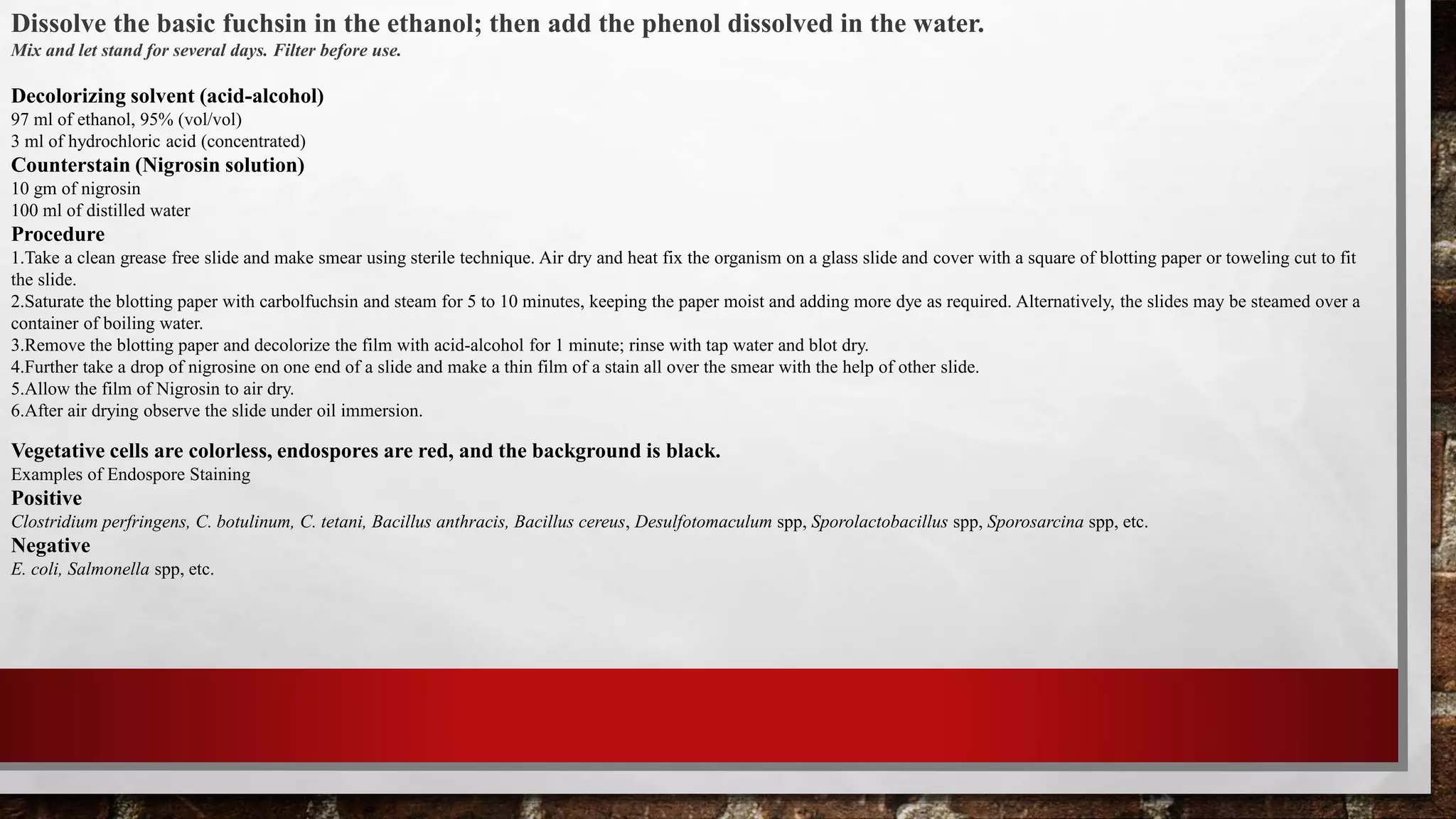
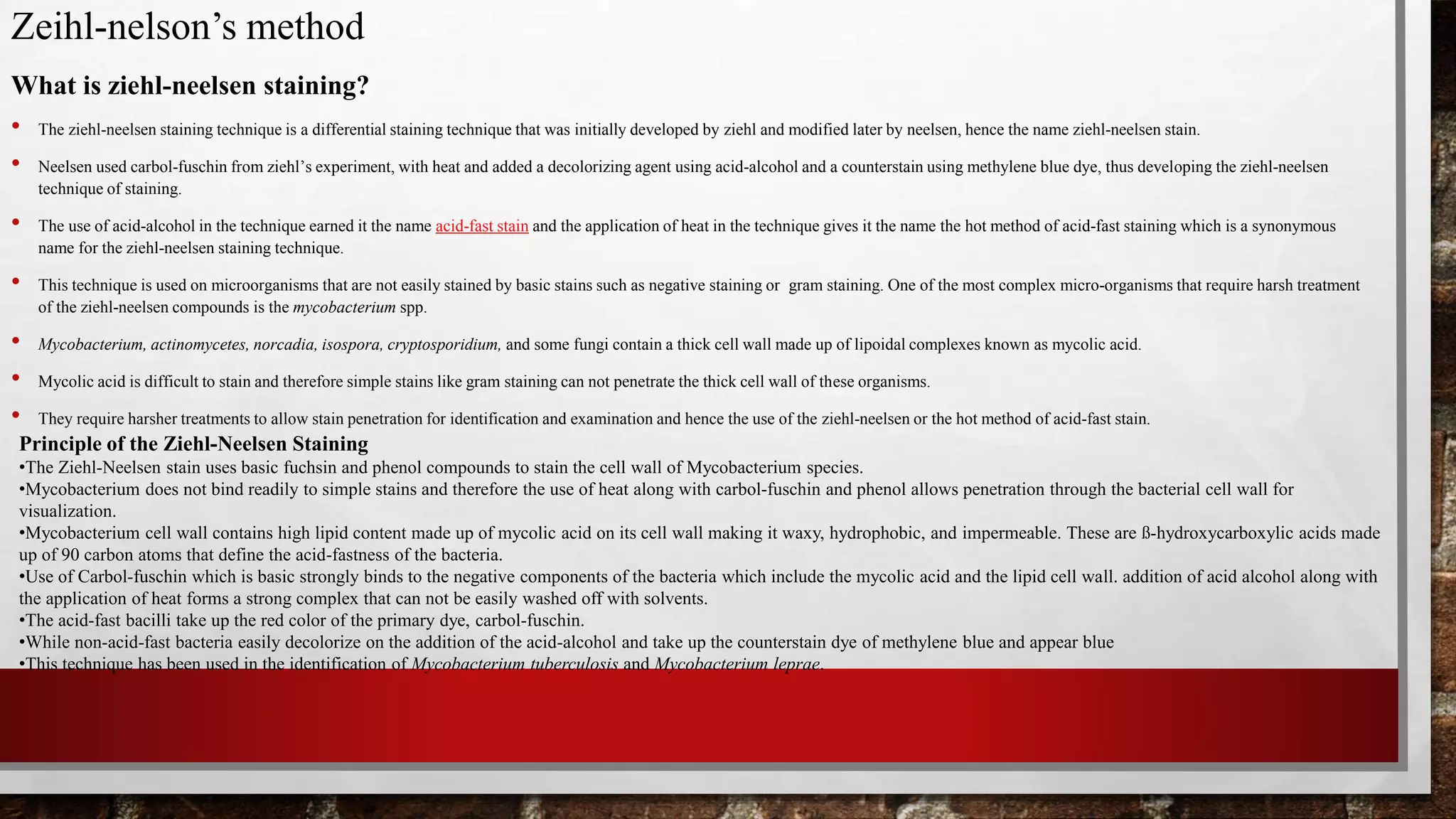
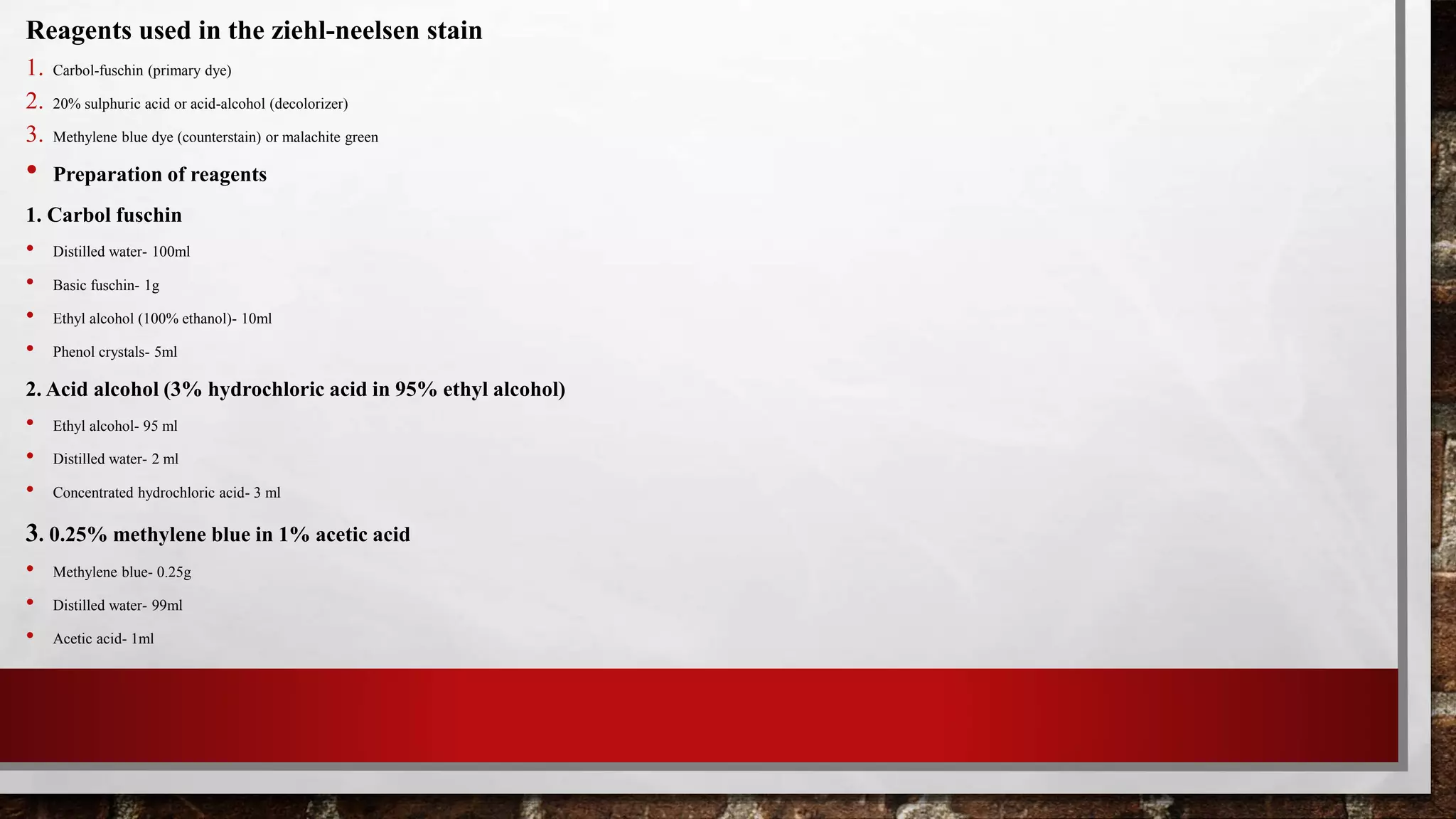
This document discusses staining techniques used to visualize bacteria under a microscope. It begins by explaining why staining is necessary given that bacteria are colorless and microscopic. It then describes different types of stains including basic stains that directly stain bacteria and acidic stains used for negative staining of the background. Key differential staining techniques are also summarized, including Gram staining which separates bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups based on cell wall structure, and acid-fast staining used to identify Mycobacterium species. The document provides details on staining methods, the mechanisms of different staining techniques, and their importance in classifying and identifying bacterial specimens.




















