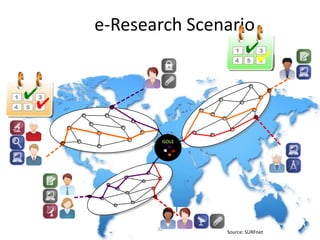
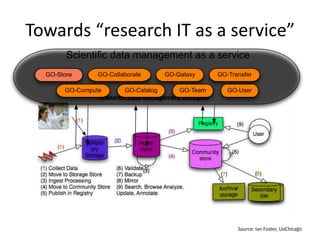
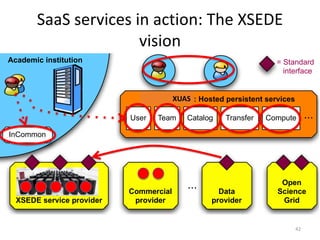
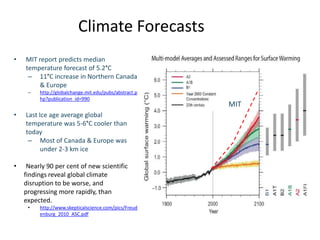
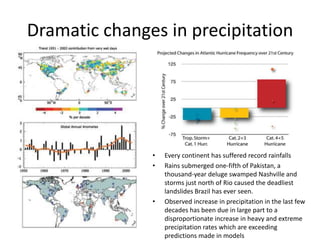
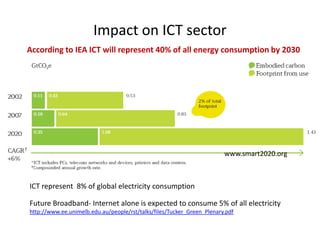
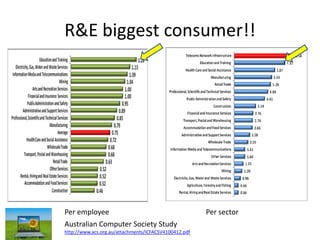
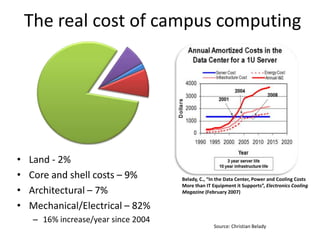
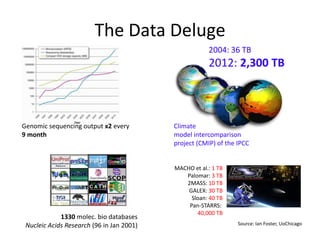
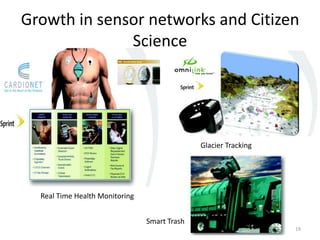
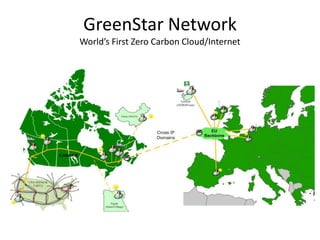
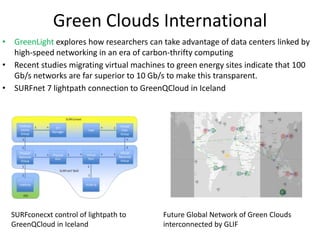
This document discusses strategies for data-intensive science in a carbon constrained world due to climate change. It argues that while efforts to reduce emissions are no longer sufficient, data and computing will be critical to adapt to climate impacts. However, the growth of data and computing also contributes to emissions. The document examines how climate change will impact weather patterns, droughts, and energy systems. It also looks at how internet and research networks can help support science and education for adaptation, such as through brokered green clouds, software-defined networks, wireless networks, dynamic optical networks, and eScience platforms. The goal is to address data and collaboration needs while reducing emissions and adapting to climate disruptions.

















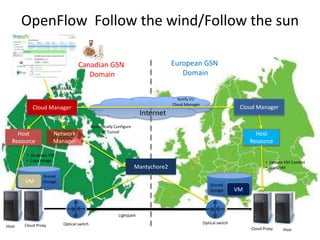
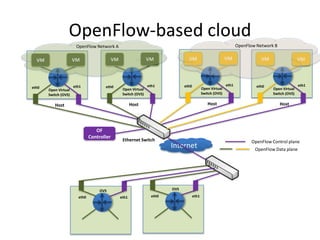
![Science Cloud Communication Services Network
• Enterprise clouds use commodity internet; computational clouds for data-intensive
science require dynamic cloud provisioning integrated with dynamic high
performance.
• TransCloud: example of dynamic networking & dynamic cloud provisioning
Example of working in the TransCloud
[1] Build trans-continental applications spanning clouds:
• Distributed query application based on Hadoop/Pig
• Store archived Network trace data using HDFS
• Query data using Pig over Hadoop clusters
[2] Perform distributed query on TransCloud, which currently spans the following
sites:
• HP OpenCirrus
• Northwestern OpenCloud
• UC San Diego
• Kaiserslautern
Source: Maxine Brown](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jointtechskeynotejanuary-120112133406-phpapp02/85/Joint-techs-keynote-january-31-320.jpg)