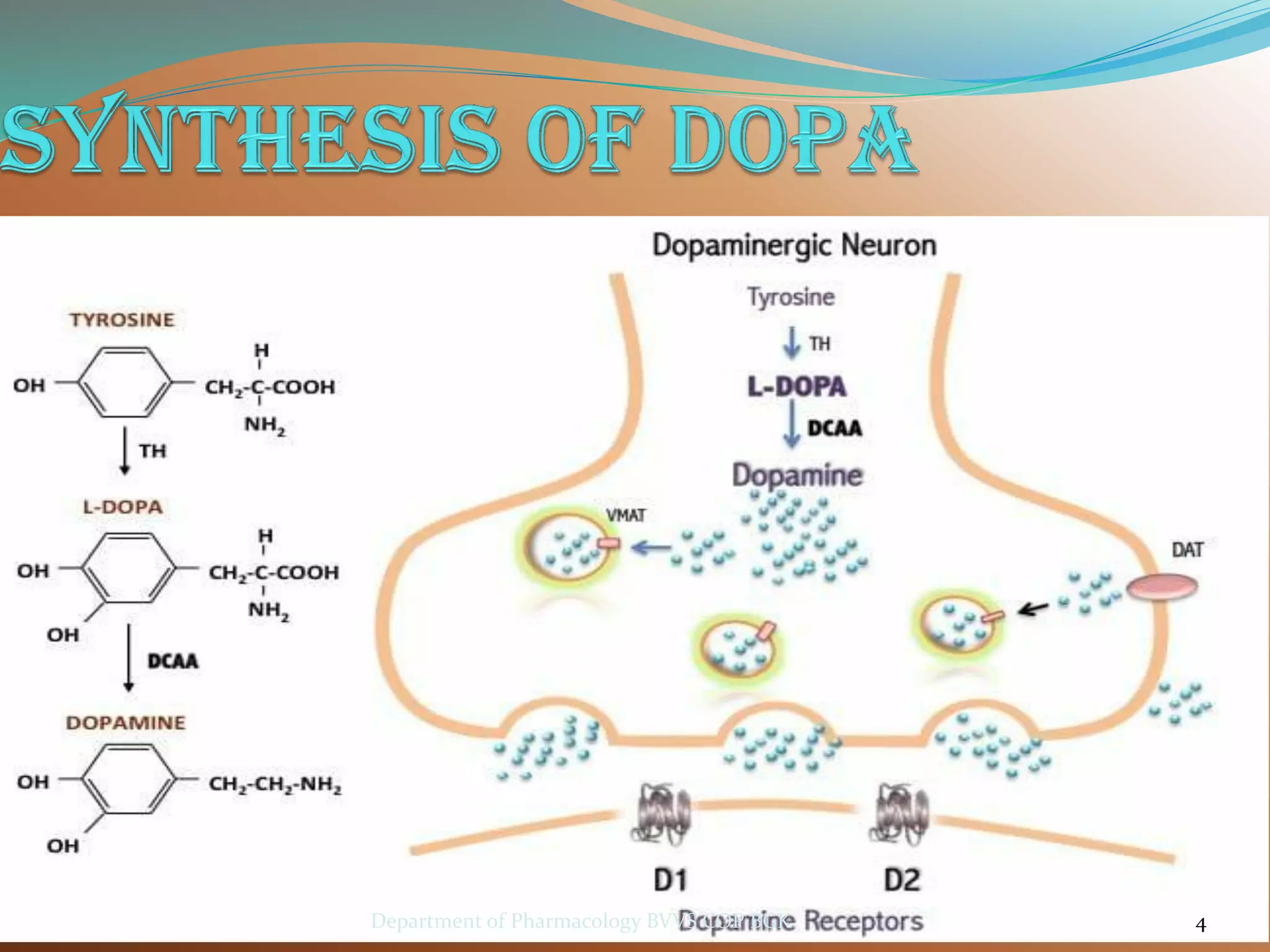
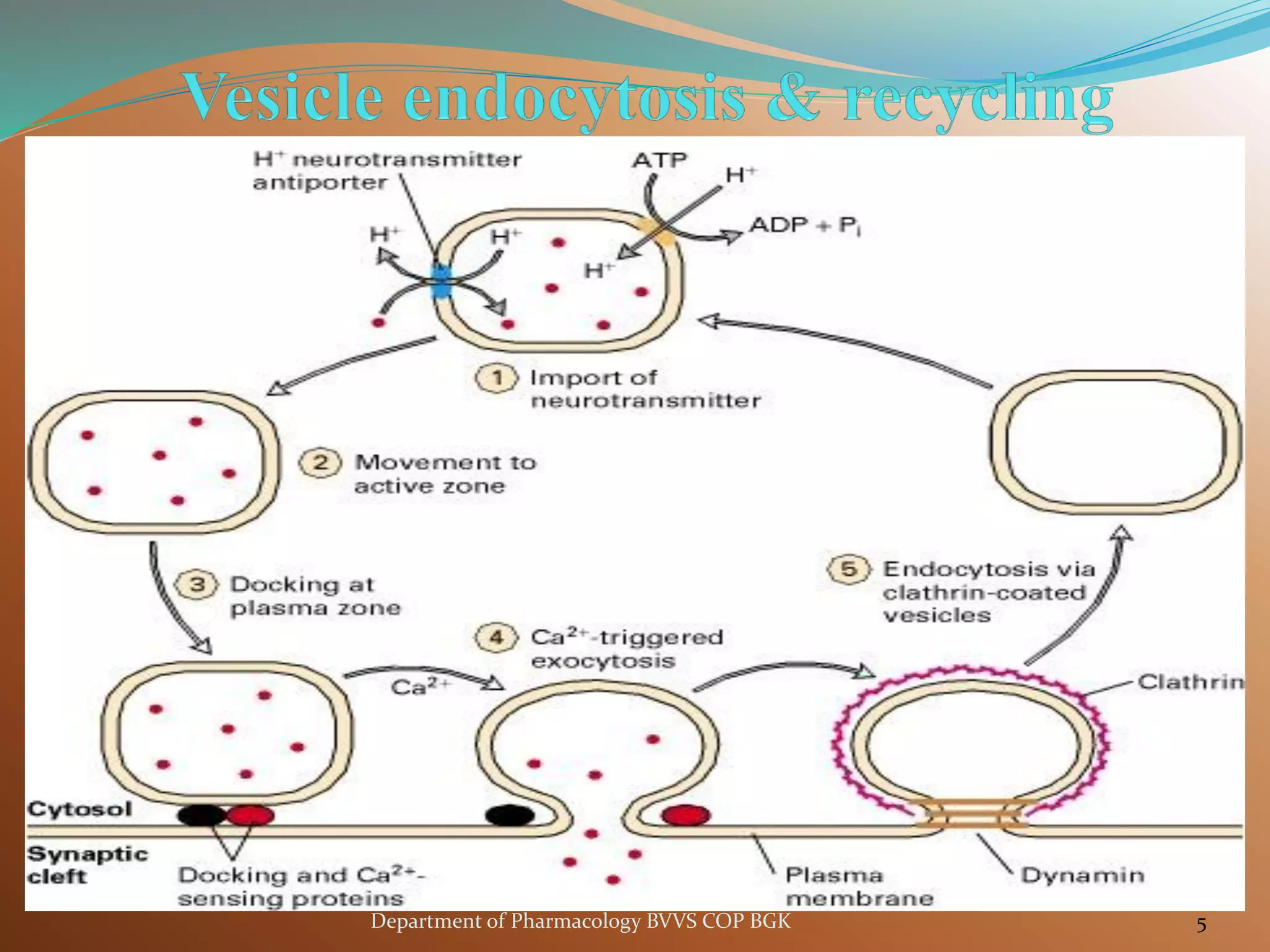
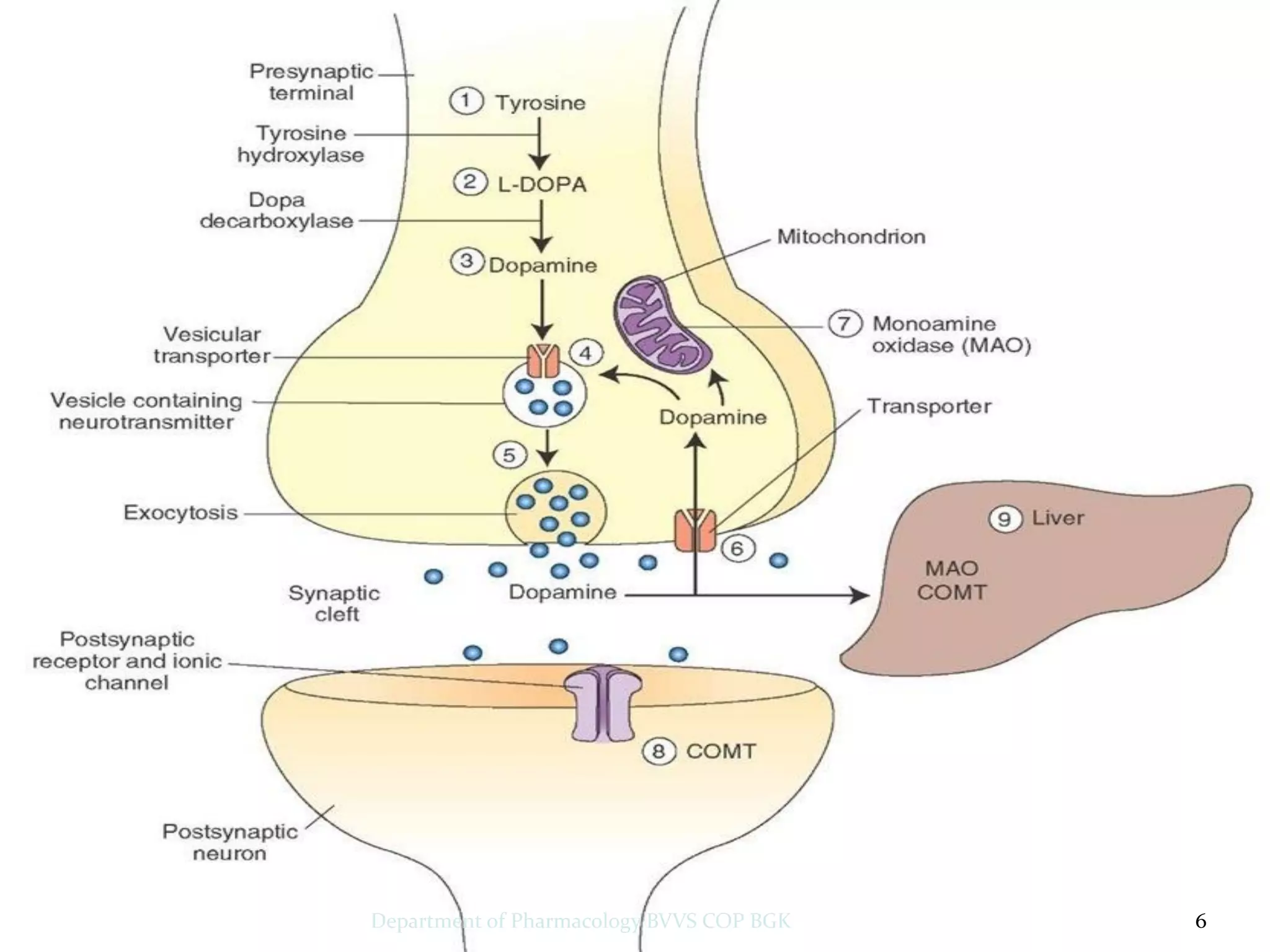
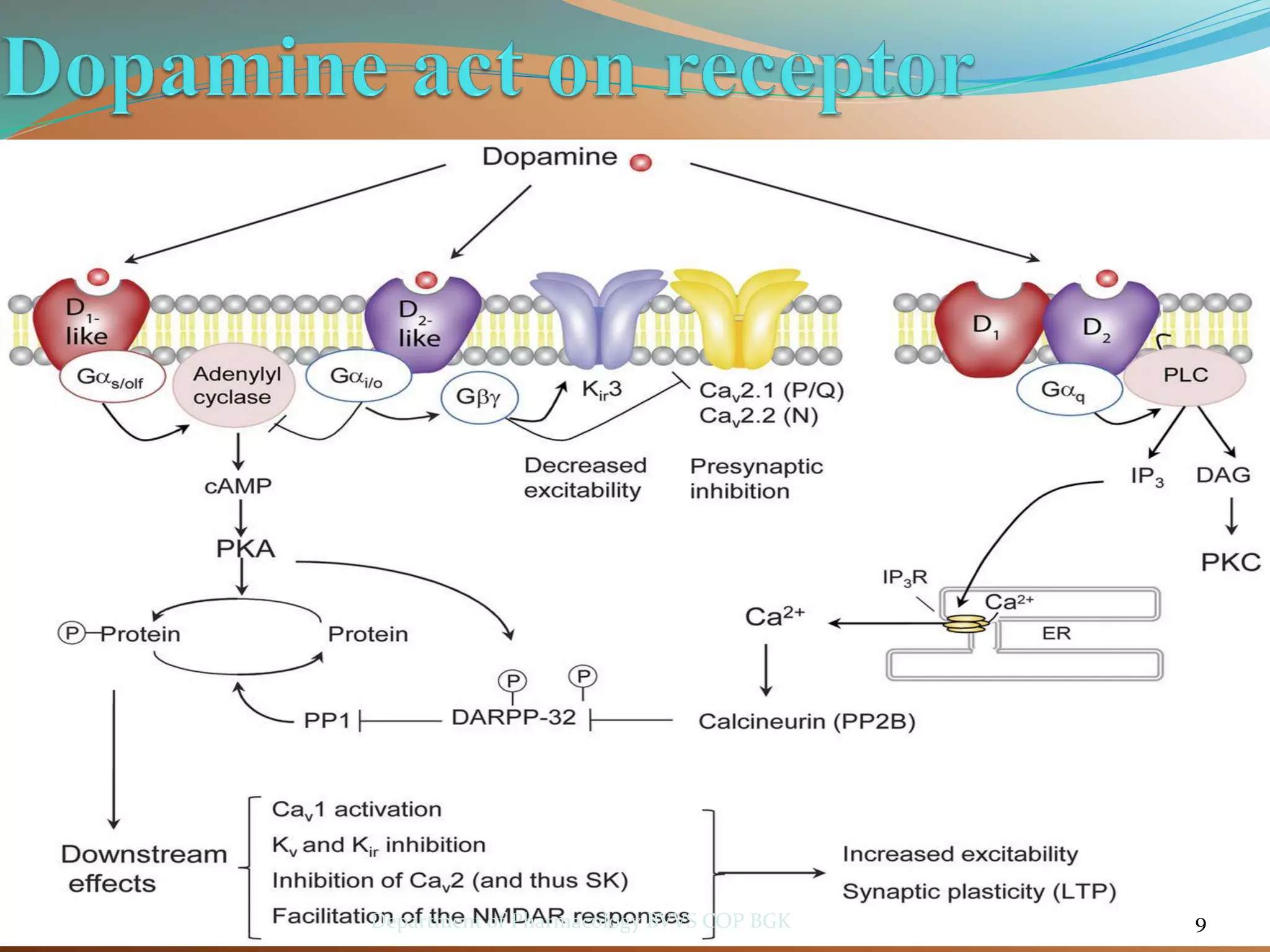