![Materials and Reagents required
• Test bacteria: 36-48 hour culture of capsulated bacteria e.G. Klebsiella pneumoniae growing on a slant of EMB agar or culture of other capsulated bacteria and non-capsulated bacteria
[note: growing klebsiella pneumoniae in milk-based media (e.G. Skim milk) increase its capsule size, making it easier to visualize.]
• Stain solutions: depending on the type of method used (crystal violet, india ink, nigrosin, copper sulfate, basic carbol fuschin solution, methylene blue solution, etc).
• Microscopic slides
• Inoculating loop
• Microscope with 100x objective lens (oil immersion)
• Immersion oil
• Gas burner
• Tissue paper
METHOD
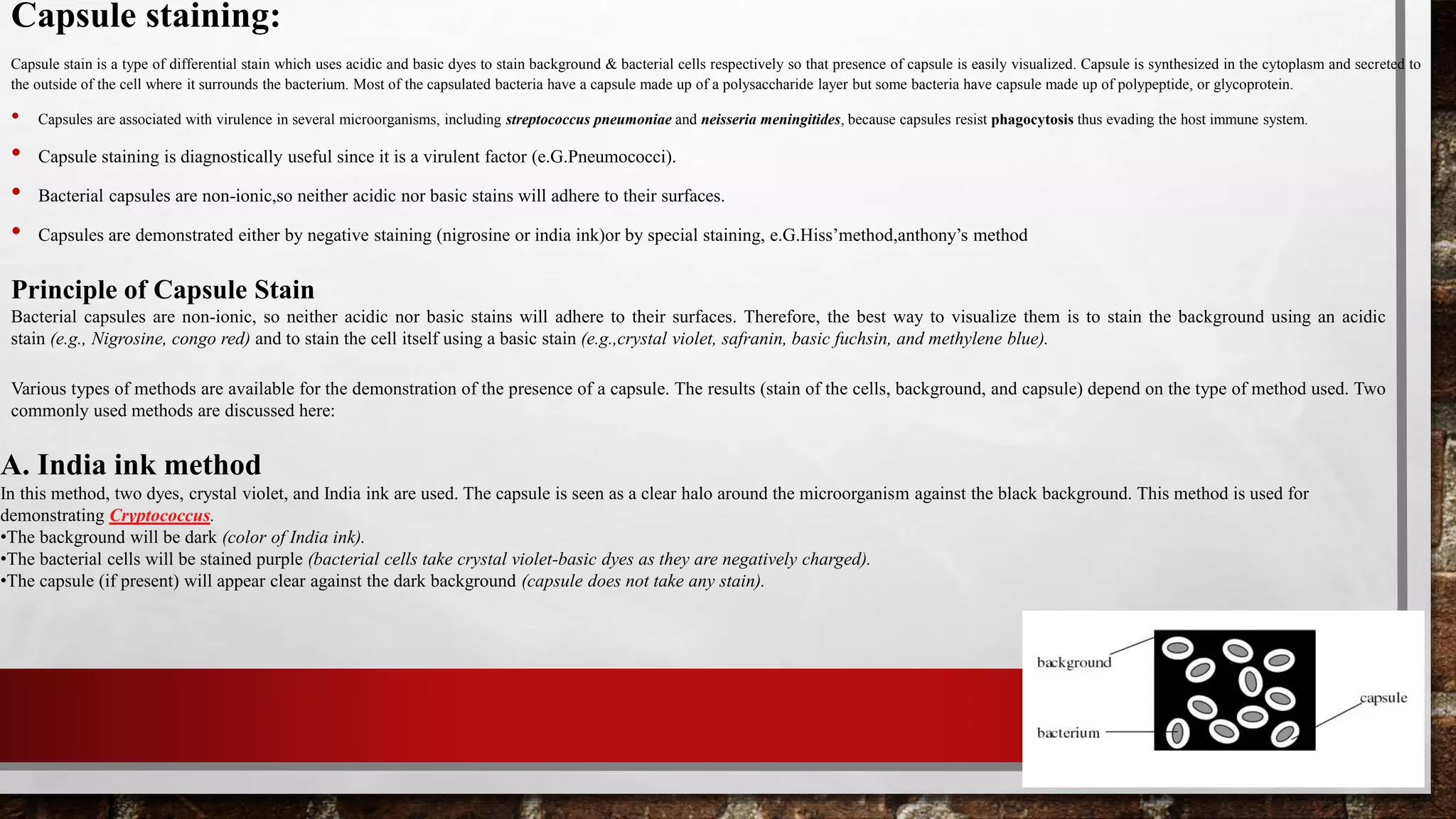
1.Place a single drop of India ink on a clean microscope slide, adjacent to the frosted edge.
