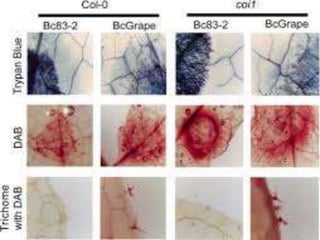
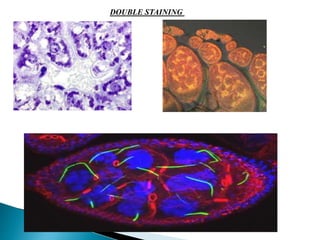
Vital staining involves using non-toxic dyes on living organisms and cellular structures. Common vital stains include neutral red, methylene blue, and Janus green B. Vital stains can be used to differentiate between living and dead cells, stain specific organelles like mitochondria, and study pathological cell changes without harming living tissues. Vital stains are classified based on their chemical properties and degree of dissociation into categories like basic, acidic, atmospheric and electro neutral. Techniques for vital staining include progressive, regressive, counterstaining, and double staining using combinations of contrasting dyes.