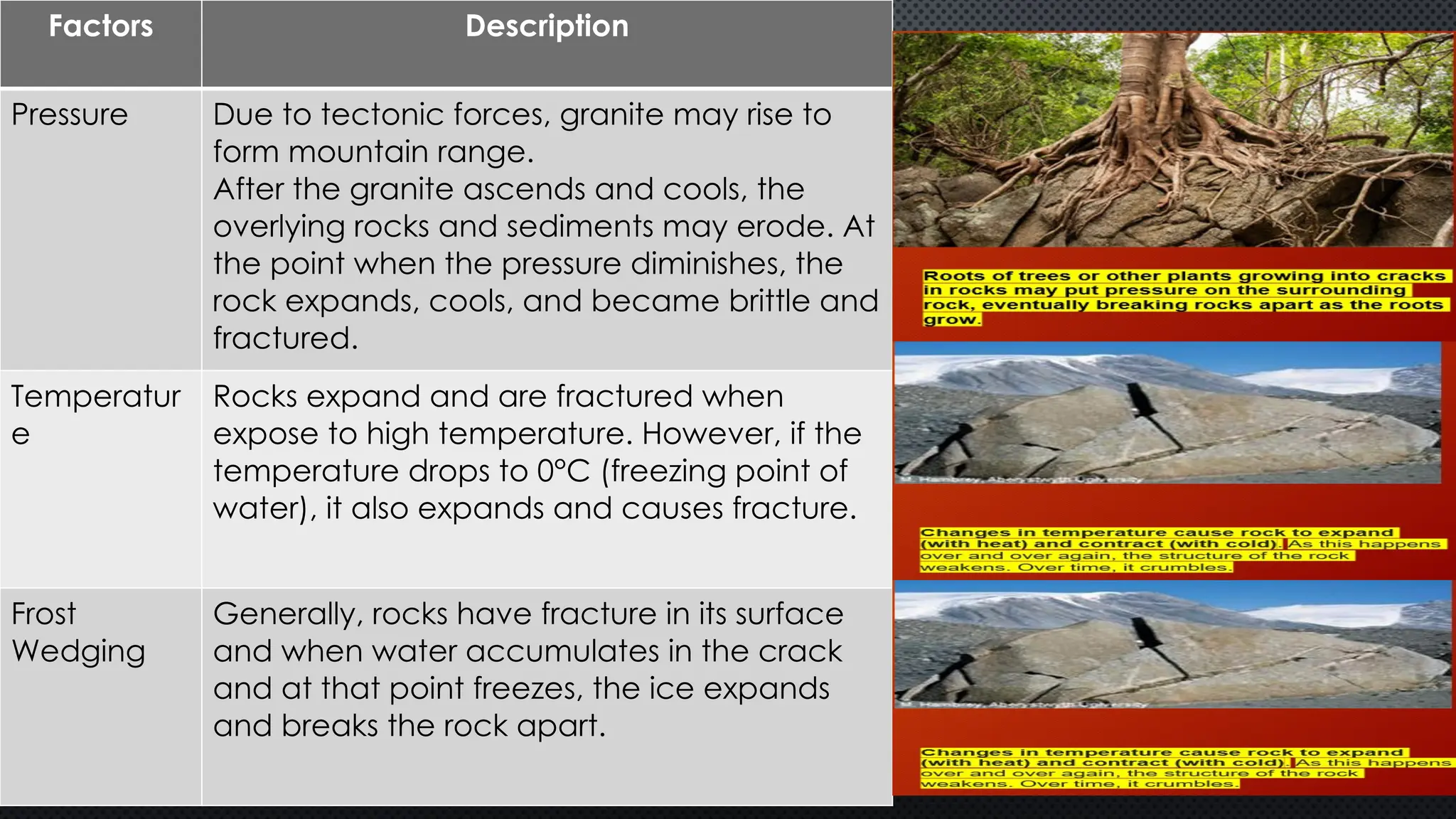
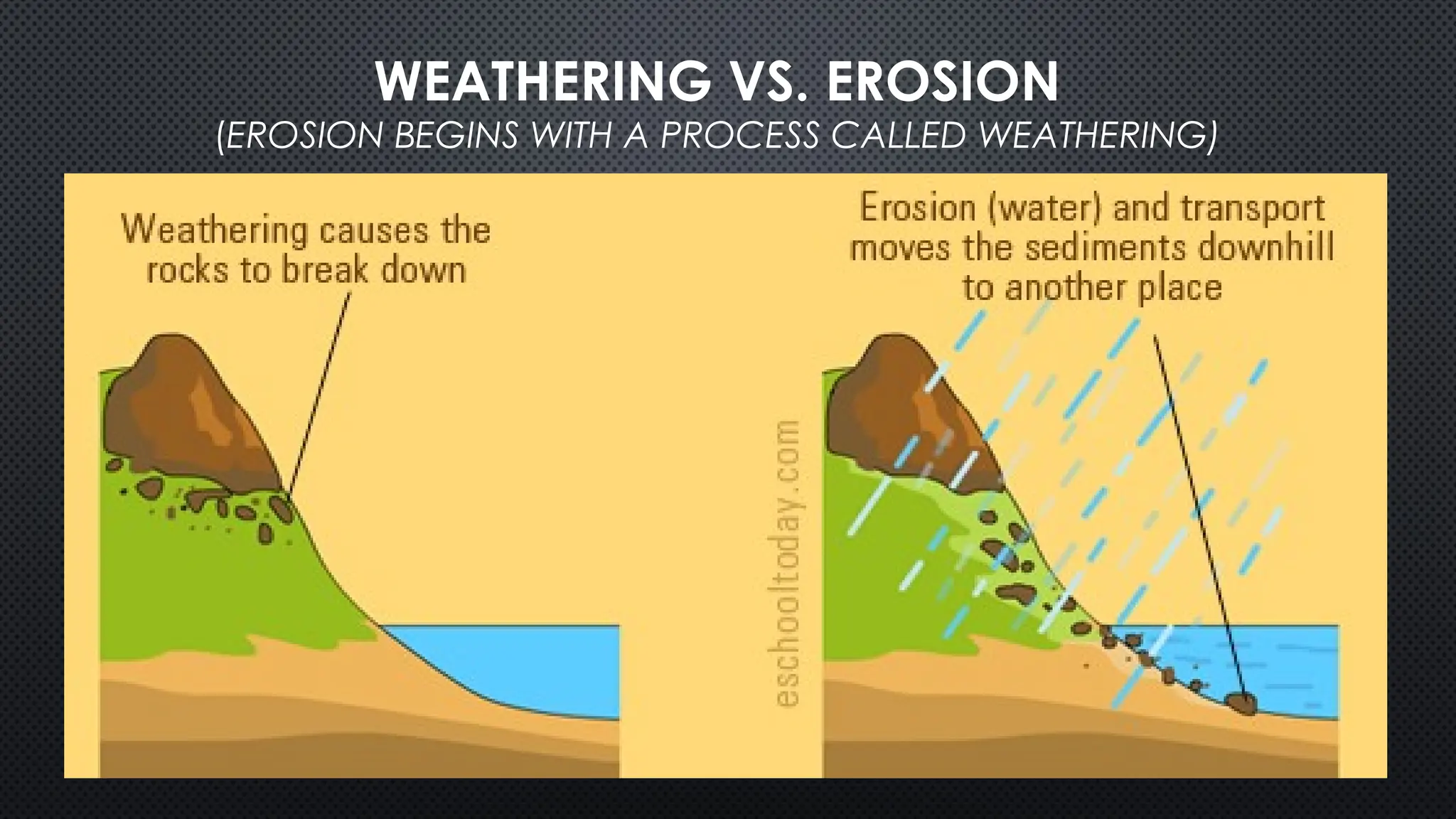
The document outlines various geological processes, focusing on the formation and transformation of rocks through weathering, erosion, and deposition. It distinguishes between exogenic and endogenic processes, describing mechanical and chemical weathering mechanisms and their environmental impacts. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of water, wind, and gravity in erosion, as well as factors influencing mass wasting.