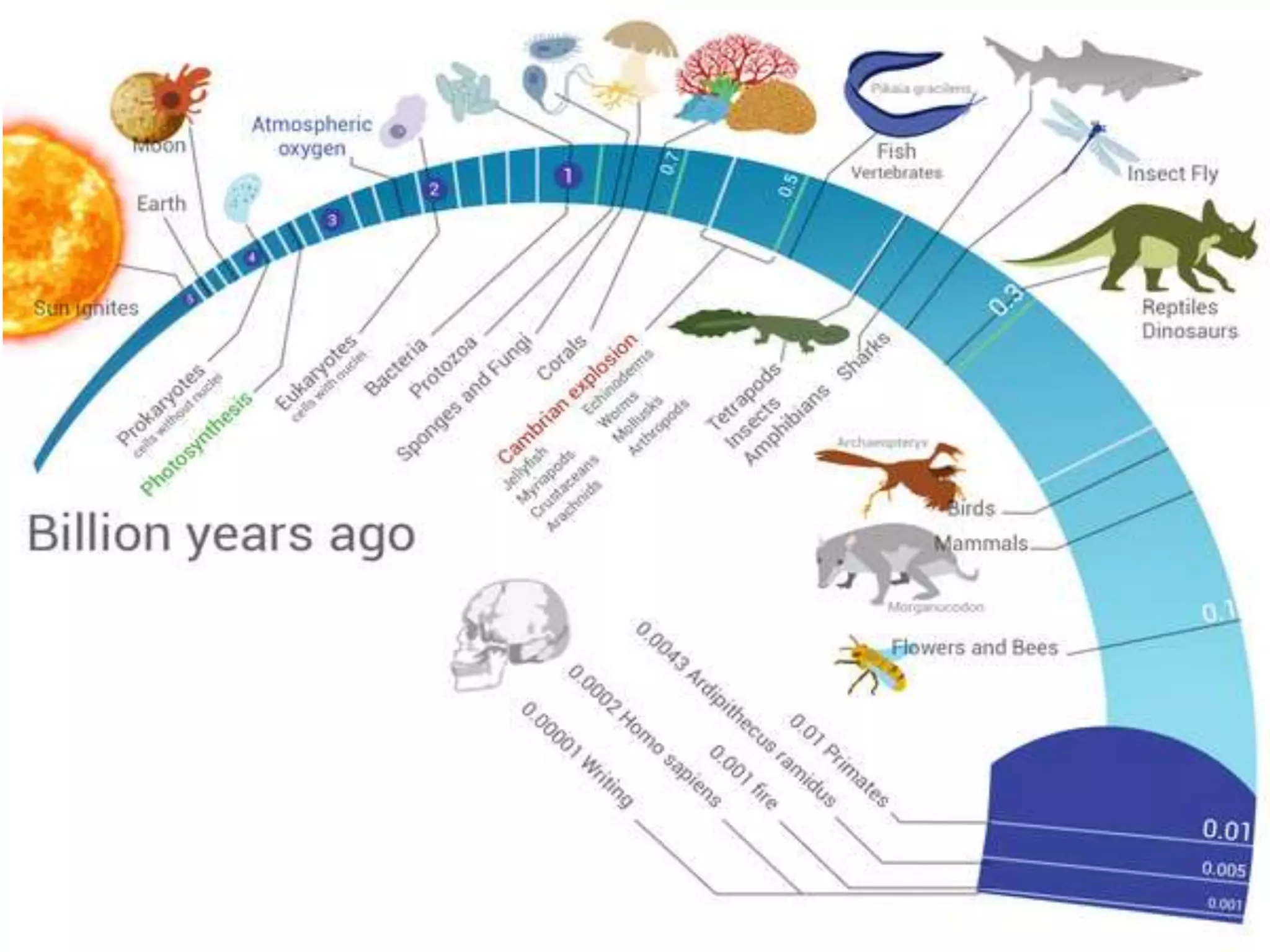
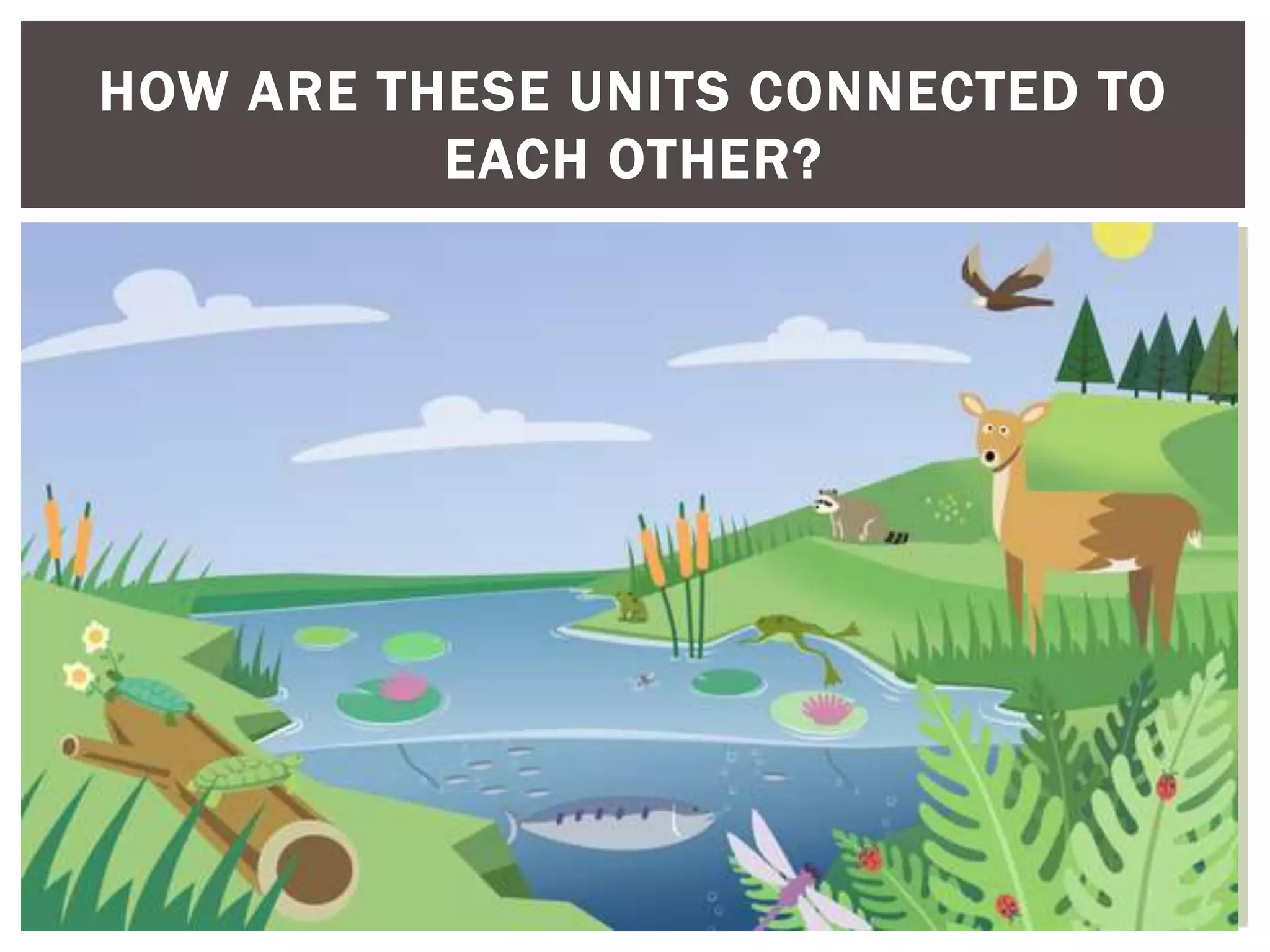
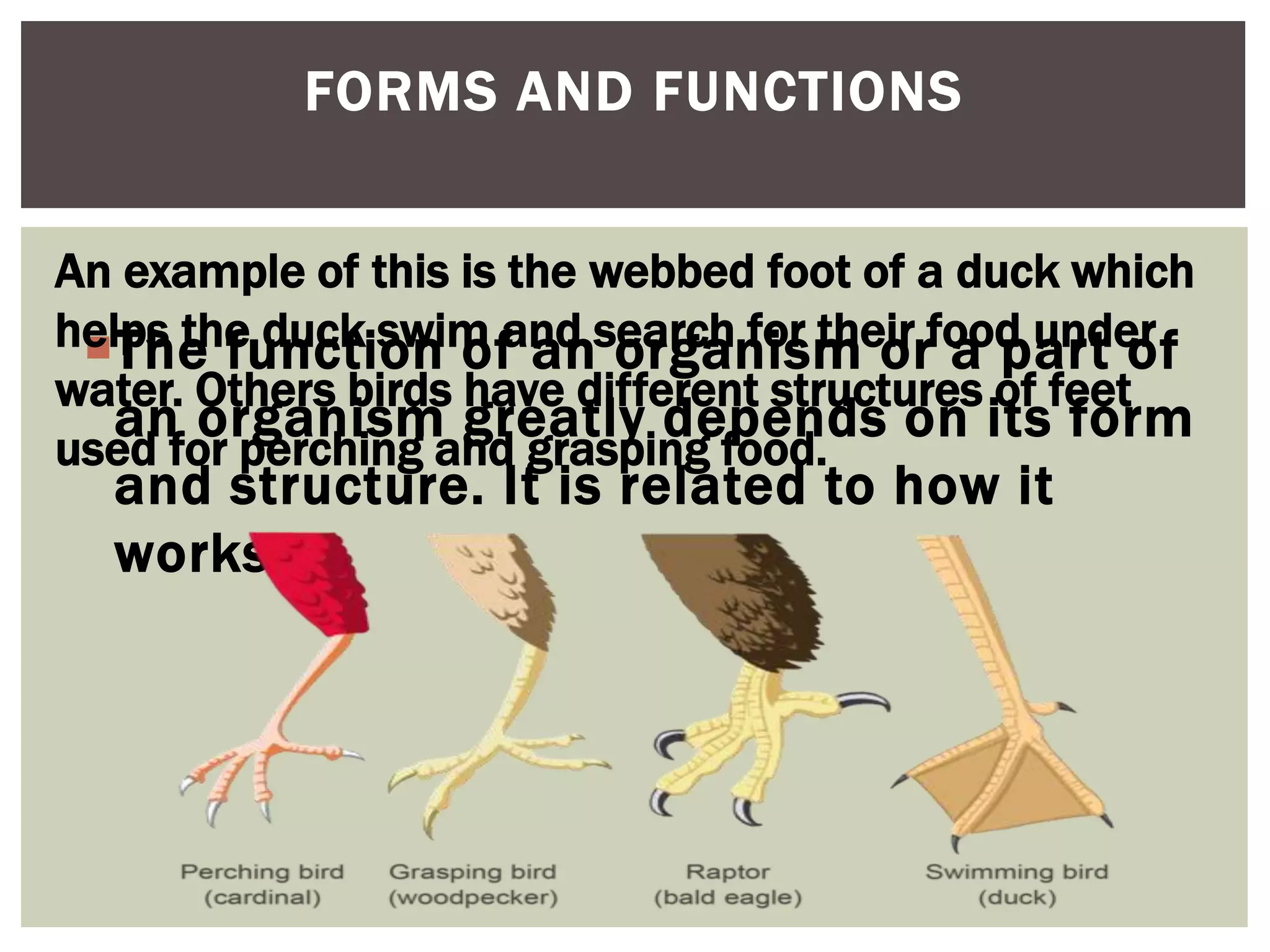
There are several theories about how life originated on Earth. One of the most widely accepted is the primordial soup theory, which proposes that life began in a "soup" of organic molecules. Scientists like Stanley Miller and Harold Urey conducted experiments to test this theory by simulating early Earth conditions and forming amino acids, the building blocks of life. Other experiments explored how self-replicating molecules like RNA could form protocells, the simplest early life forms. These experiments helped connect abiotic chemistry to the emergence of the first living organisms and showed how the basic requirements for life could arise naturally under plausible early Earth conditions.