2.Using a flamed loop and sterile technique, remove some Klebsiella pneumoniae from culture tube or plate and mix it into the drop of India ink. Be sure there are no large clumps of
organism, but try to avoid spreading the drop. Place the end of another clean microscope slide at an angle to the end of the slide containing the organism. Spread out the drop out into a
film. This is done by contacting the drop of India ink with the clean microscope slide and using the capillary action of the dye/ slide to spread the India ink across the smear.
3.Allow the film to air dry (will take 5-7 minutes). DO NOT heat or blot dry! Heat will melt the capsule!
4.Saturate the slide with crystal violet for 1 minute and rinse slightly & very gently with water. Be cautious water may remove the capsule from the cell.
5.Let the slide air dry for a few minutes. DO NOT blot the slide! Blotting will remove the bacteria from the slide and/or distort the capsule.
6.Observe the slide under oil immersion.
Results: Look for purple cells surrounded by a clear halo on a dark background. The halo is the capsule. You may need to decrease the amount of light
in order to make the capsule easier to see.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stainingtechniqueinmicrobiology-220101111237/75/Staining-Technique-in-microbiology-26-2048.jpg)
![B. Anthony’s stain method
In this type of capsule staining procedure, the primary stain is crystal violet, and all parts of the cell take up the purple crystal violet stain. There is no mordant in the
capsule staining procedure. A 20% copper sulfate solution serves a dual role as both the decolorizing agent and counterstain. It decolorizes the capsule by washing out the
crystal violet, but will not decolorize the cell. As the copper sulfate decolorizes the capsule, it also counterstains the capsule. Thus, the capsule appears as a faint blue halo
around a purple cell.
Materials and Reagents required
•Test bacteria: 36-48 hour culture of capsulated bacteria e.G. Klebsiella pneumoniae growing on a slant of EMB agar or culture of other capsulated bacteria and non-capsulated bacteria
[note: growing klebsiella pneumoniae in milk-based media (e.G. Skim milk) increase its capsule size, making it easier to visualize.]
•Stain solutions: depending on the type of method used (crystal violet, india ink, nigrosin, copper sulfate, basic carbol fuschin solution, methylene blue solution, etc).
•Microscopic slides
•Inoculating loop
•Microscope with 100x objective lens (oil immersion)
•Immersion oil
•Gas burner
•Tissue paper
Method:
1.Place a single drop of crystal violet on a clean microscope slide, adjacent to the frosted edge.
2.Using a flamed loop and sterile technique, add three loopful of test bacterium (any capsulated bacteria such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae) from broth culture. If
you are adding bacteria from a culture plate make sure that there are no large clumps of the organism, but try to avoid spreading the drop.
3.Place the end of another clean microscope slide at an angle to the end of the slide containing the organism. Spread out the drop out into a film. This is done by contacting the drop of
crystal violet with the clean microscope slide and using the capillary action of the dye/ slide to spread the crystal violet across the smear.
4.Allow the film to air dry (will take 5-7 minutes). DO NOT heat or blot dry! Heat will melt the capsule!
5.Tilt the slide and rinse with 20% copper sulfate solution. DO NOT RINSE WITH WATER! Water will remove the capsule from the cell.
6.Let the slide air dry for a few minutes. DO NOT blot the slide! Blotting will remove the bacteria from the slide and/or distort the capsule.
7.Observe the slide under oil immersion.
Results: Look for purple cells surrounded by a clear or faint blue halo on transparent background. The halo is the capsule. You may need to decrease the amount of light in order to make the
capsule easier to see.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stainingtechniqueinmicrobiology-220101111237/75/Staining-Technique-in-microbiology-27-2048.jpg)