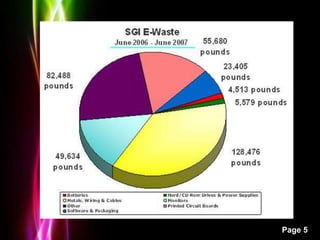
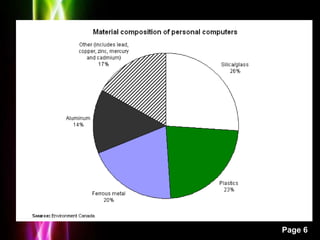
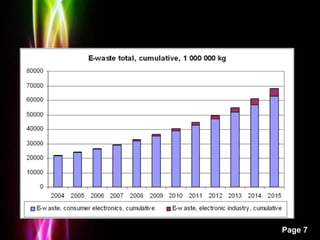
This presentation discusses electronic waste (e-waste) and its impacts. It begins with an introduction to e-waste, defining it as electronic appliances such as computers, phones, and TVs that are disposed of by their original users. It then outlines the impacts of e-waste, such as the release of toxic materials like lead and dioxins when e-waste is burned. The presentation notes that e-waste is one of the fastest growing waste streams and discusses the problems associated with improper e-waste disposal and management in India. It concludes by stressing the importance of creating a national framework for environmentally sound e-waste management through public awareness, detailed inventories, and pilot collection/recycling schemes.