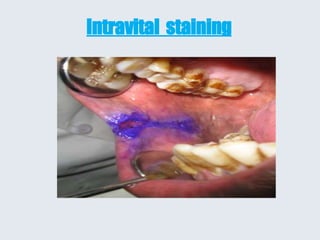
- Vital stains are used to stain living cells and tissues. Common vital stains include toluidine blue, Lugol's iodine, acetic acid, trypan blue, and Congo red.
- These stains can help identify potentially cancerous lesions, as malignant cells often take up less of the stain compared to normal cells.
- Supra vital stains are applied to detached living cells in vitro and help distinguish different cell types based on which structures they stain, such as mitochondria or DNA. Common supra vital stains include methylene blue, Janus green, and acridine orange.
- Vital staining is a useful diagnostic technique but has limitations as only select structures