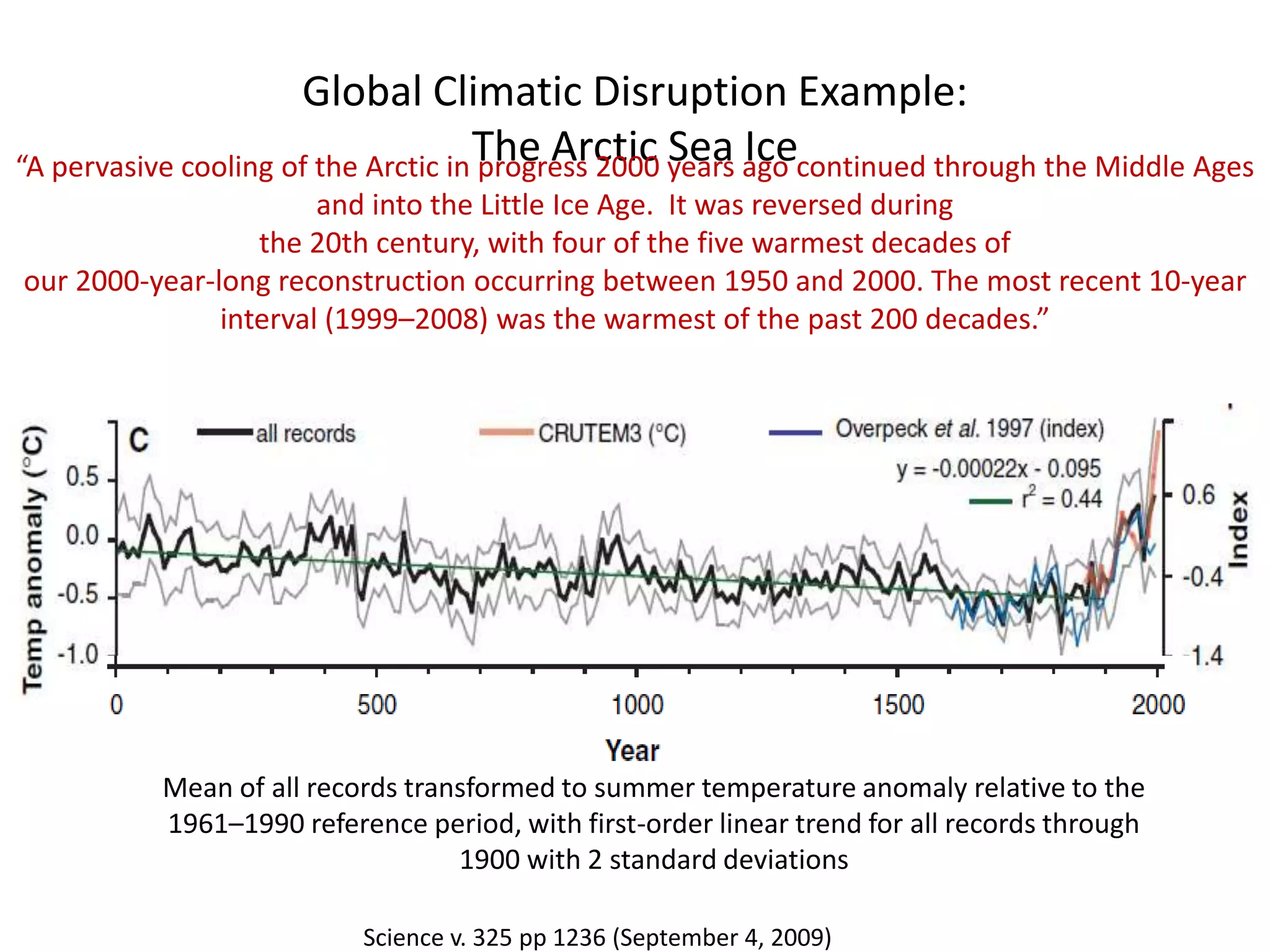
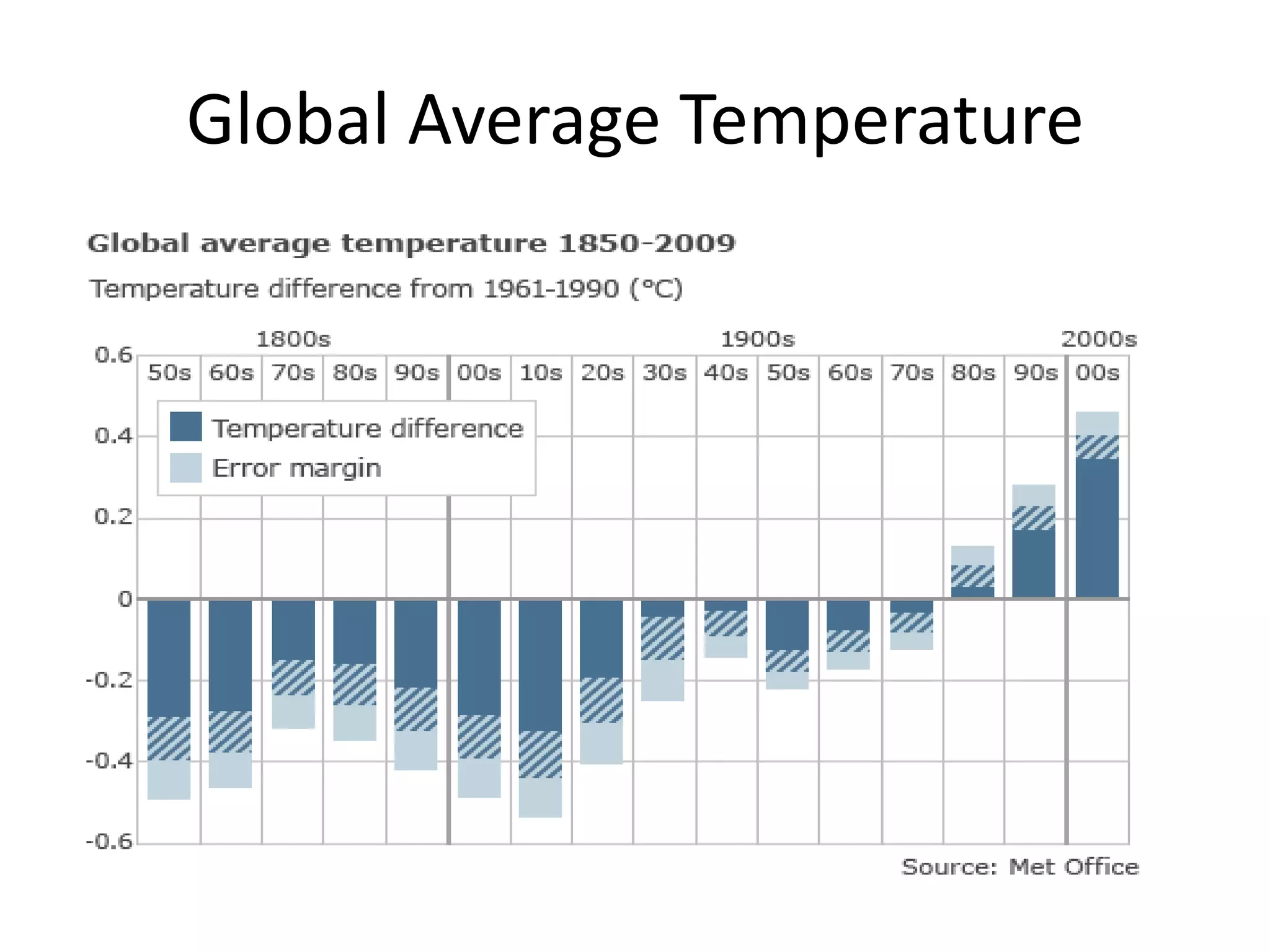
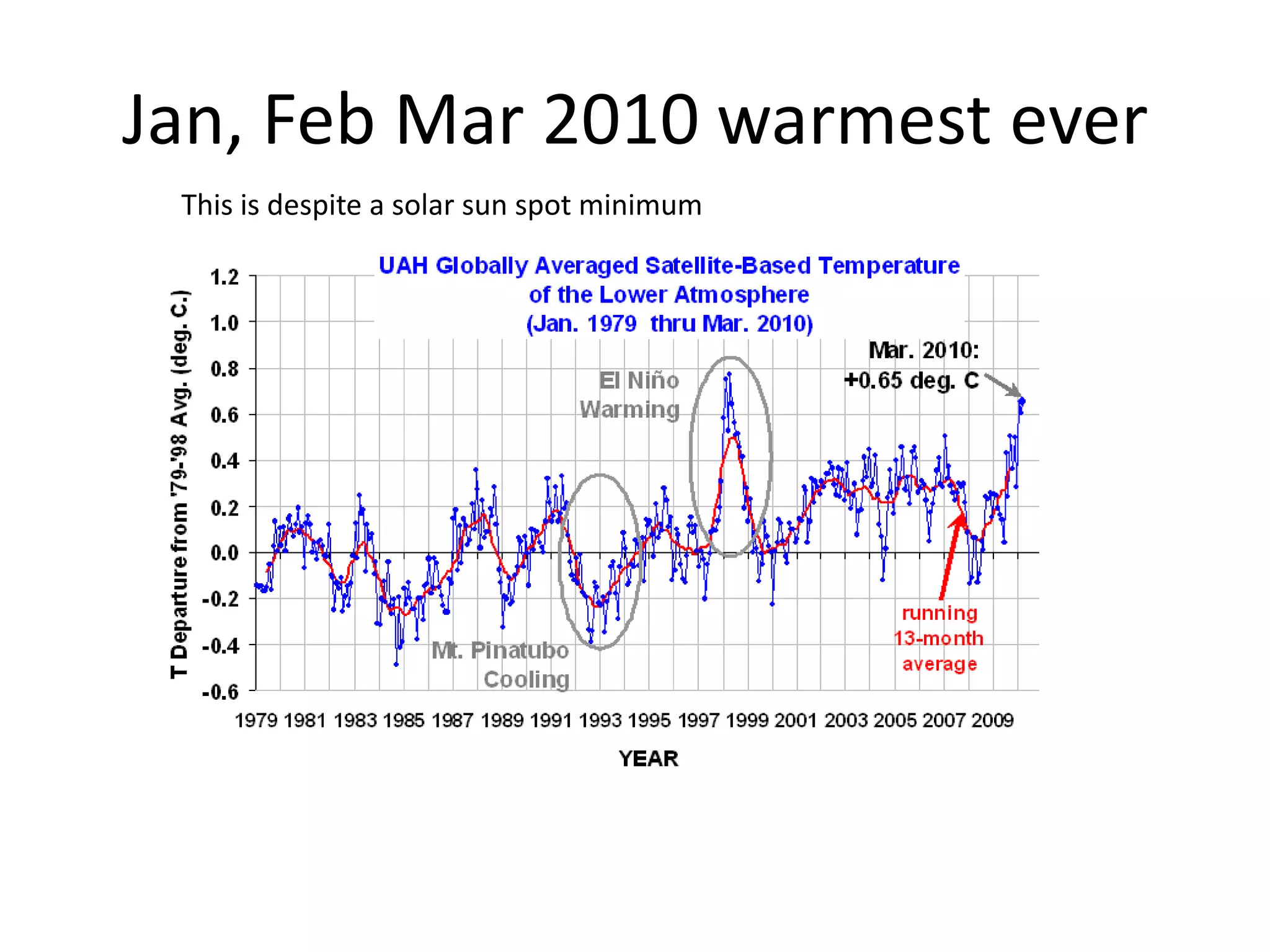
