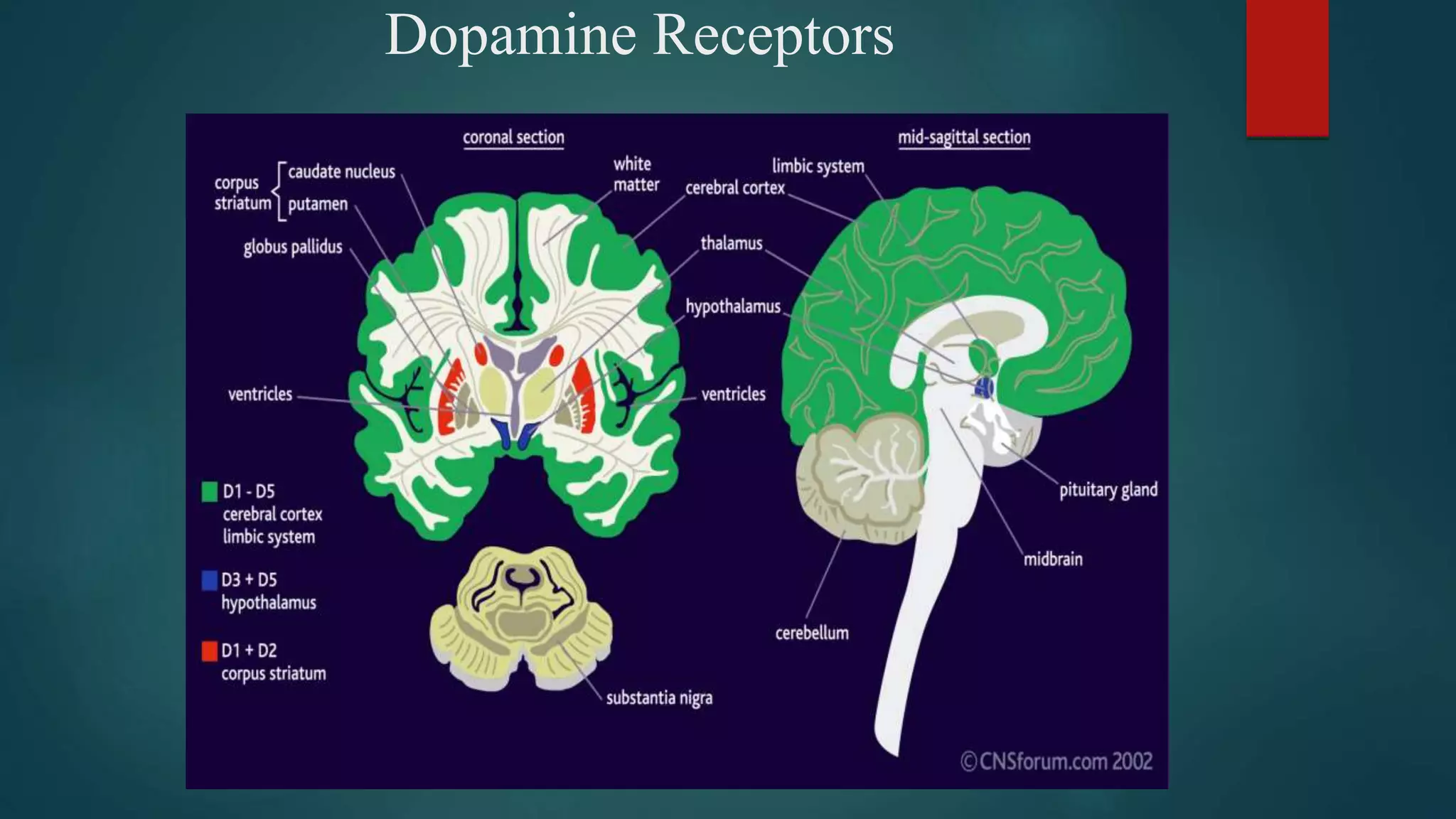
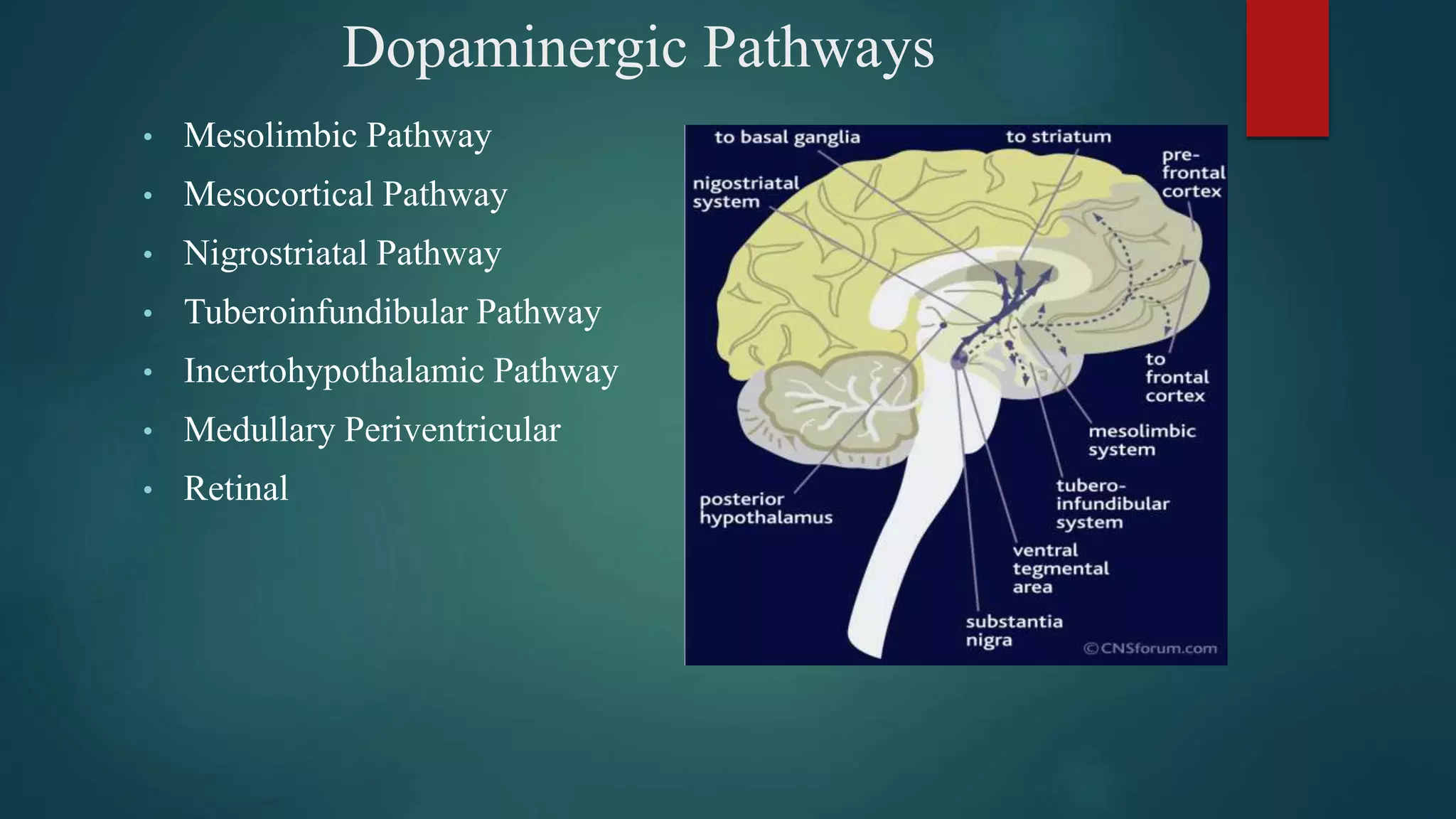
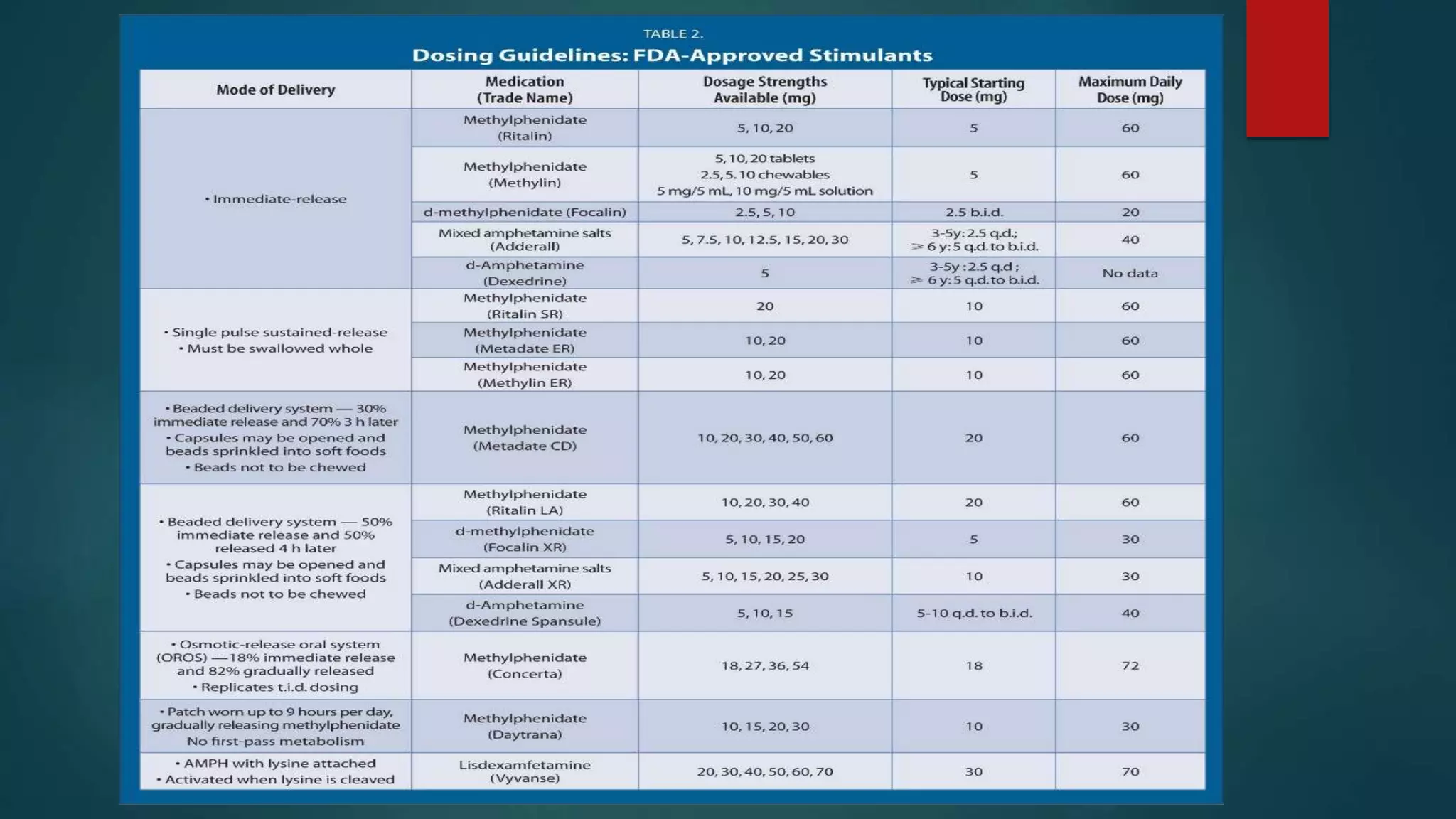
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter involved in many functions including movement, learning, sleep and reward pathways. It is synthesized from phenylalanine and tyrosine and metabolized by monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyltransferase. There are five types of G protein-coupled dopamine receptors which are located throughout the brain and body. Dopamine pathways include the mesolimbic, mesocortical and nigrostriatal pathways which are involved in reward, cognition and movement respectively. Dopamine dysregulation is implicated in disorders like Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia and addiction.