This document provides an overview of dopamine, including its history, synthesis, receptors, functions, pathways, and relevance to various psychiatric and neurological conditions. Some key points:
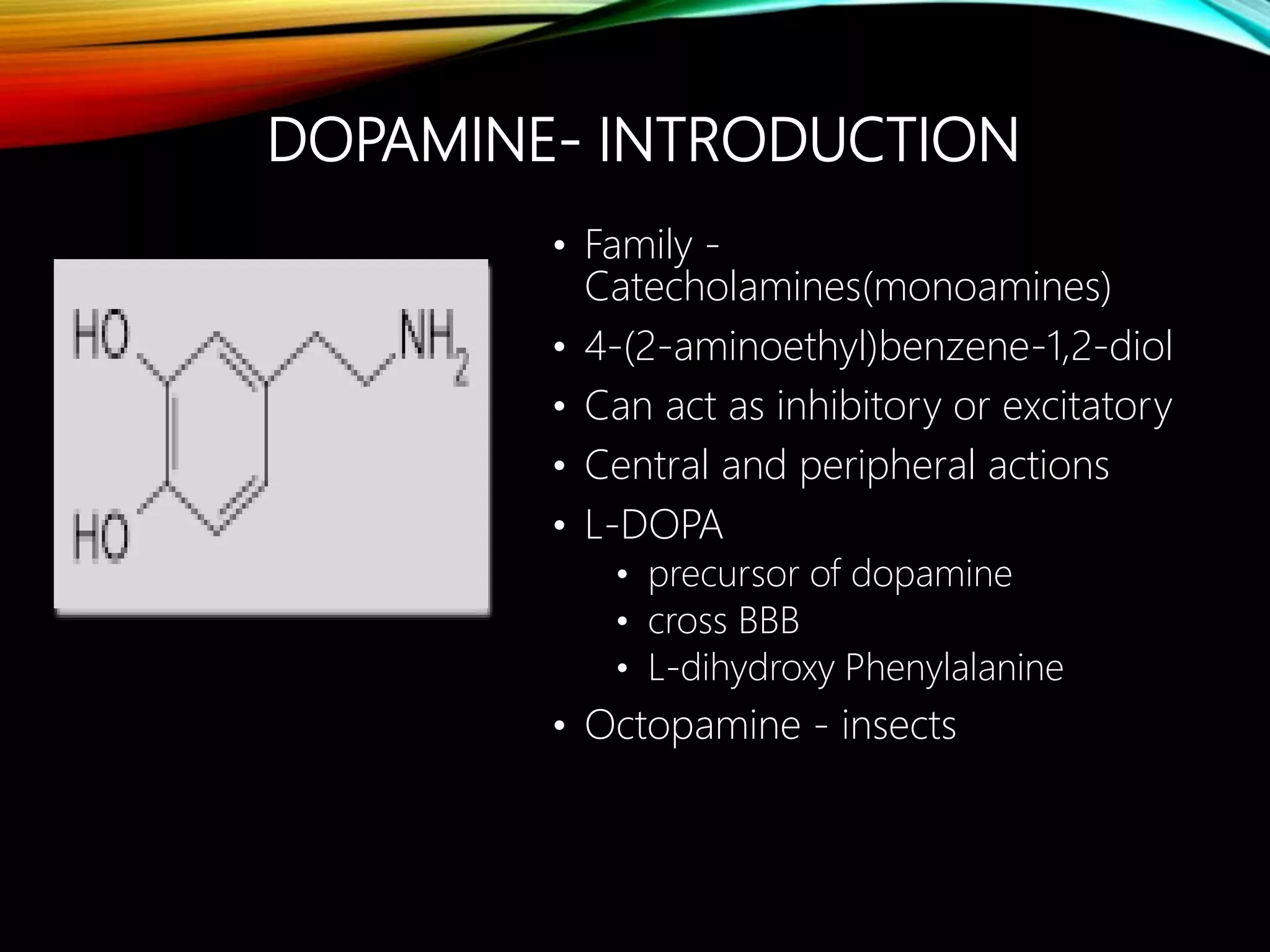
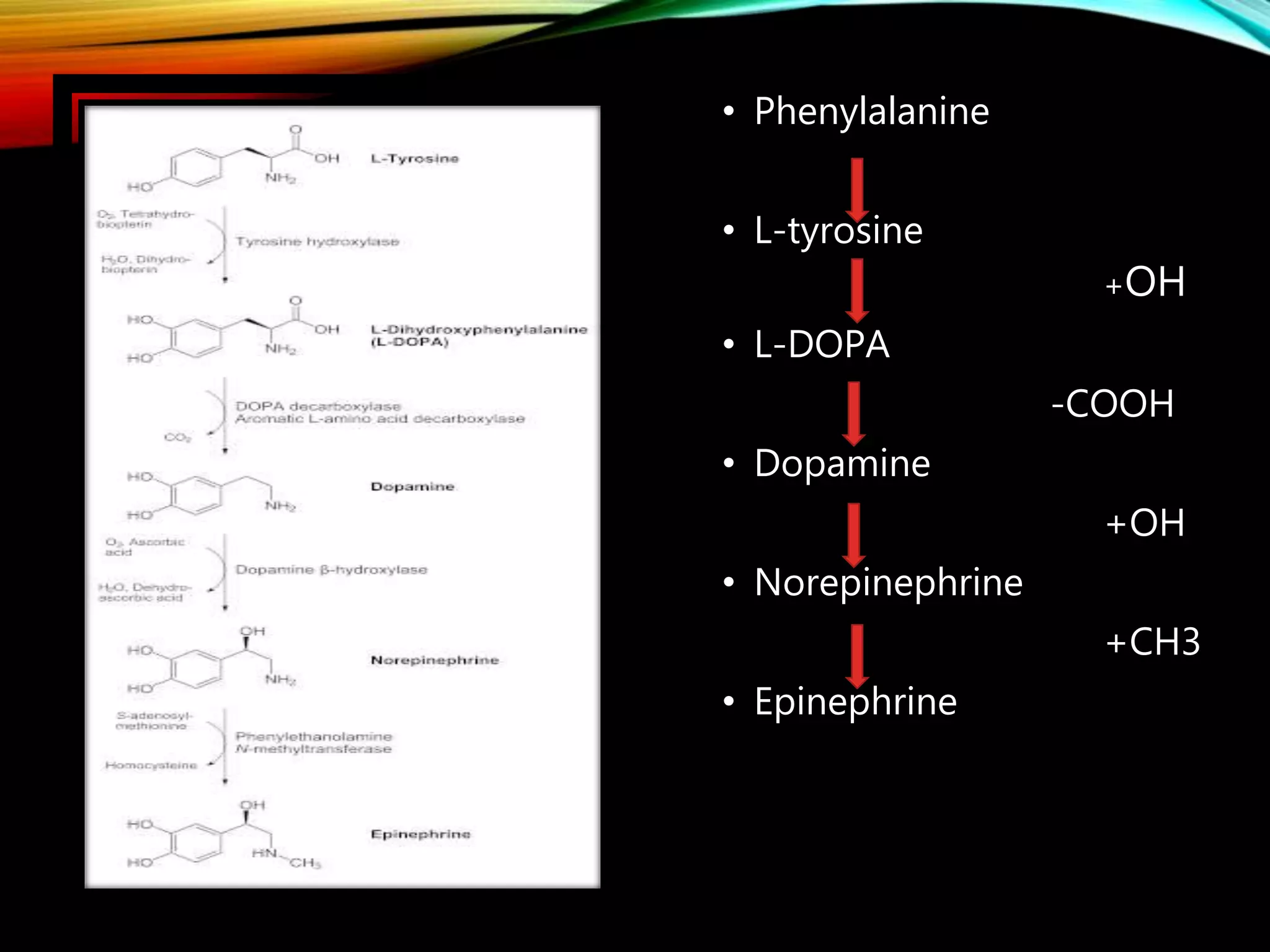