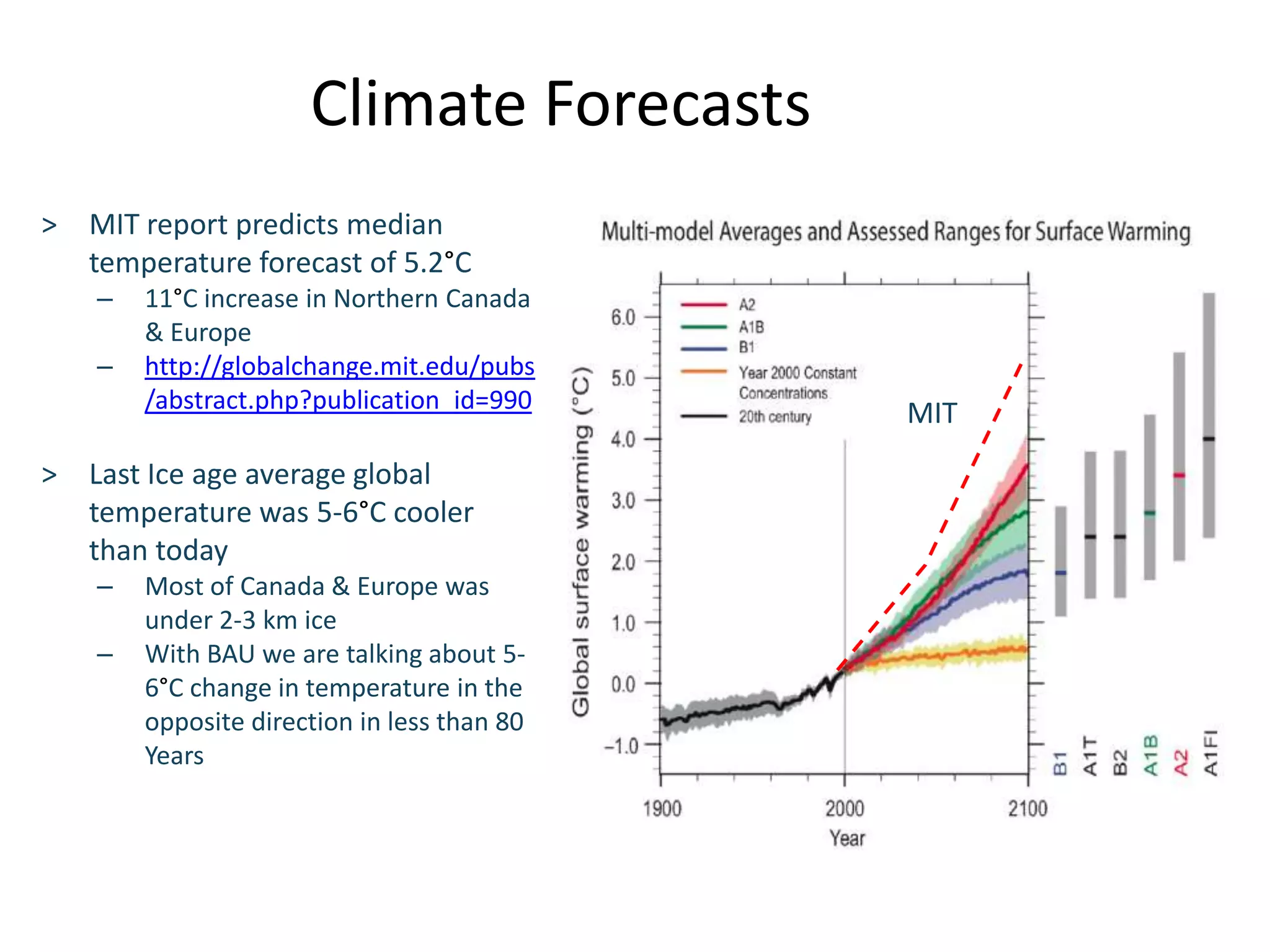
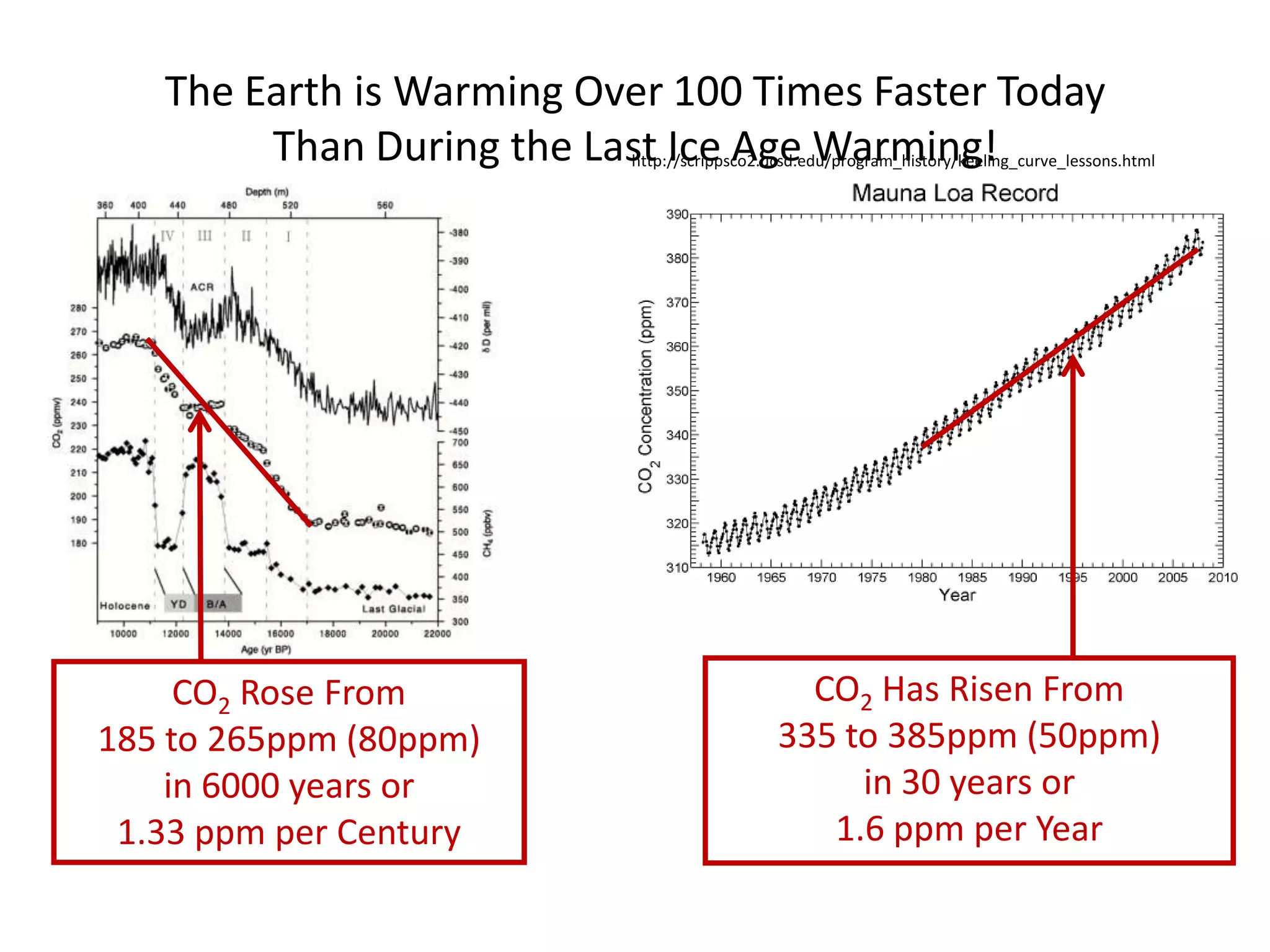
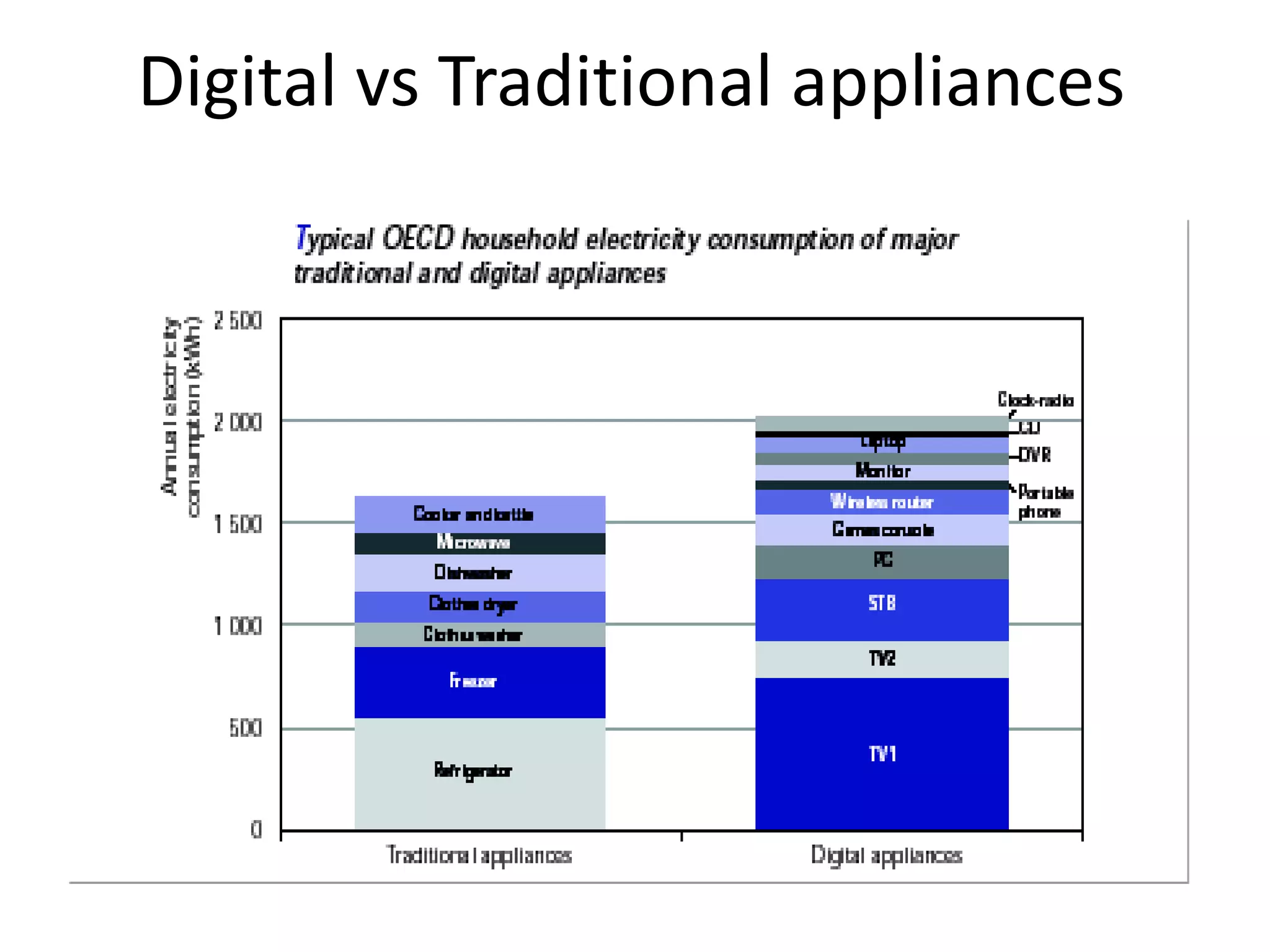
