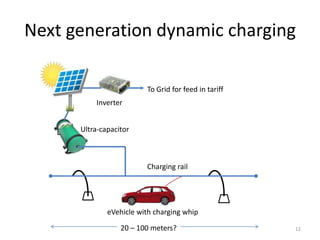
This document discusses the concept of dynamic or on-the-move charging of electric vehicles. It outlines some current limitations of electric vehicles like high costs, limited range, and long charging times. It then proposes using dynamic charging systems that would allow electric vehicles to charge while in motion or stopped briefly rather than requiring lengthy stationary charging sessions. Some key advantages noted are smaller batteries, more frequent smaller charges extending battery life, and reducing range anxiety. Two approaches - induction and overhead capacitive charging - currently being tested are described. The concept proposes a next-generation dynamic system using ultracapacitors charged by solar panels and discharged to vehicles' batteries while in motion. Key research areas are identified to develop such a system. Initial target markets like drive