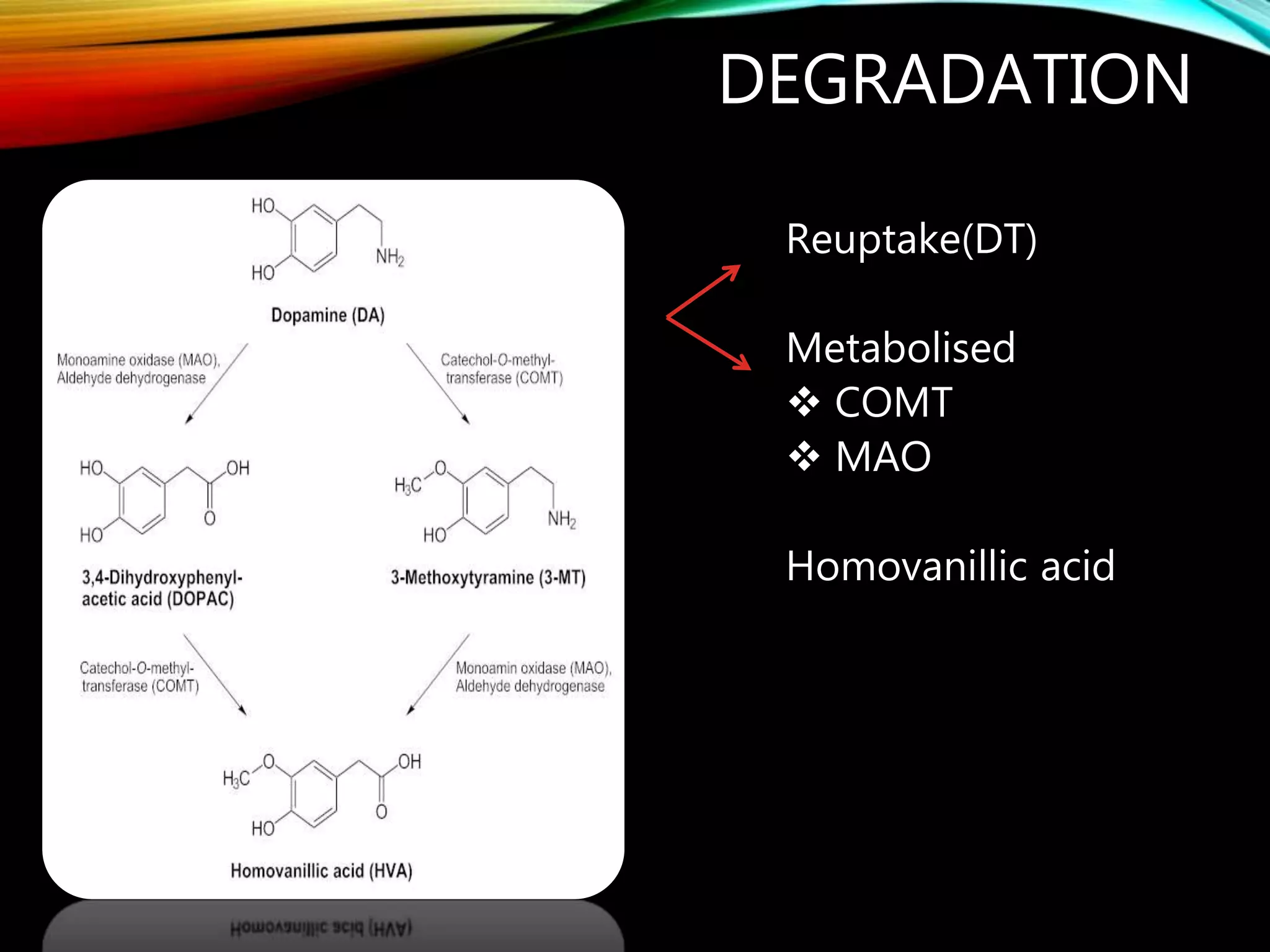
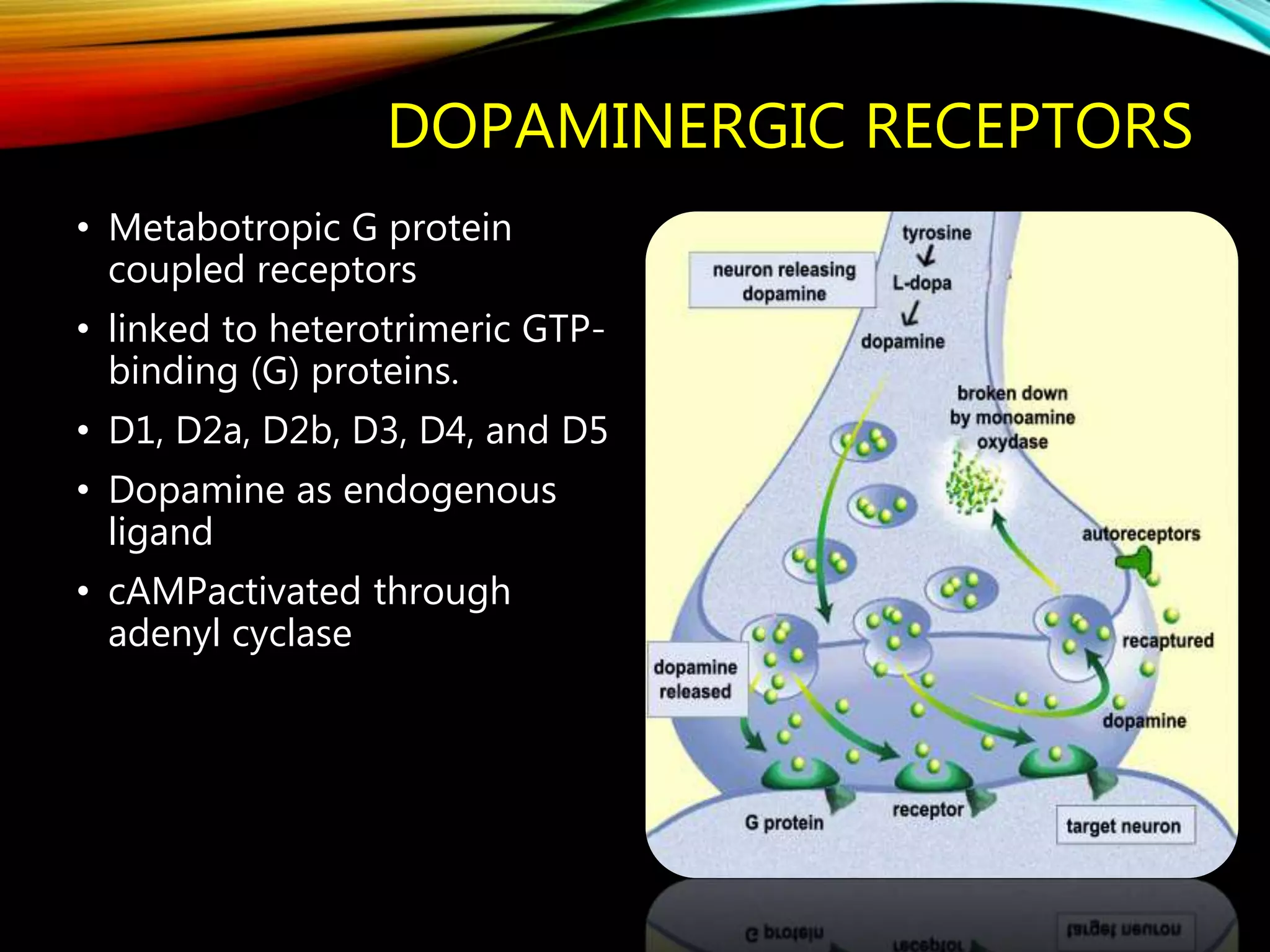