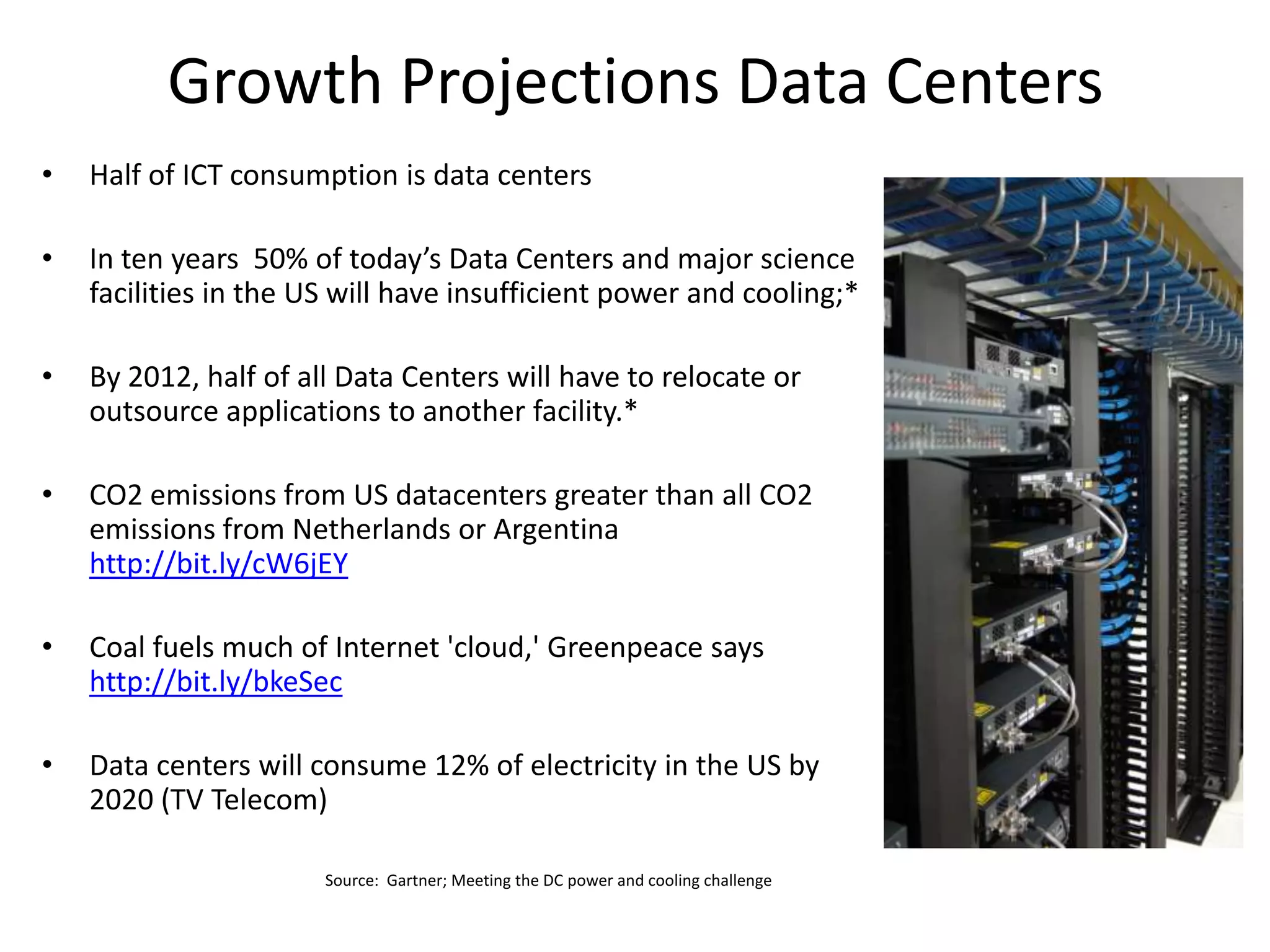
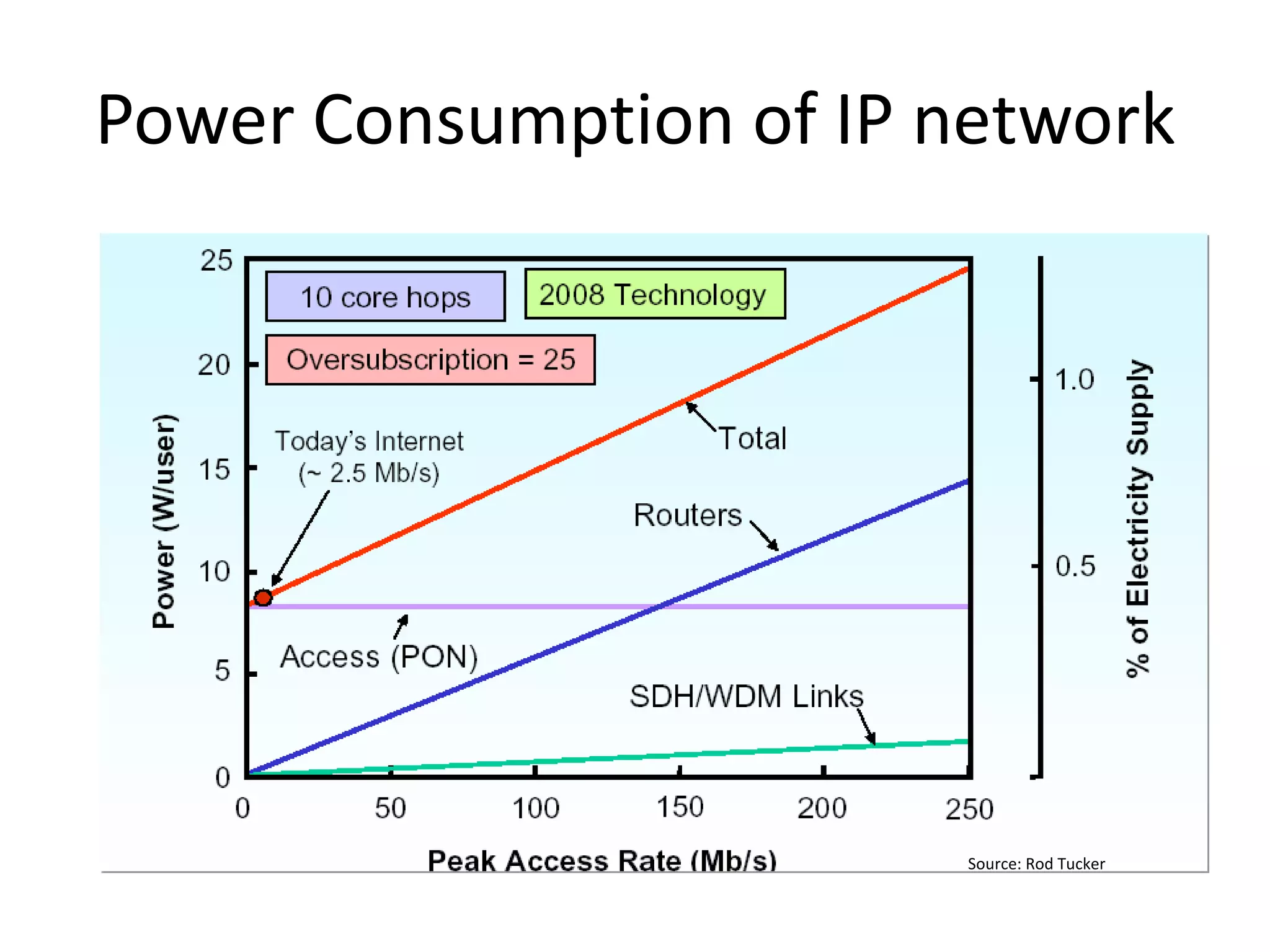
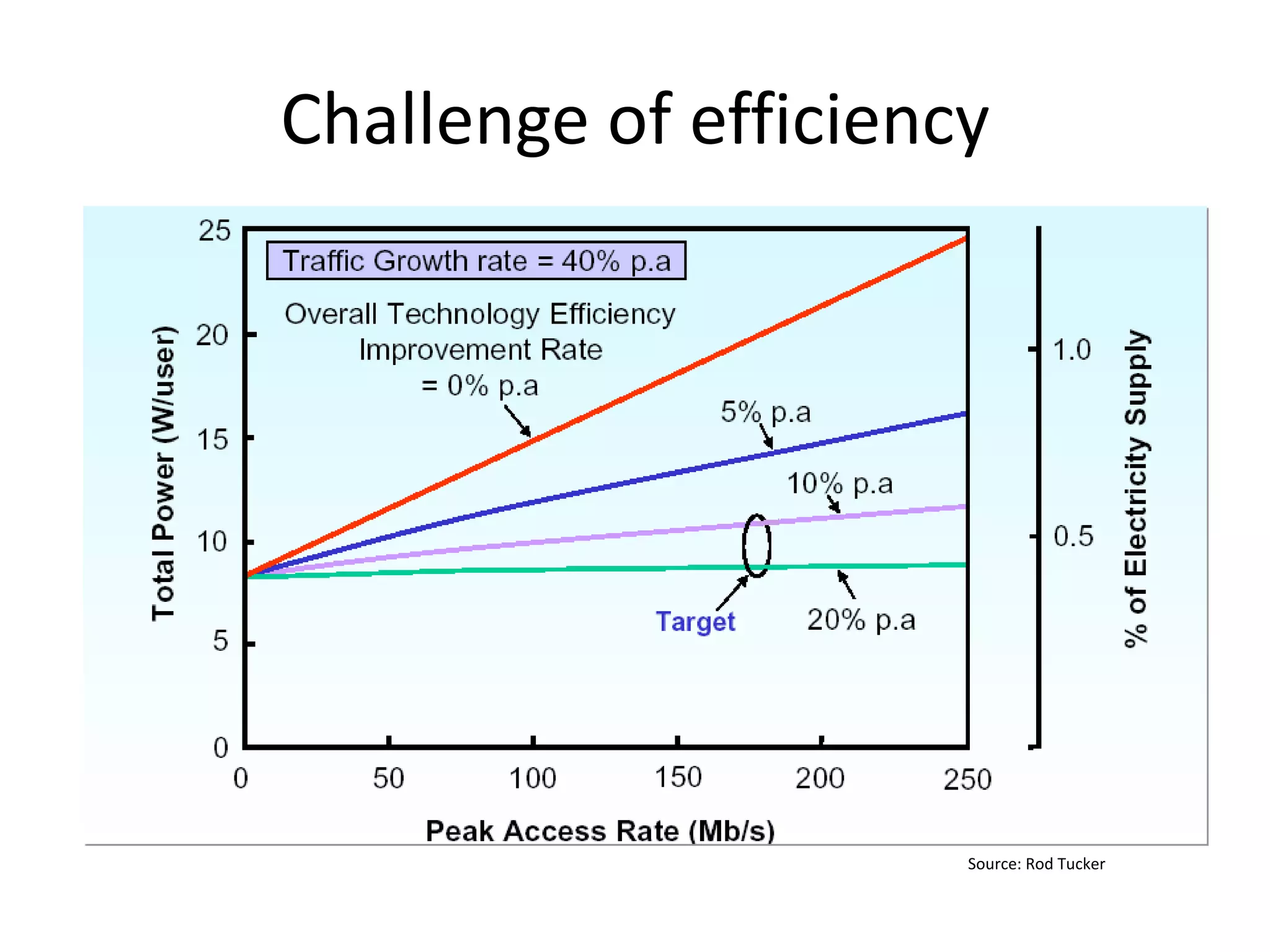
