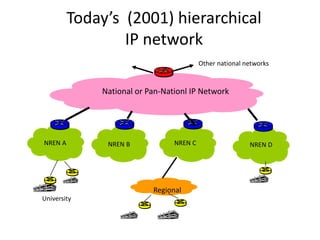
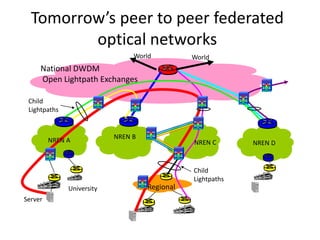
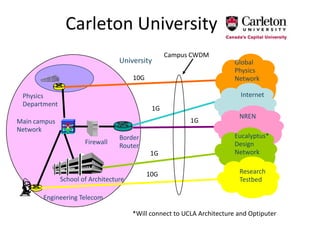
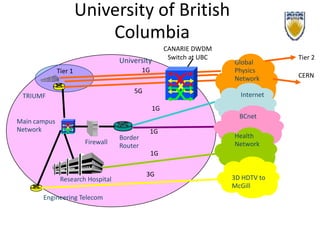
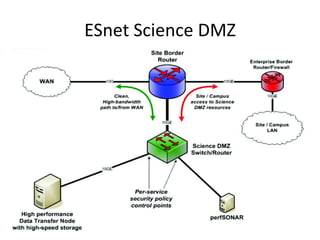
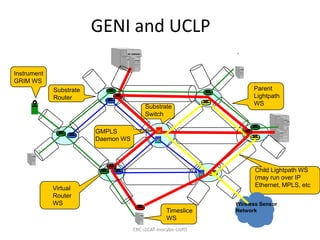
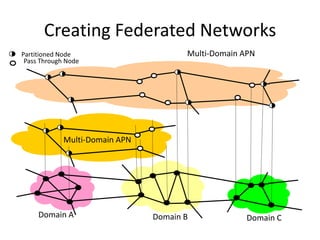
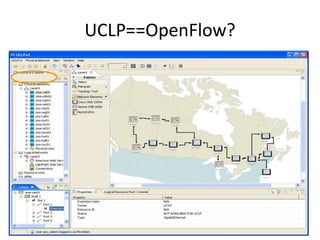
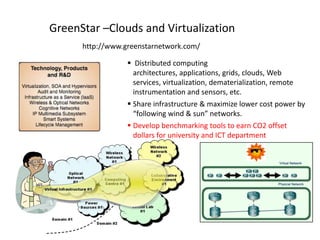
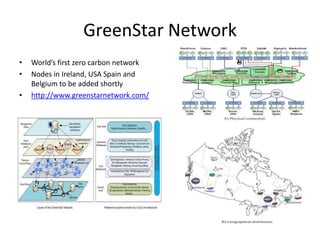
This document discusses the evolution of research and education networks from hierarchical IP networks of the past to more direct optical connections through peer-to-peer federated optical networks in the future. It notes the limitations of past hierarchical networks and outlines a vision for optical lightpath exchanges (GOLEs) that allow for end-to-end solutions across independent networks. Specific examples of Canadian universities integrating into this new federated network model are provided. The challenges of increasing costs, energy consumption, and climate change impacts on networks are also discussed, along with predictions that federated optical networks and relocating data centers to colder climates can help significantly reduce energy costs and emissions.