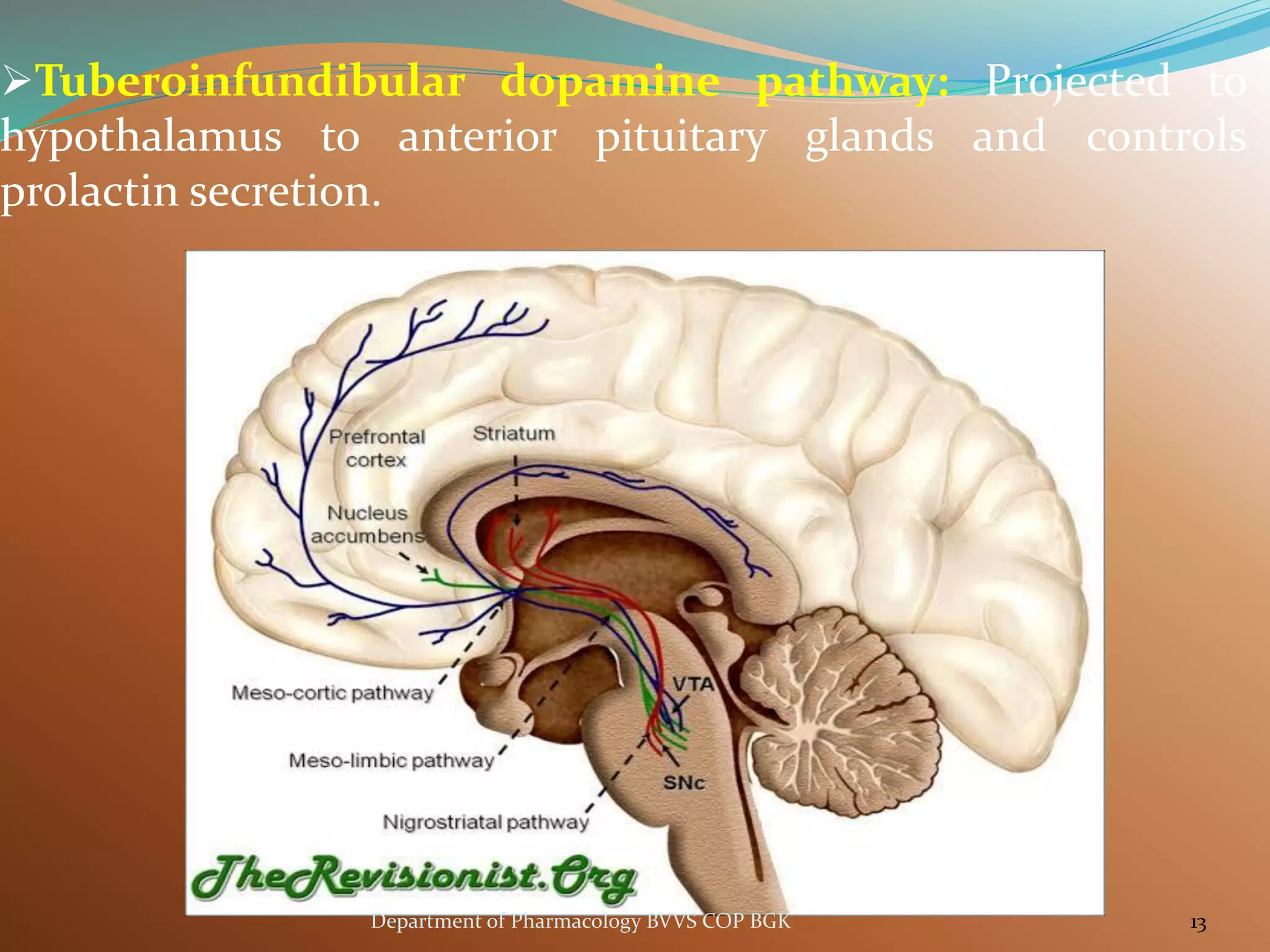
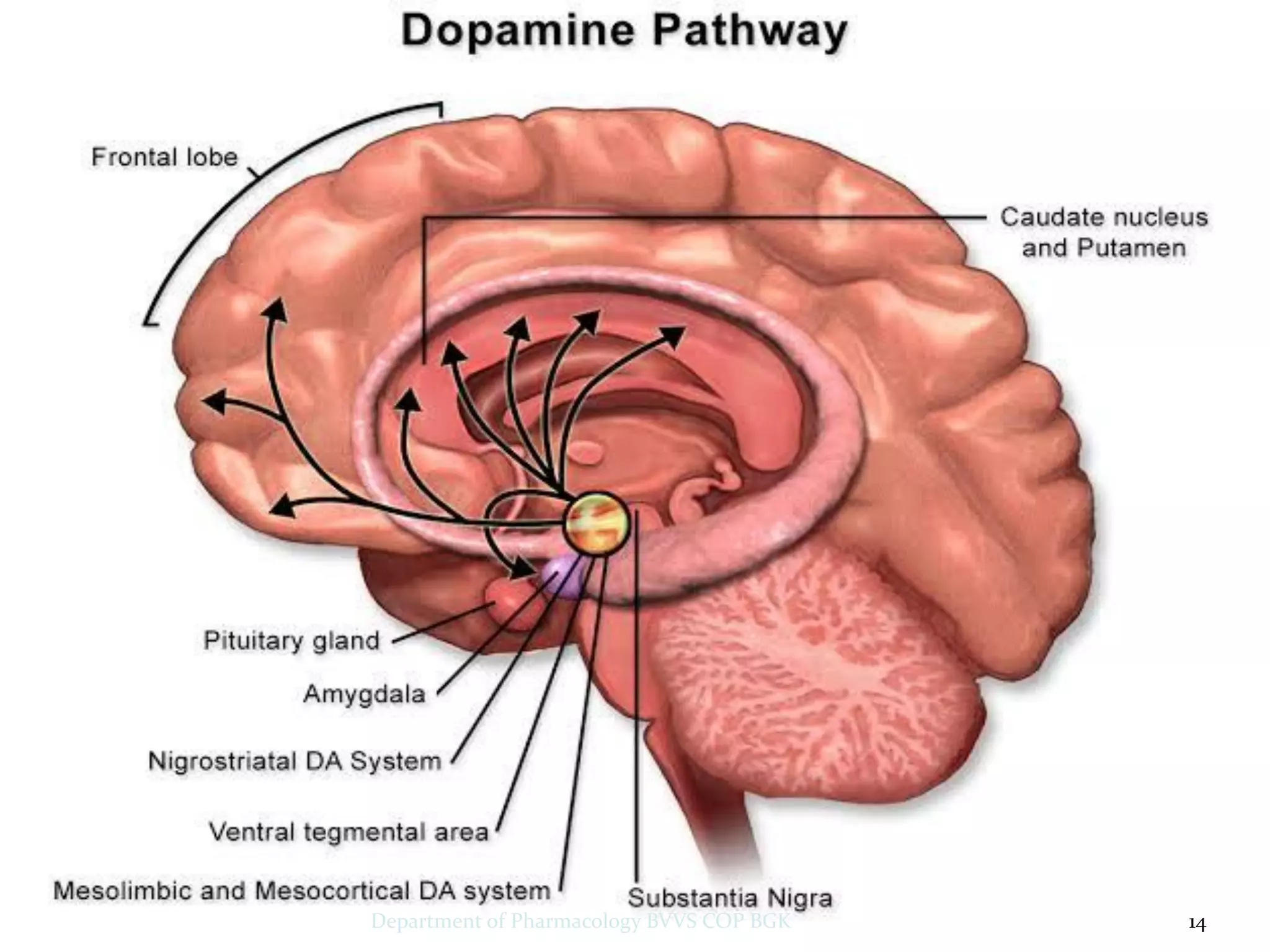
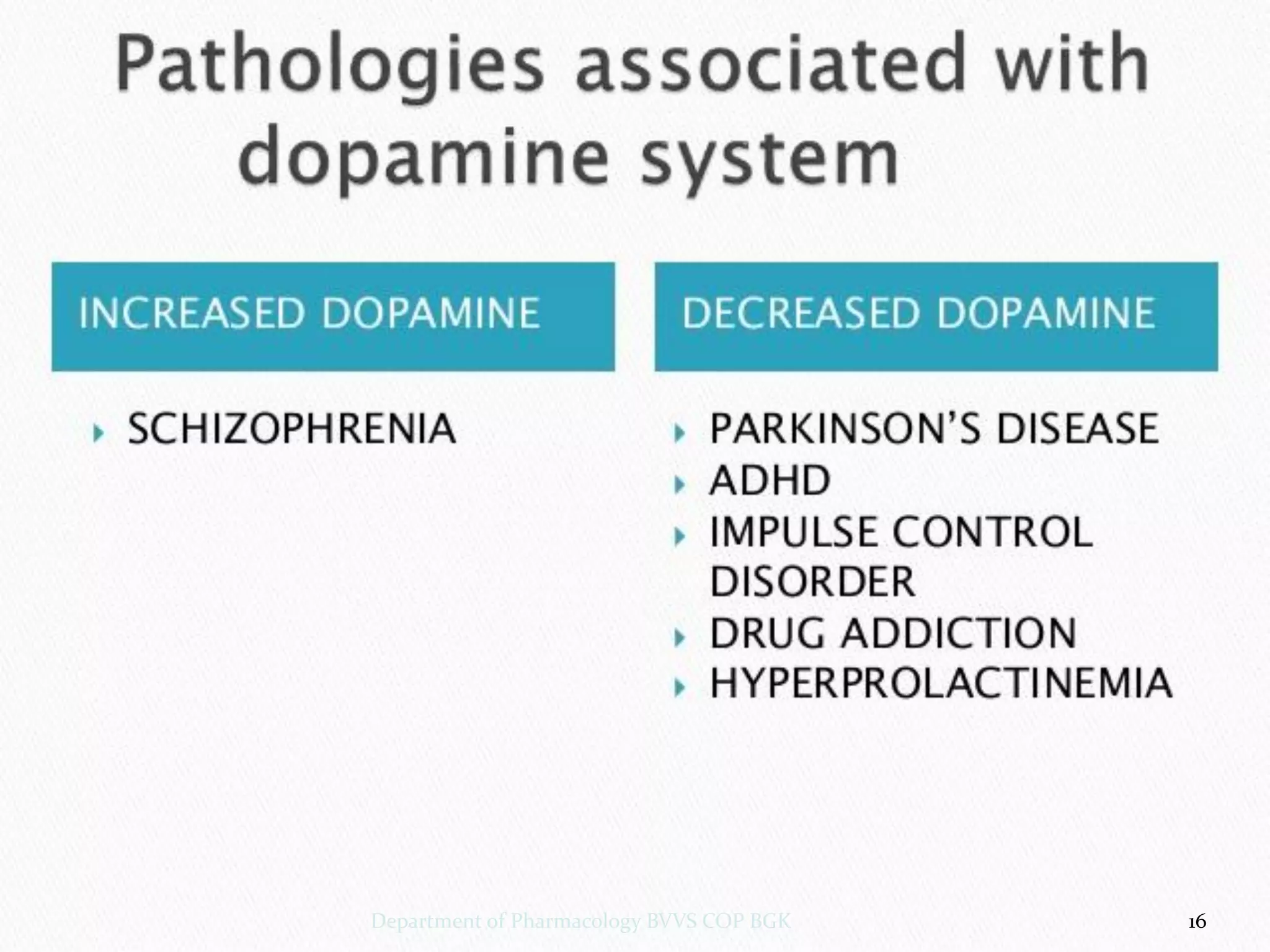
