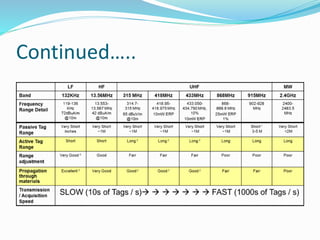
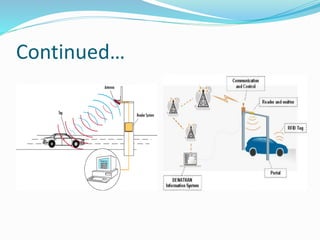
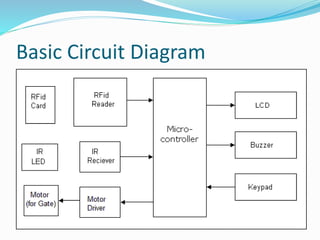
The document describes an automatic toll collection system using RFID technology. The system aims to reduce waiting times at toll queues, provide an easy payment method for travelers, and reduce illegal toll gate entry. The system works by using passive RFID tags attached to vehicles that are read by antennas at the toll gate. When a vehicle approaches with a tag, the tag information is wirelessly transmitted to a central database. If the account is in good standing, the toll is deducted from the driver's prepaid account and a green light lets the vehicle pass through without stopping. The automatic RFID toll collection system provides a contactless and paperless way to pay tolls and helps reduce traffic at toll gates.