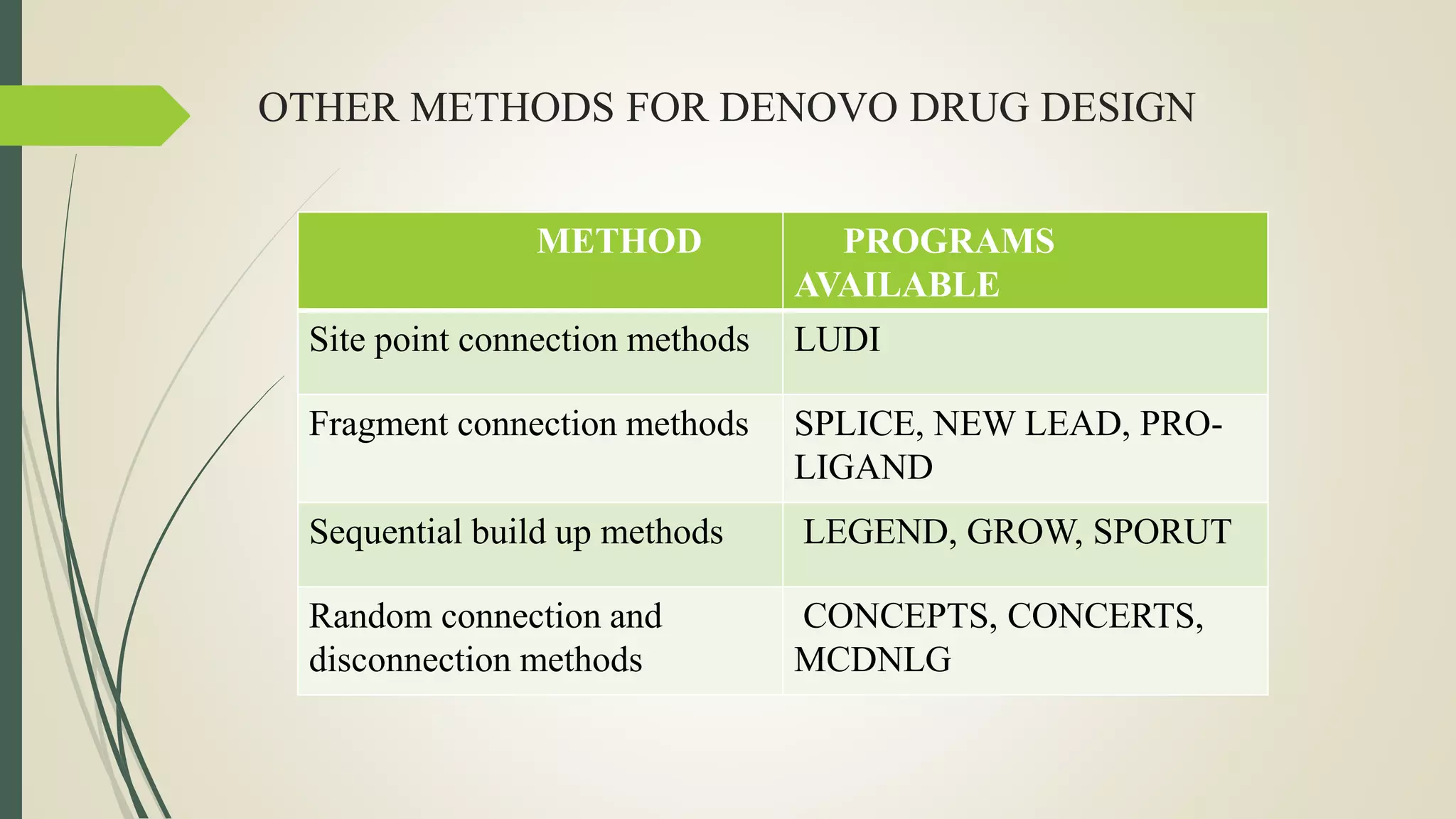
This document discusses de novo drug design, which involves using a target receptor's 3D structure to design new molecules that can interact with it, without relying on existing leads. The key steps of computer-based de novo design are generating primary constraints from the receptor, deriving interaction sites in the binding pocket, building up ligand structures using methods like growing and linking fragments, scoring the ligands to evaluate binding affinity, and applying secondary constraints related to drug properties. Successful applications of de novo design include HIV protease inhibitors and COMT inhibitors.















![REFERENCE
Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry-sixth edition, published by
lippincott williams and wilkins, page num-69-70.
Sanmati K jain and avantika agarwal- “ De novo drug design: an
overview”. Indian journal of pharmaceutical
sciences.,2004,66[6]:721-728.
http://journal.chemistrycentral.com/content/2/S1/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HIV-1_protease.
Schneider G.; Fechner U.; “Computer-based de novo design of
drug-like molecules.” Nat Rev Drug Discov 2005 Aug; 4(8), 649-
63.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/denovo-220211131134/75/Denovo-17-2048.jpg)
