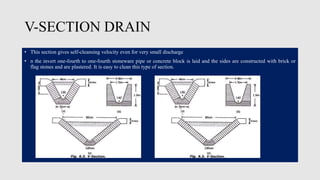
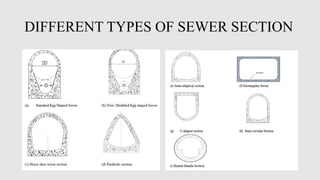
This document provides an overview of drains, sewers, and related infrastructure. It discusses surface drains, classifications of drains, types of sewers including main trunk sewers, branch sewers, and lateral sewers. It also covers sewer sections, materials, joints, appurtenances like manholes, and best practices for laying and testing sewer lines. The key topics covered include the purpose and design of different drain and sewer components as well as construction and maintenance considerations.