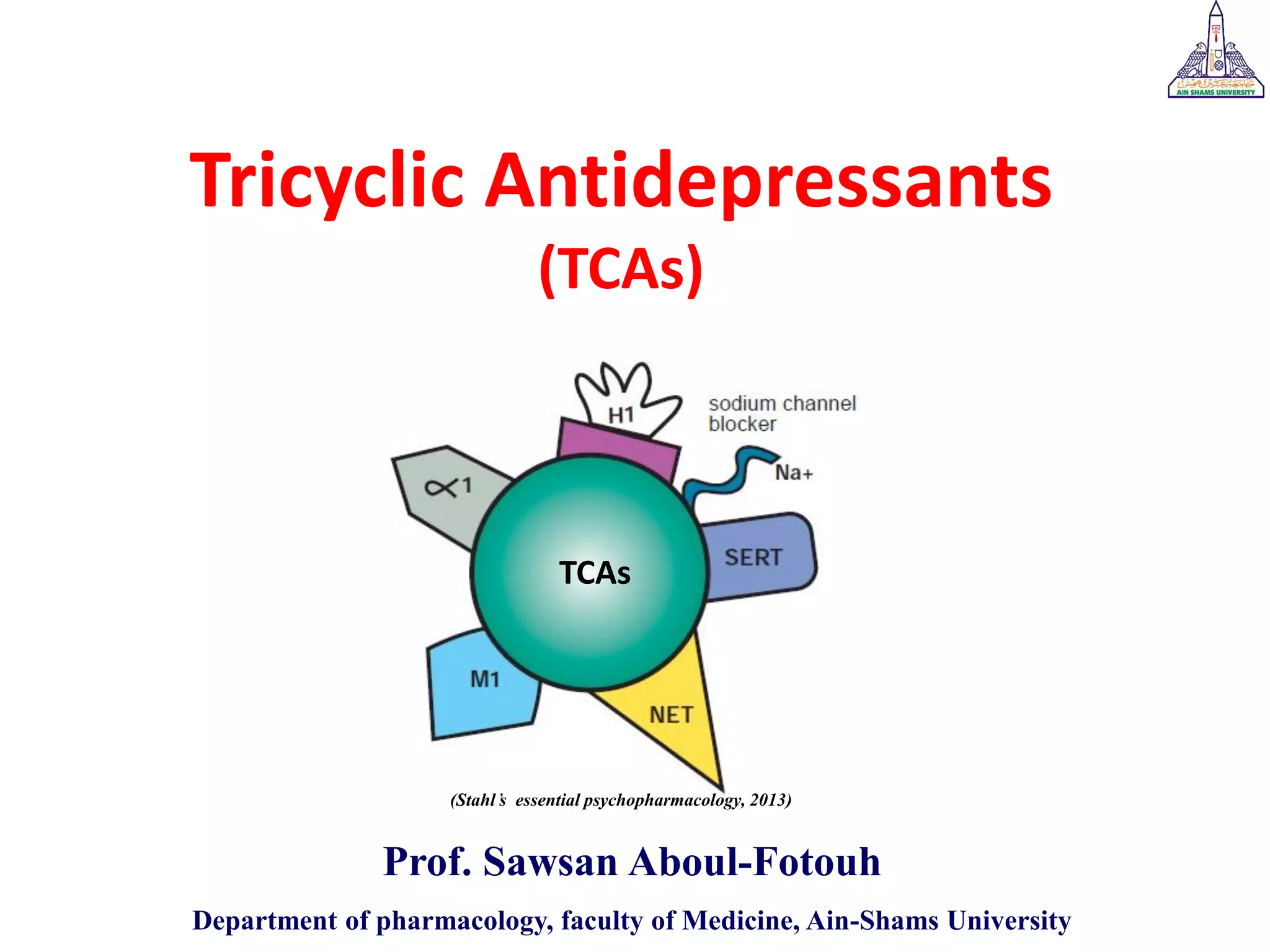
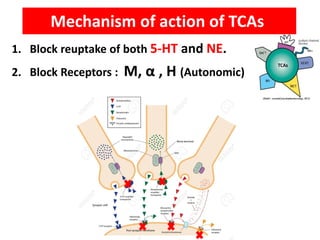
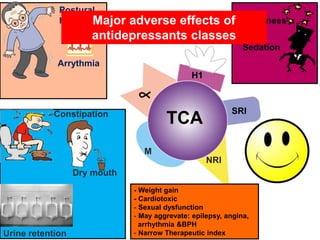
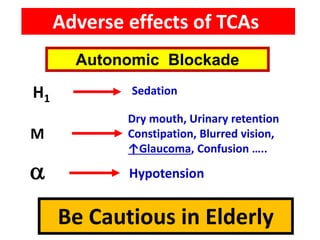
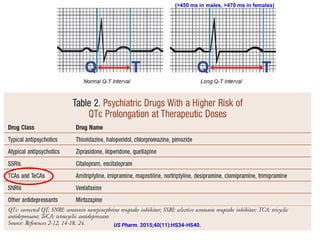
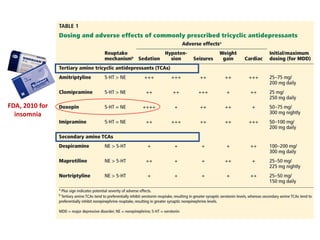
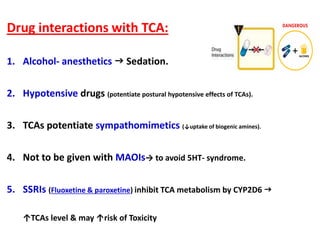
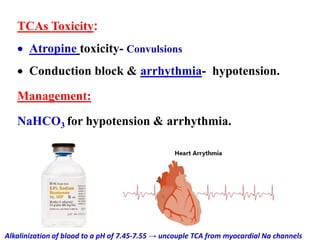
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) like imipramine, amitriptyline, and clomipramine work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. They also block receptors like muscarinic, alpha, and histamine receptors. Common adverse effects include dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, sedation, orthostatic hypotension, and cardiac issues like arrhythmia. TCAs can have dangerous interactions with other drugs and should be used cautiously in certain patient populations such as the elderly, those with heart conditions, epilepsy, or suicidal thoughts. While primarily used to treat depression and anxiety, TCAs are also used for other conditions like migraine,