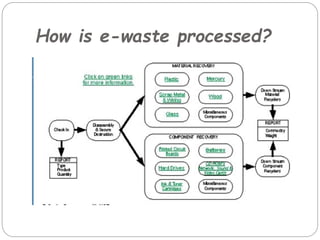
This document provides an overview of e-waste (electronic waste) processing. It begins by defining e-waste and listing some of the common electronic devices that are considered e-waste. It then discusses some of the drawbacks of e-waste, such as security and privacy risks from discarded hard drives and environmental pollution caused by chemicals in electronics. The document outlines the need for e-waste processing to reduce pollution and notes some of the equipment used in processing, including equipment for processing cathode ray tubes, printed circuit boards, and cables/wires. It provides a brief overview of how e-waste is typically processed, including dismantling, shredding, and separating materials. It also mentions some of the difficulties in processing