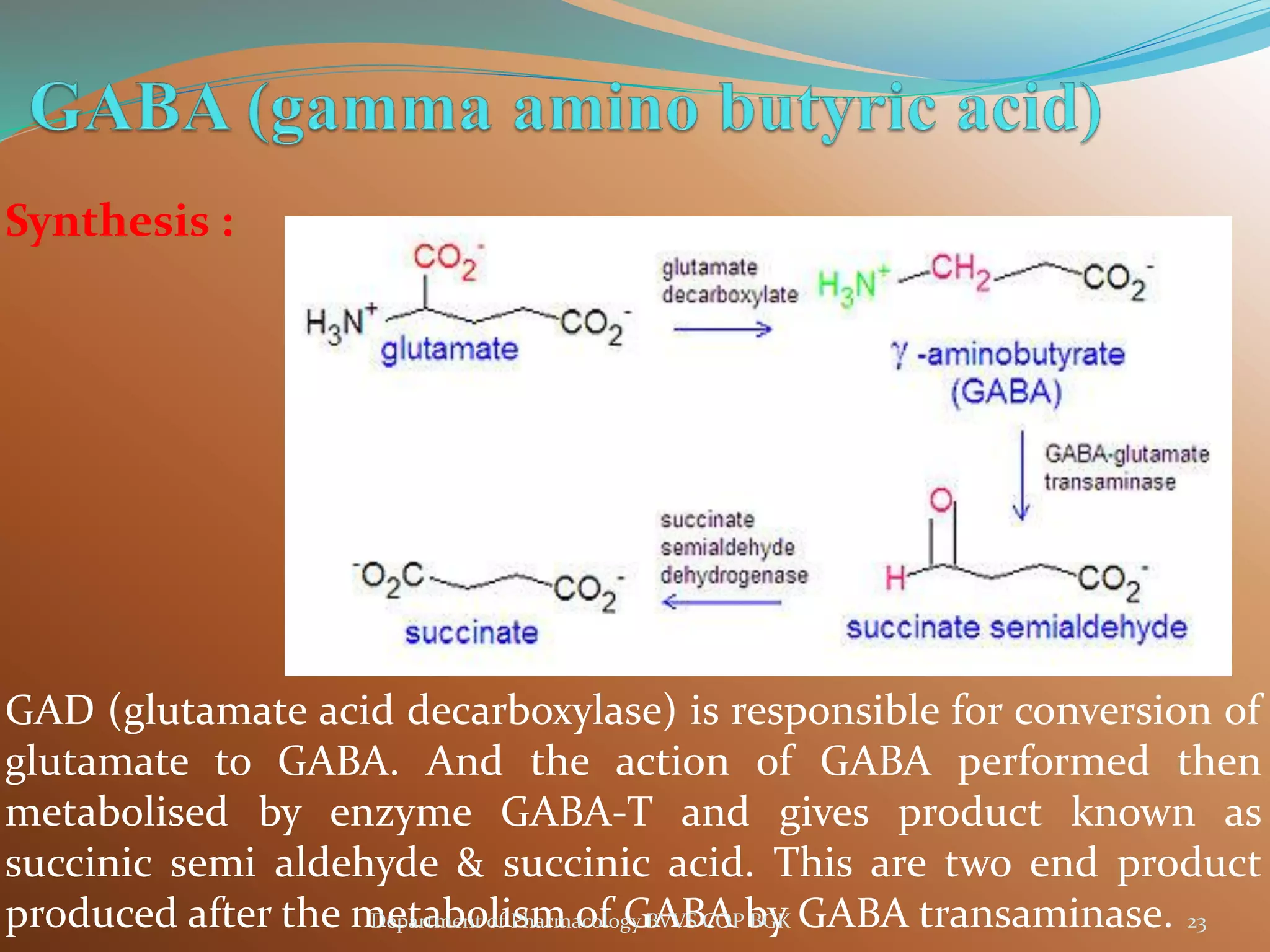
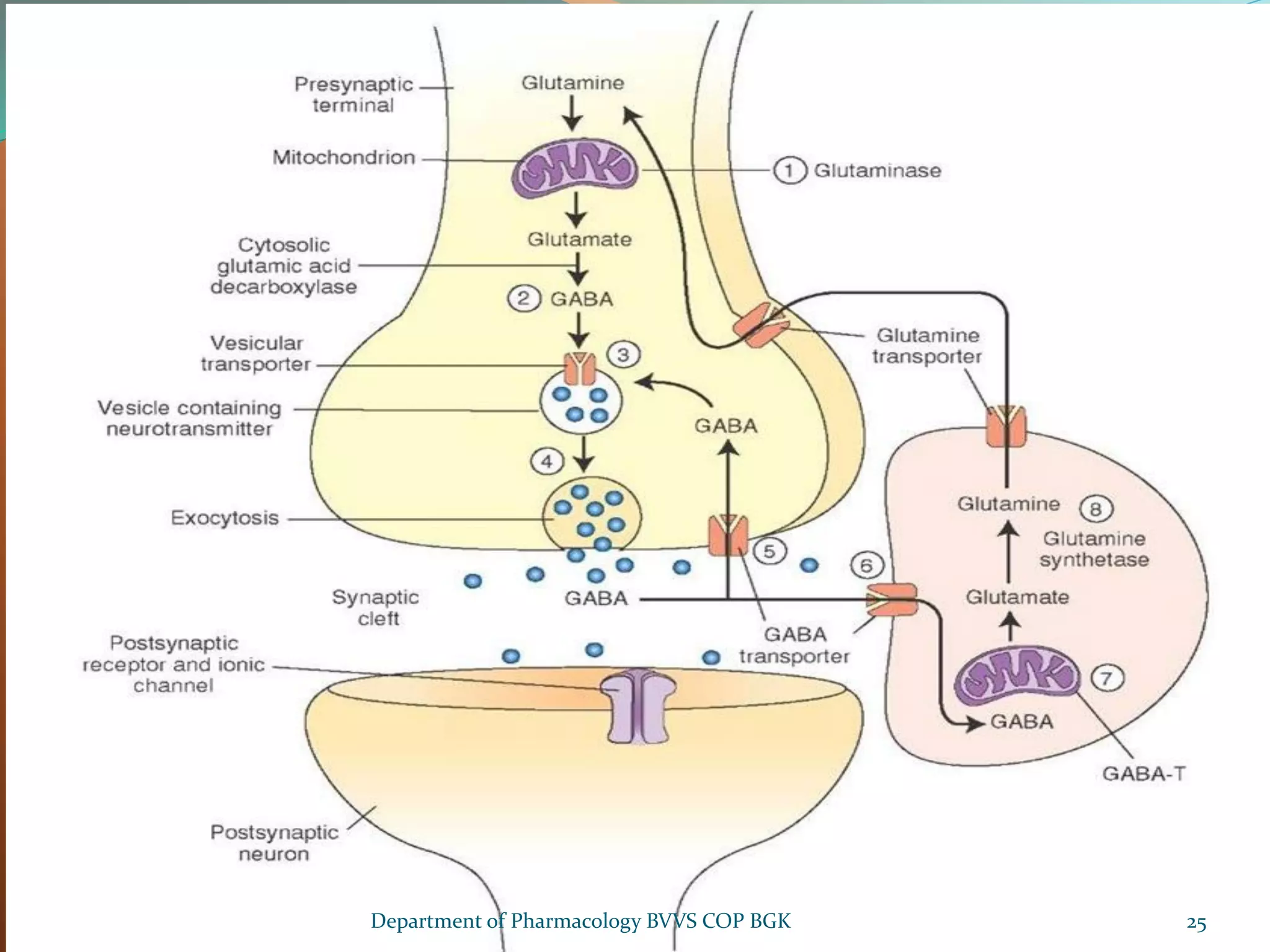
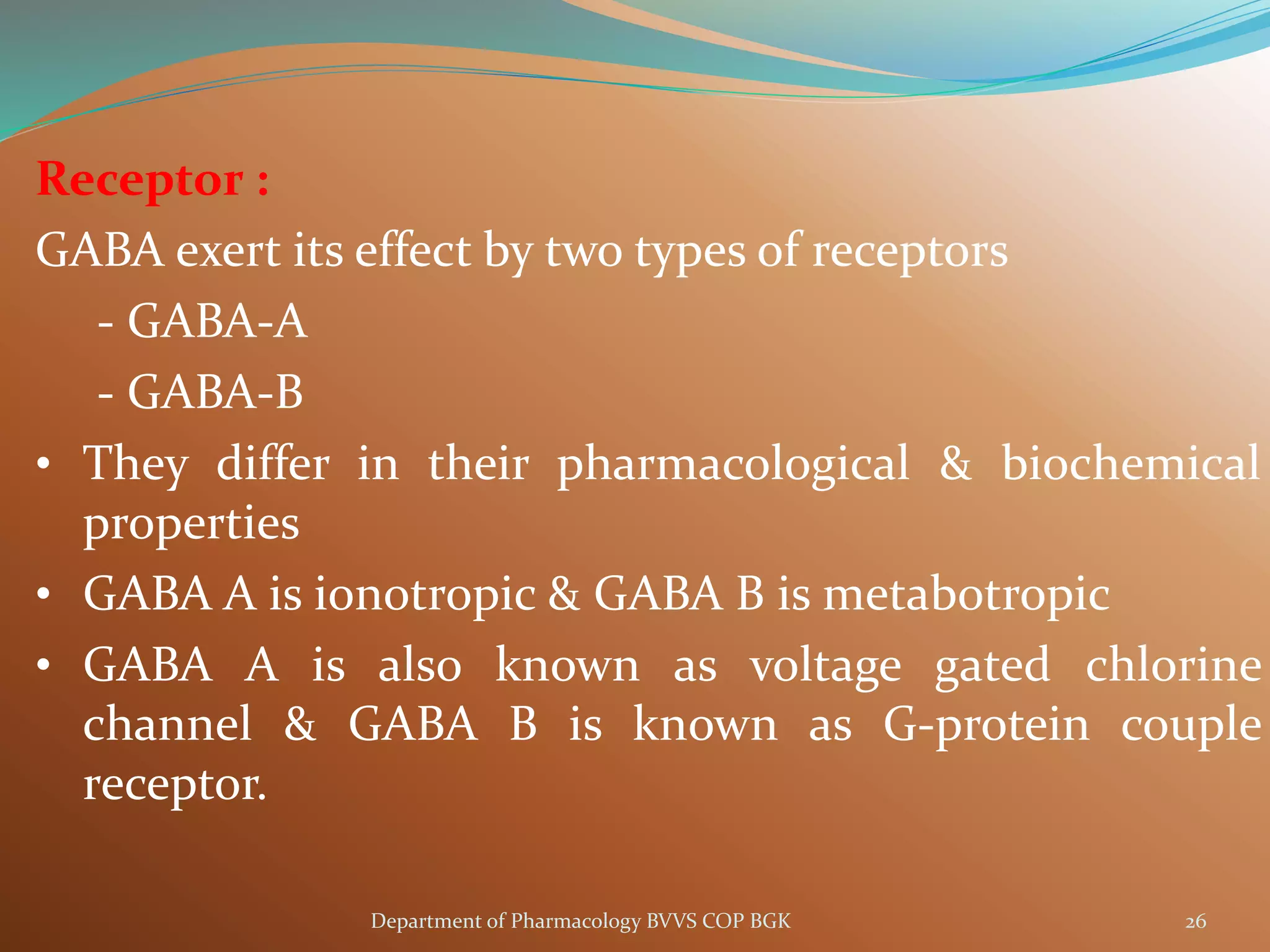
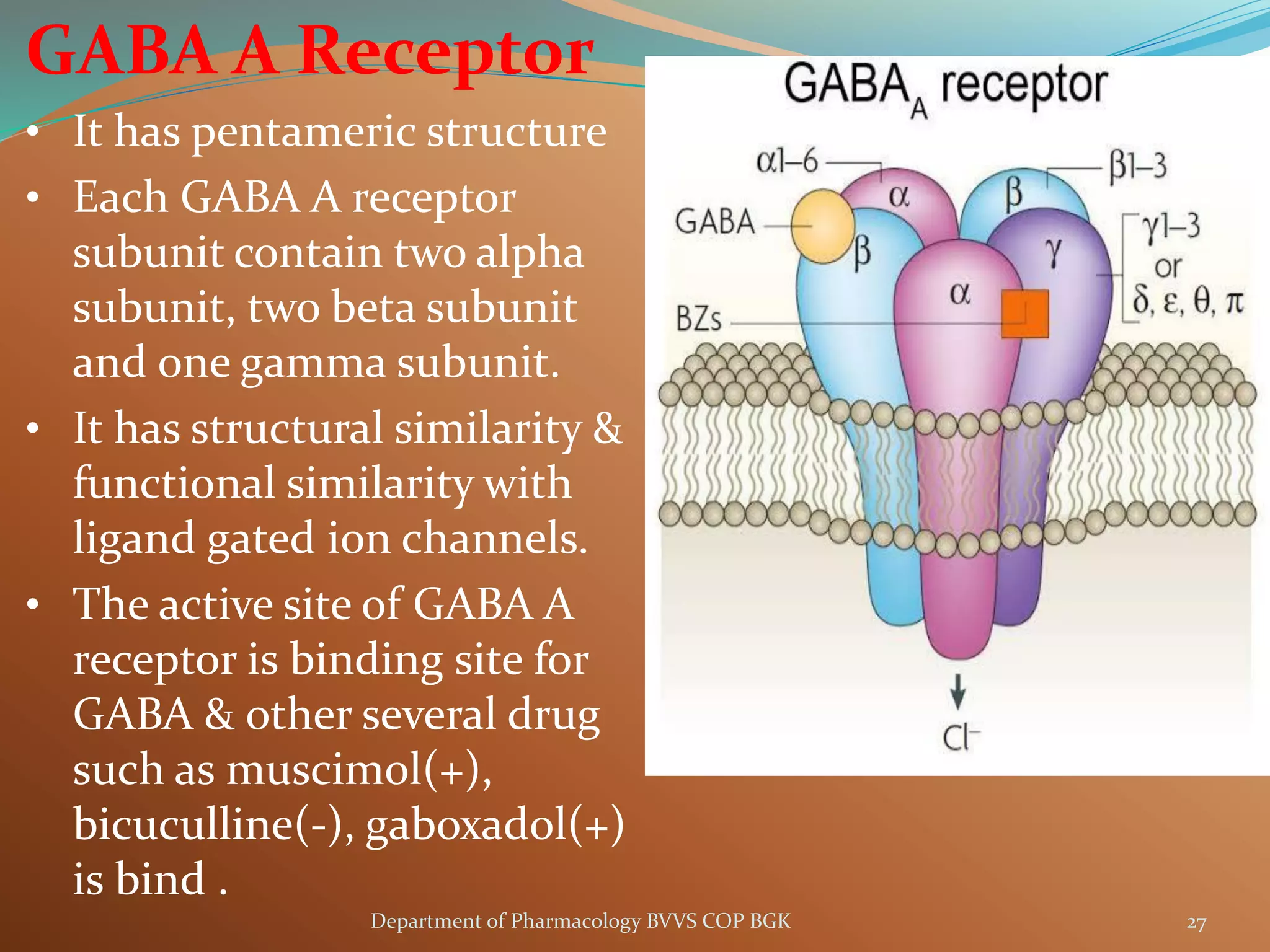
