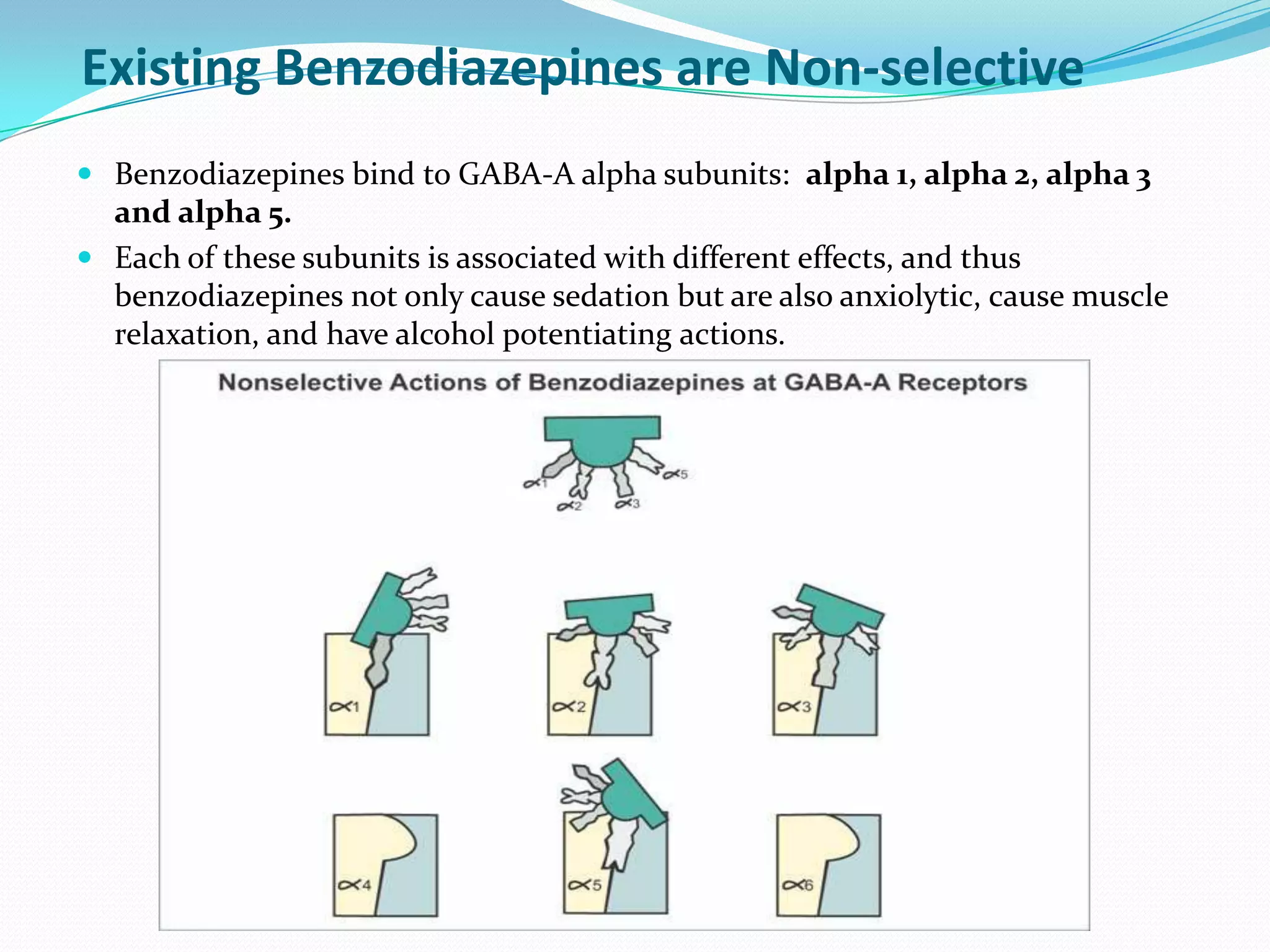
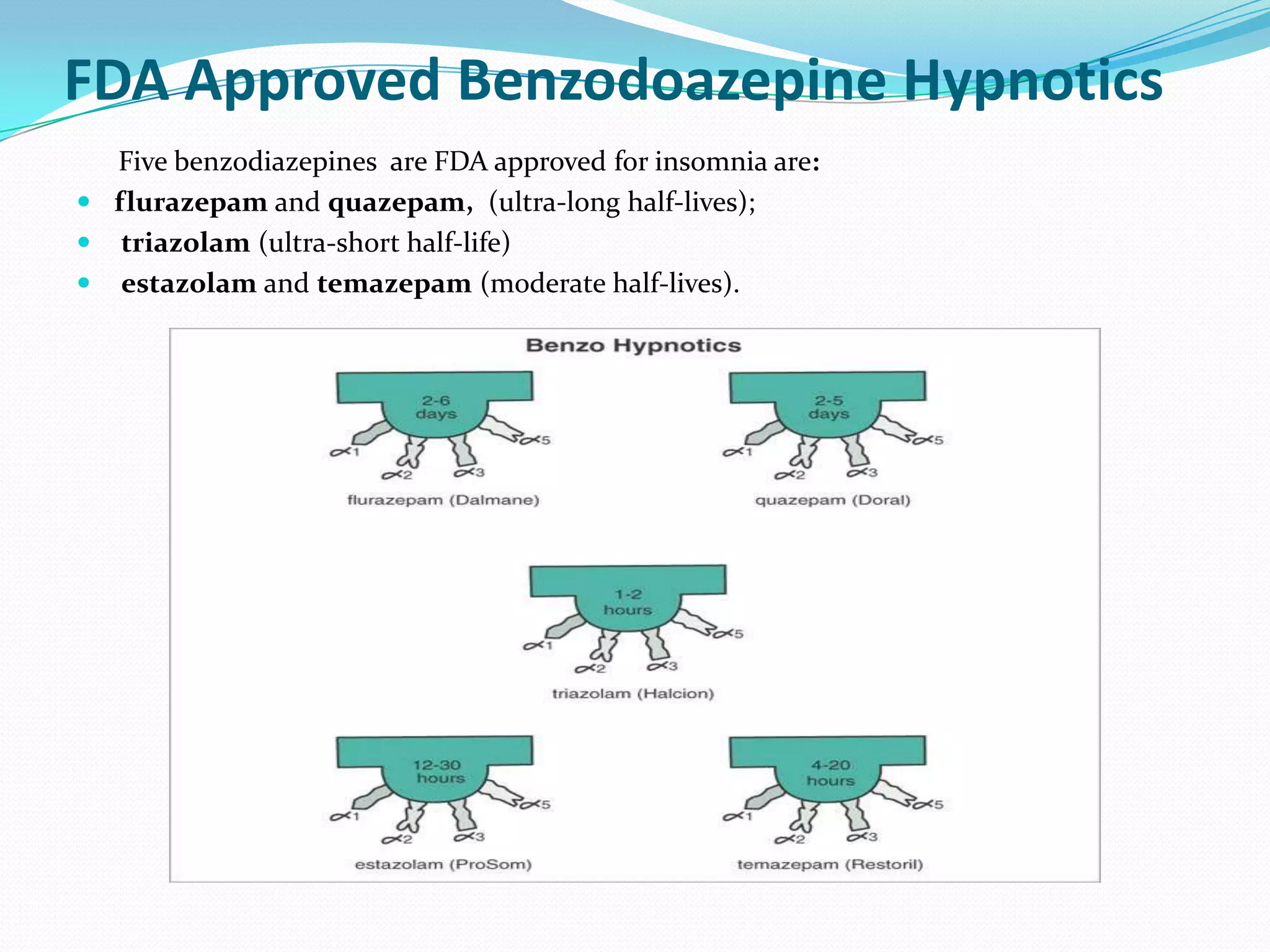
This document discusses the mechanisms of action of benzodiazepines. It notes that benzodiazepines augment the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA at GABA-A receptors. They can be selective for different GABA receptor subunits involved in sleep, anxiety, or addiction. The hypnotic and anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines are explained by their actions on GABA receptors in the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamic regions involved in sleep/wake regulation. Adverse effects and issues with dependence and withdrawal are also covered. Novel approaches to anxiolytic drugs targeting GABA receptors without addiction liability are mentioned.