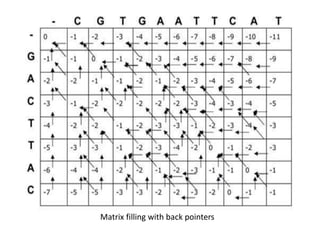
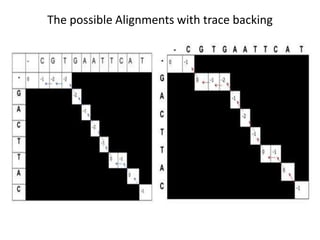
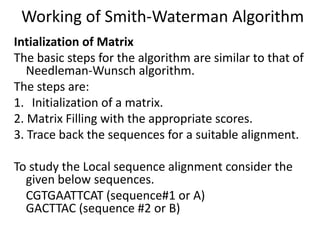
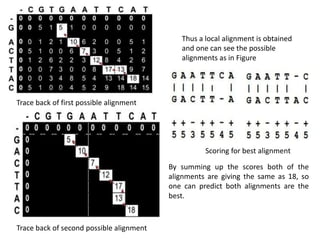
The document discusses global and local sequence alignment algorithms. It explains that global alignment algorithms align sequences from start to end by adding gaps, while local alignment finds regions of highest similarity. The Needleman-Wunsch algorithm performs global alignment using dynamic programming to find the best end-to-end match. The Smith-Waterman algorithm performs local alignment using dynamic programming to find the best local matches between sequences. Both algorithms initialize a scoring matrix and fill it using neighboring cell scores to trace back the highest scoring alignments.


![Global Alignment
This is generally known as the Needleman-Wunsch
algorithm, after the first paper in the field of
computational molecular biology to apply dynamic
programming to the global alignment problem.
[Needleman, S.B. & Wunsch, C.D. (1970) “A general
method applicable to the search for similarities in
the amino acid sequences of two proteins.” J. Mol.
Biol. 48:443-453.]
The Needleman-Wunsch algorithm creates a global
alignment over the length of both sequences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-230521122442-1799724f/85/5-Global-and-Local-Alignment-Algorithms-pptx-3-320.jpg)


![Local alignment
Smith & Waterman proposed simply that a local
alignment of two sequences allow arbitrary-
length segments of each sequence to be aligned,
with no penalty for the unaligned portions of the
sequences. Otherwise, the score for a local
alignment is calculated the same way as that for a
global alignment.
[Smith, T.F. & Waterman, M.S. (1981)
“Identification of common molecular
subsequences.” J. Mol. Biol. 147:195-197.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-230521122442-1799724f/85/5-Global-and-Local-Alignment-Algorithms-pptx-6-320.jpg)