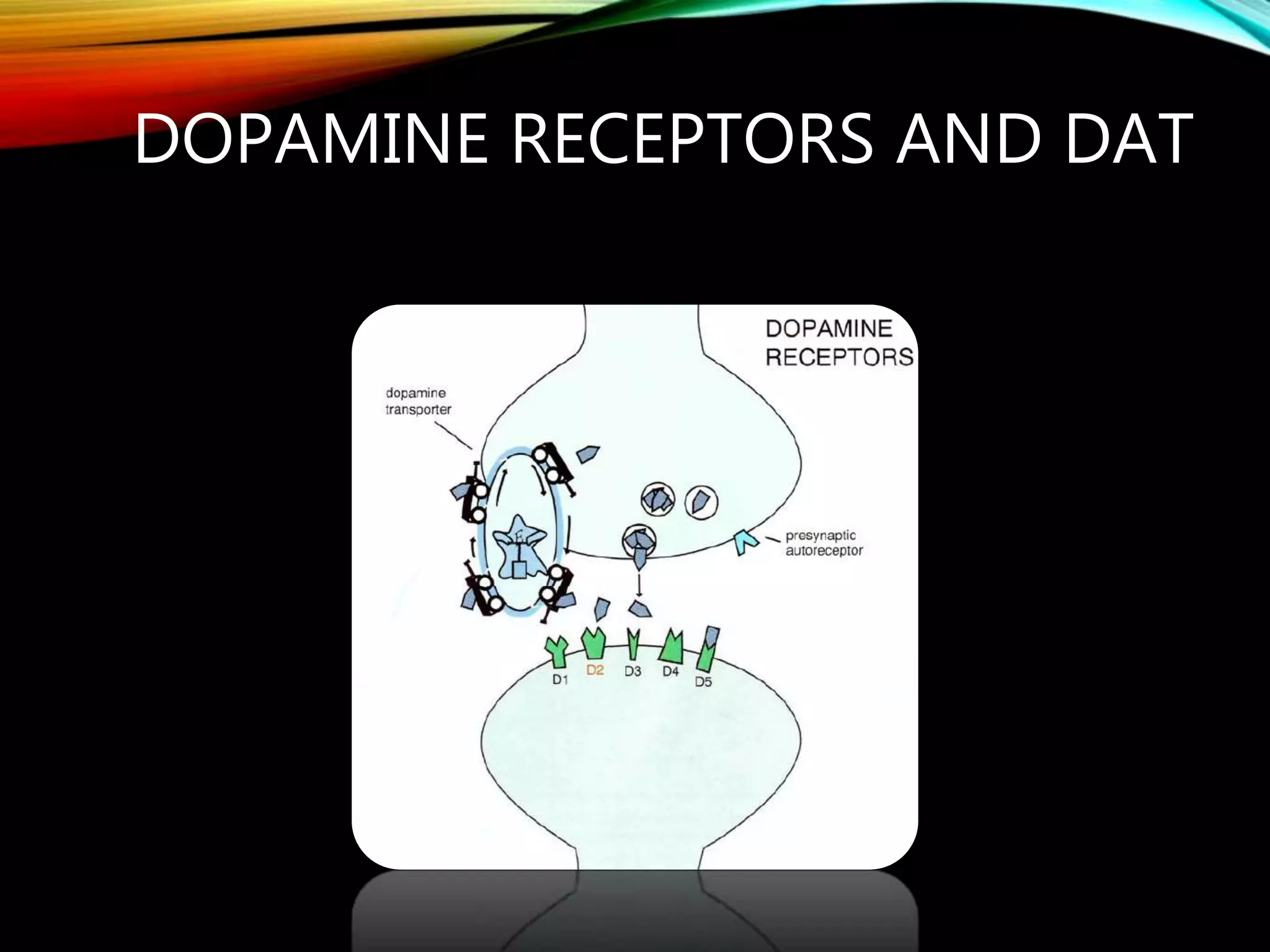
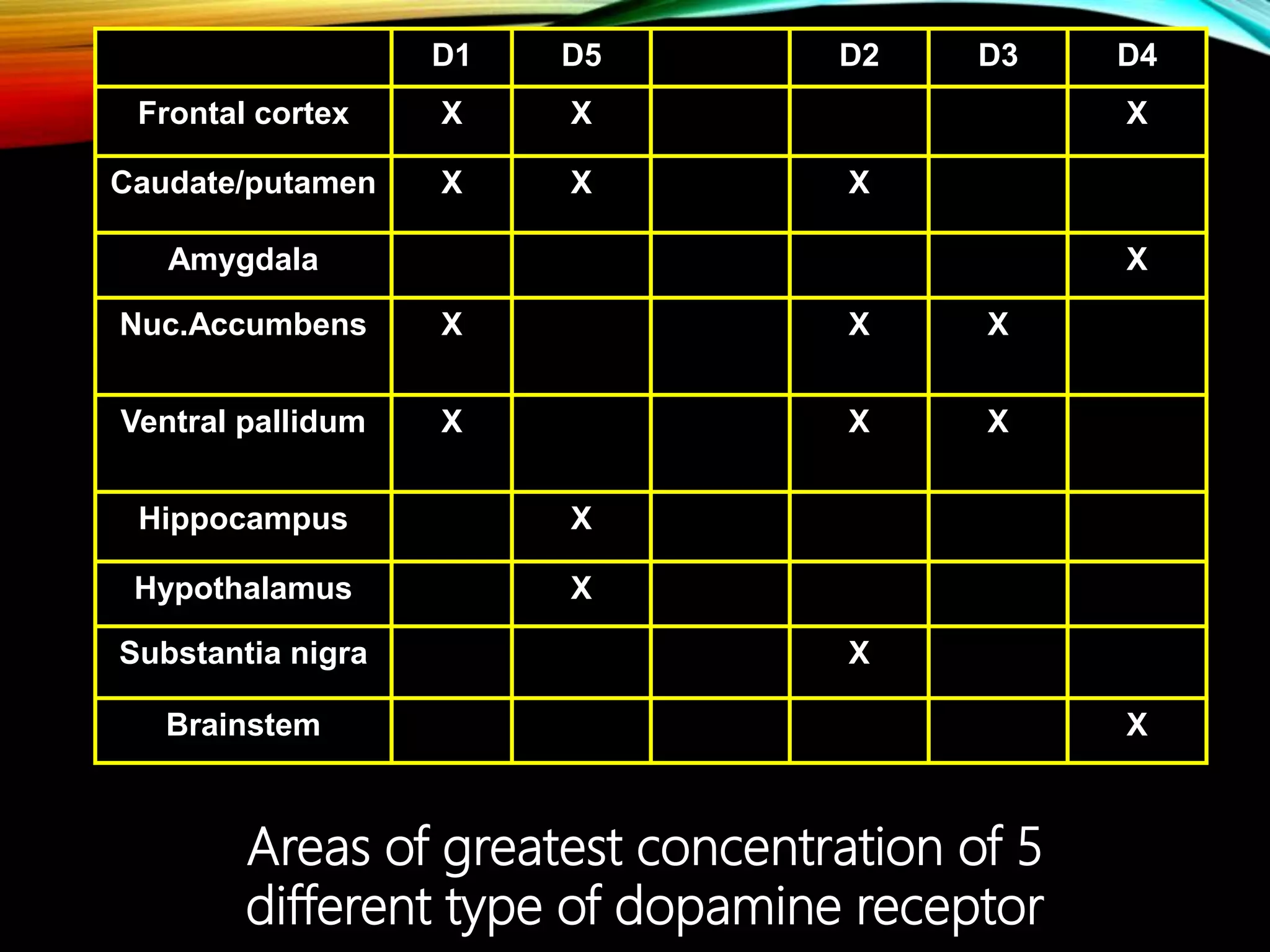
- Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine. It acts through D1-D5 G protein-coupled receptors.