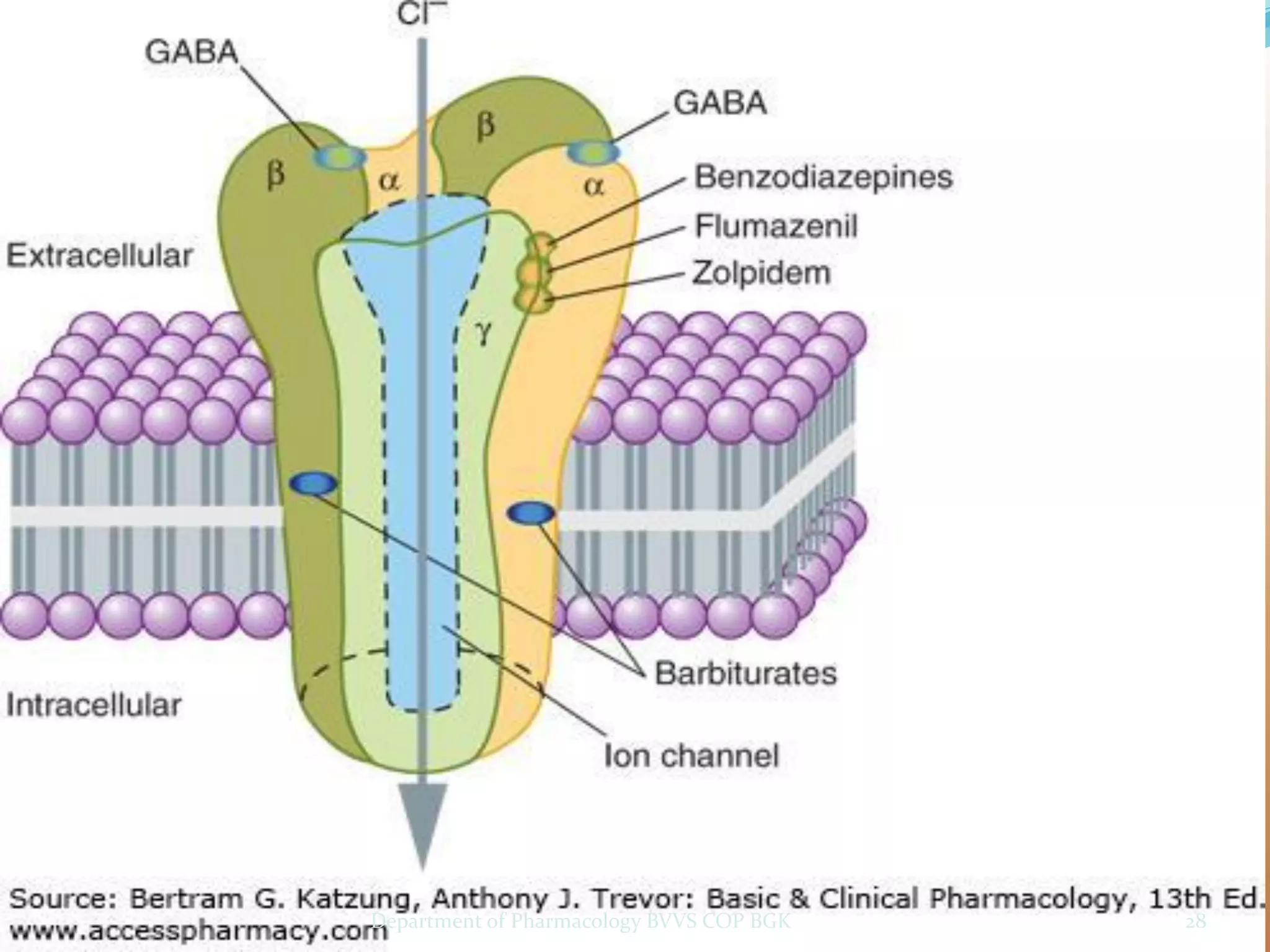
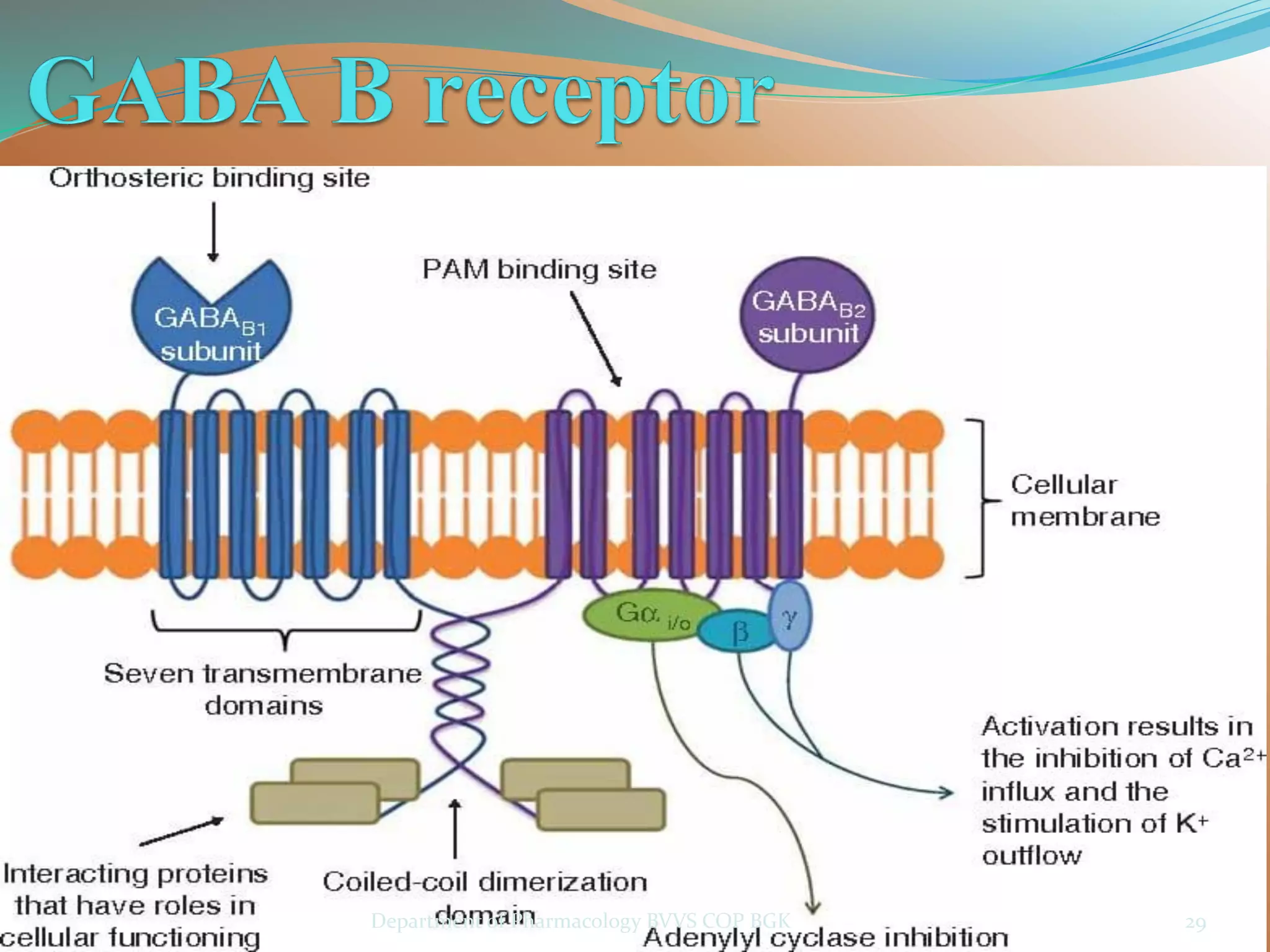
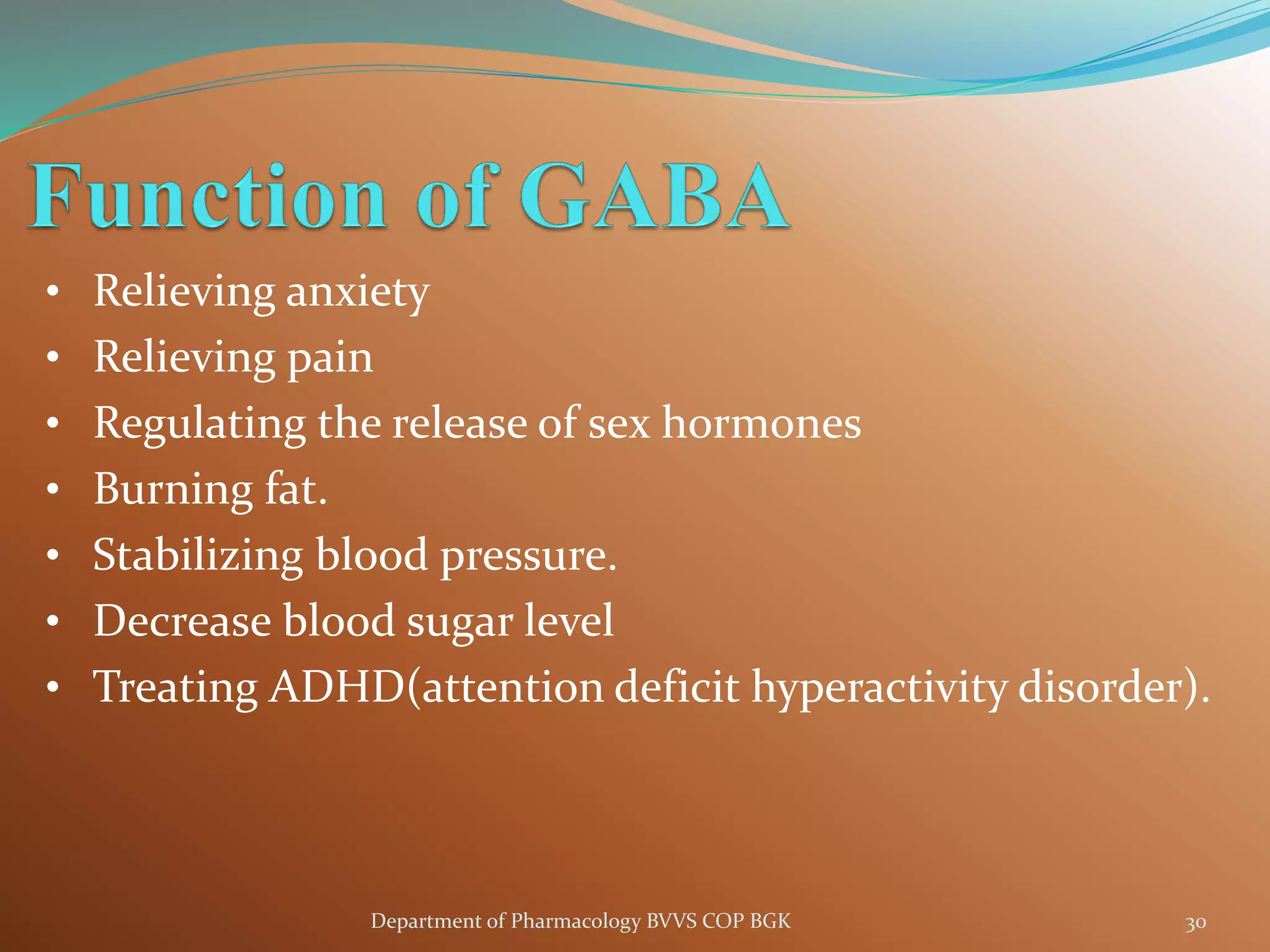
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that regulates cardiac, vascular and endocrine function. It is produced in the midbrain and hypothalamus and also functions in the kidneys. Dopamine acts through D1, D2, alpha and beta adrenergic receptors on the cell membrane. It is involved in movement, behavior, prolactin release and other processes through its receptors in areas like the striatum, nucleus accumbens and frontal cortex. Imbalances in dopamine signaling are implicated in disorders such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia and substance abuse.