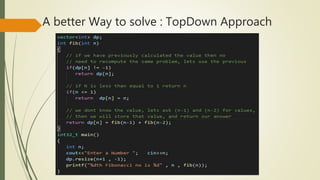
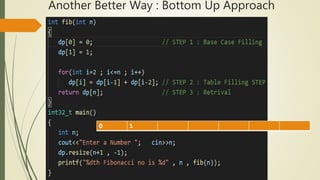
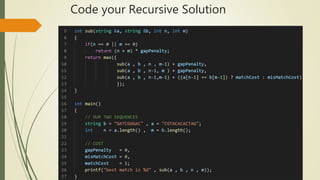
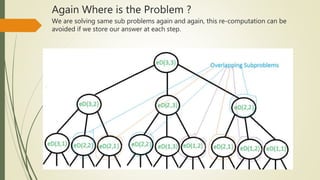
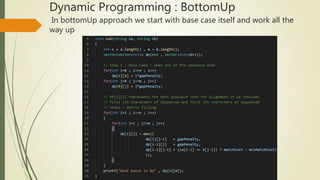
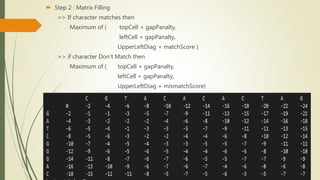
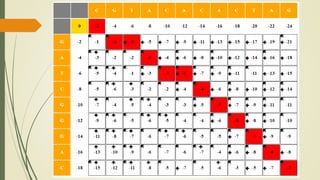
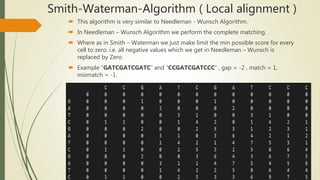
Dynamic programming can be used to solve the sequence alignment problem of finding the optimal cost of aligning two sequences. It avoids recomputing the same subproblems as recursion by storing the results in a 2D table. The Needleman-Wunsch algorithm uses a bottom-up dynamic programming approach to fill the table and find the optimal alignment cost between the sequences. It then traces back through the table to retrieve the optimal alignment. The Smith-Waterman algorithm is similar but limits scores to be non-negative to find local rather than global alignments.