1. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a technique that measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as they are heated.
2. When a sample undergoes a chemical or physical change like melting or decomposition, it will absorb or release heat, causing its temperature to differ from the reference material. This temperature difference is plotted against temperature or time to produce a DTA curve.
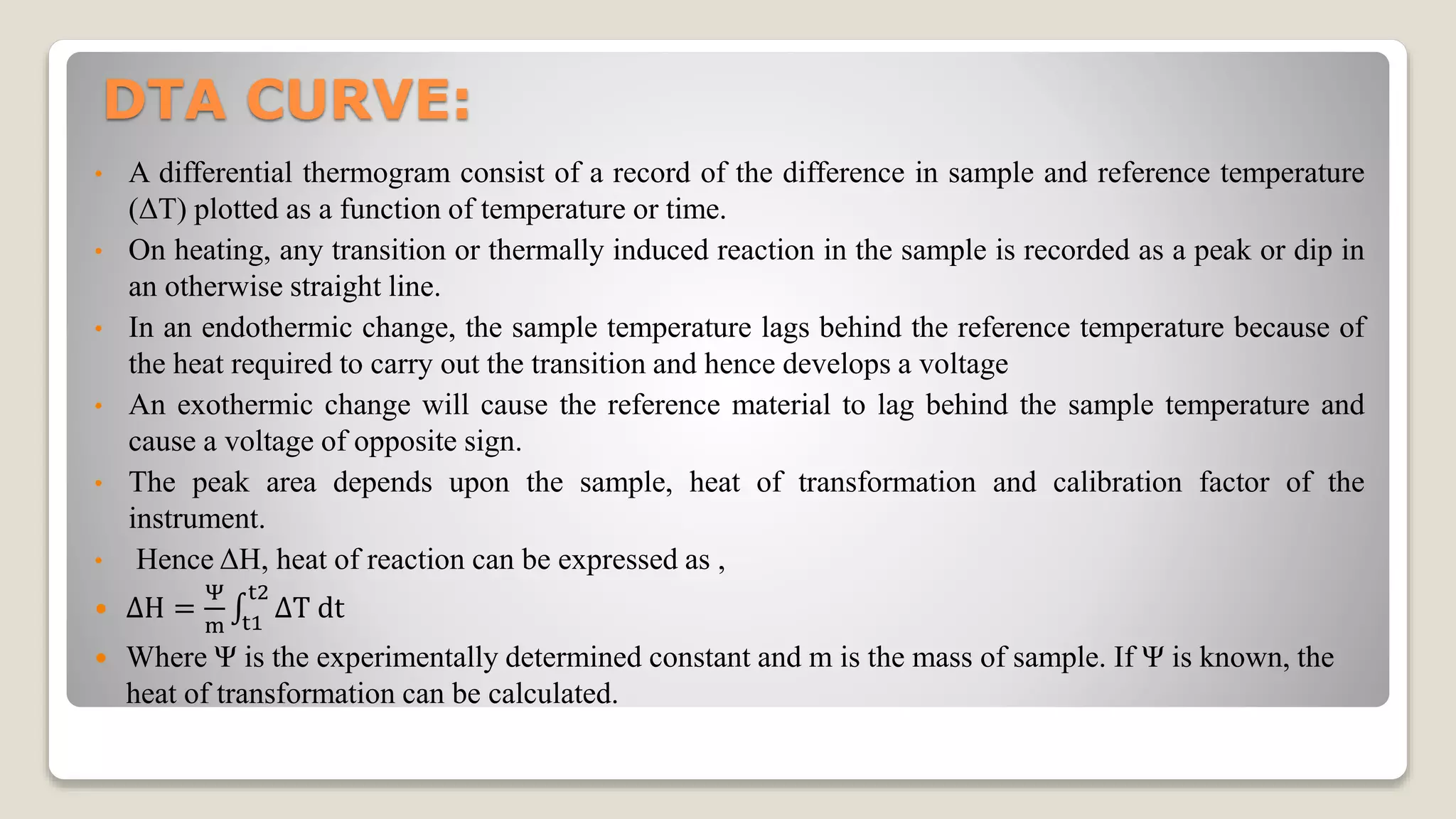
3. Endothermic processes like melting cause negative peaks on the DTA curve as the sample temperature lags the reference. Exothermic processes like oxidation cause positive peaks as the sample temperature exceeds the reference. The shape, size, and temperature of peaks provide information about the sample.