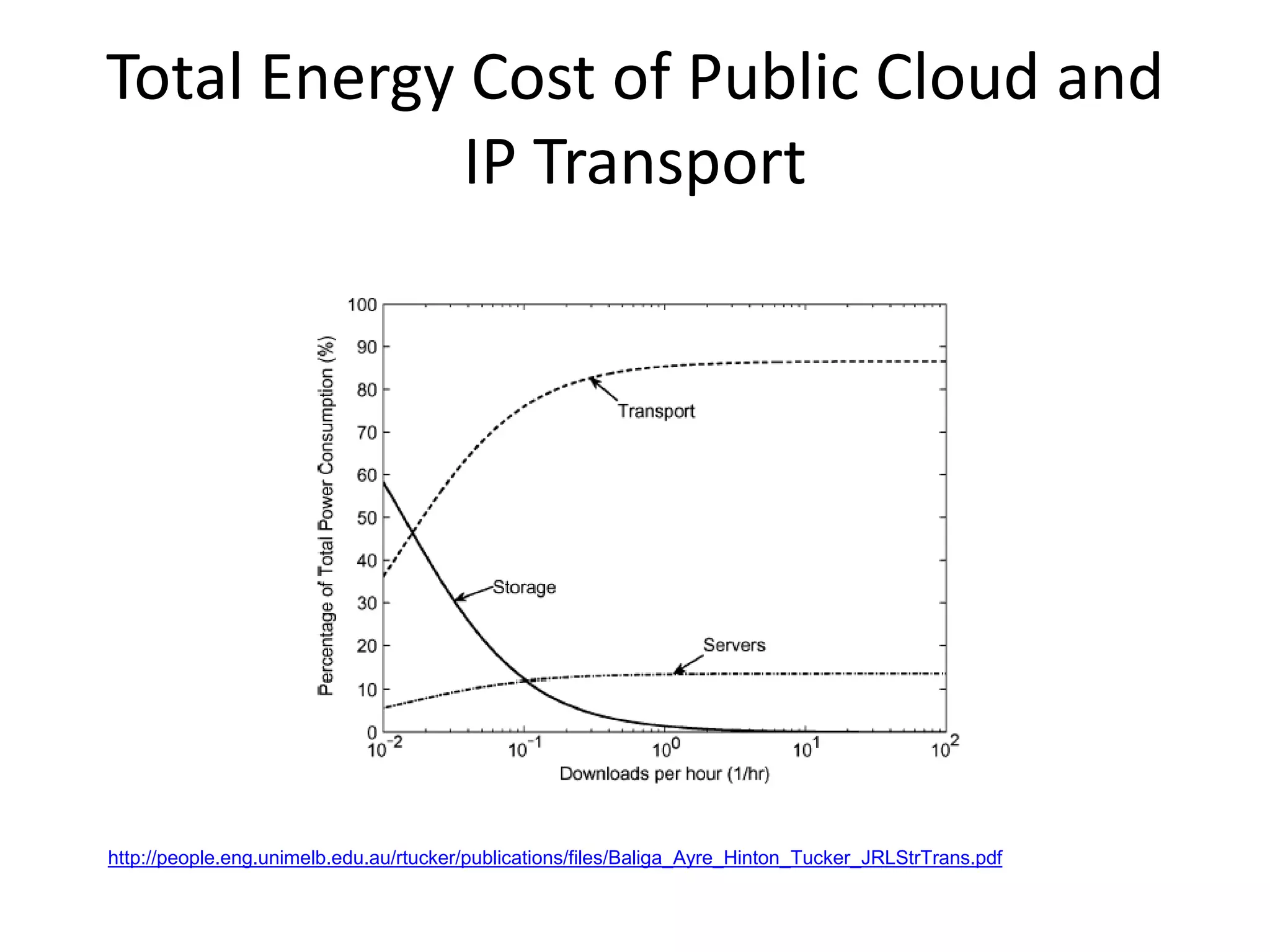
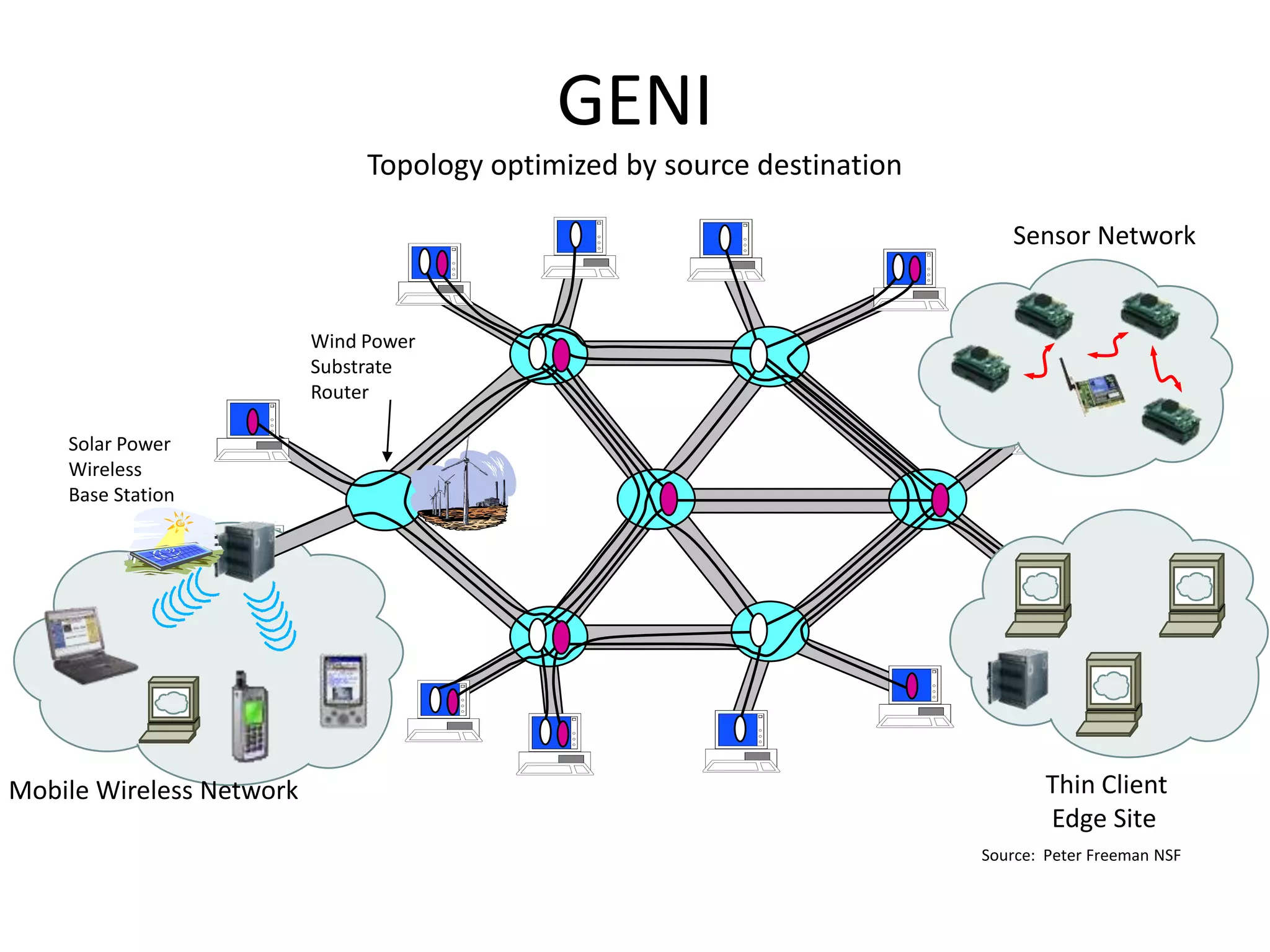
This document discusses the urgent need to address climate change through reducing carbon emissions, especially from information and communication technologies (ICT). It notes that ICT carbon emissions are growing rapidly and will account for 40% of energy use by 2030 if unchecked. Transitioning to renewable energy powered "green" networks and data centers is essential to achieving necessary emissions reductions. The document advocates building smart systems that can adapt to the intermittent availability of renewable power sources like wind and solar.