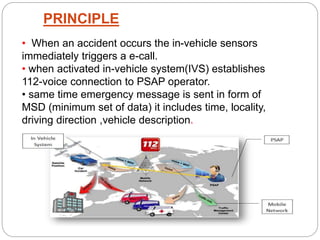
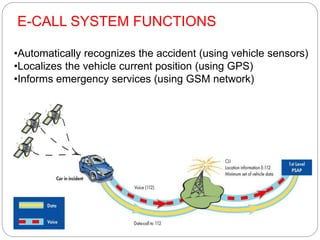
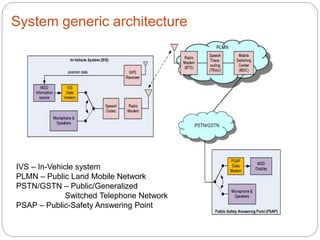
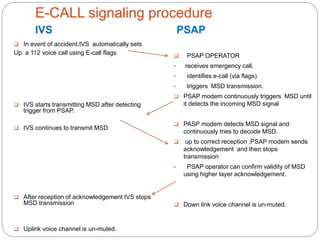
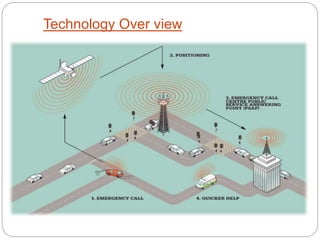
The document discusses e-call systems, which automatically connect to emergency services in the event of a vehicle accident. E-call systems use in-vehicle sensors to detect accidents and GPS to locate the vehicle. They then make an emergency 112 voice call and transmit a minimum set of data about the time, location, and vehicle. This allows emergency responders to arrive faster, which can save thousands of lives each year by reducing the time between an accident and medical assistance. The technology is complex but becoming mandatory in new European vehicles by 2015 due to its life-saving benefits.