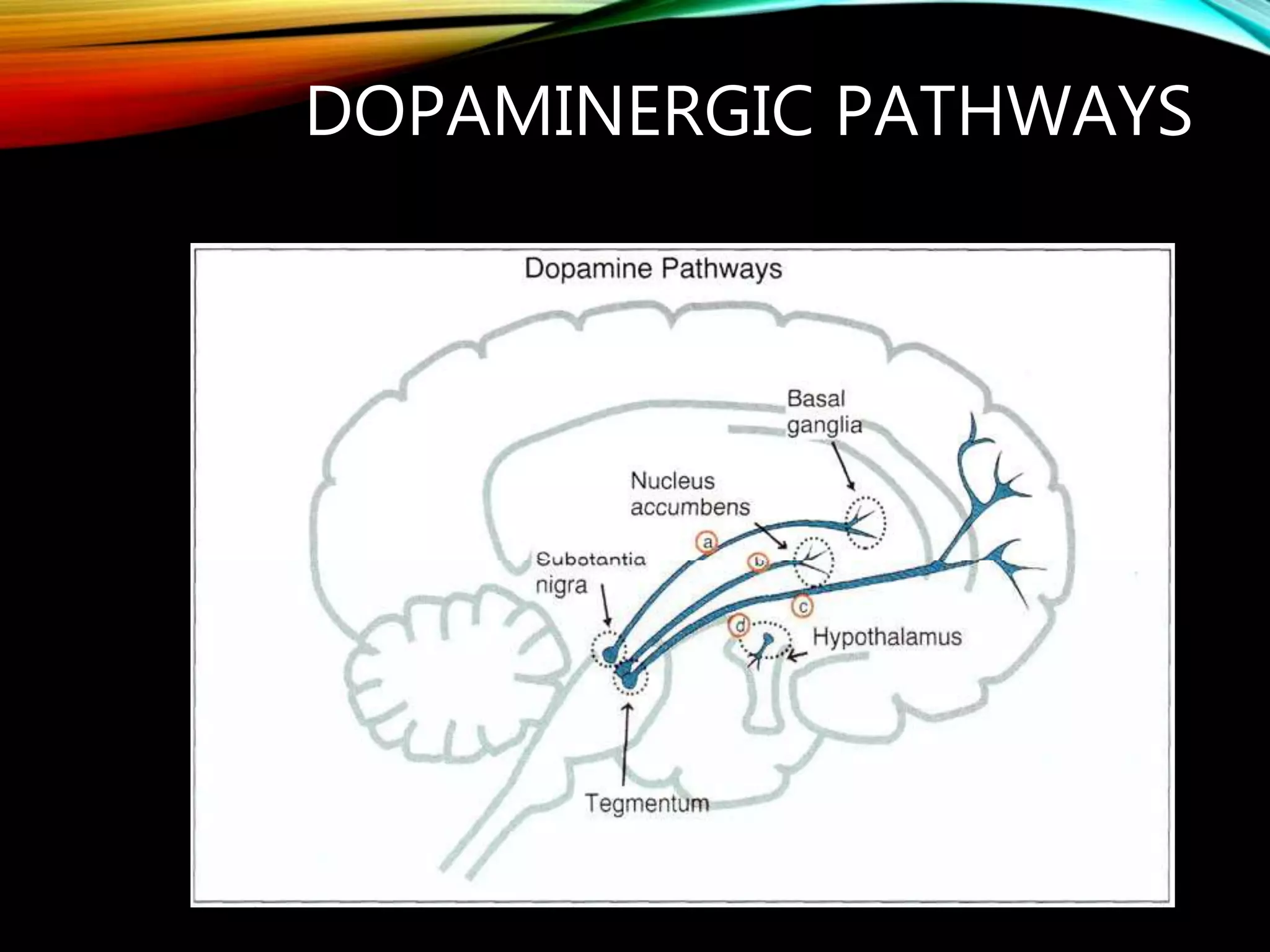
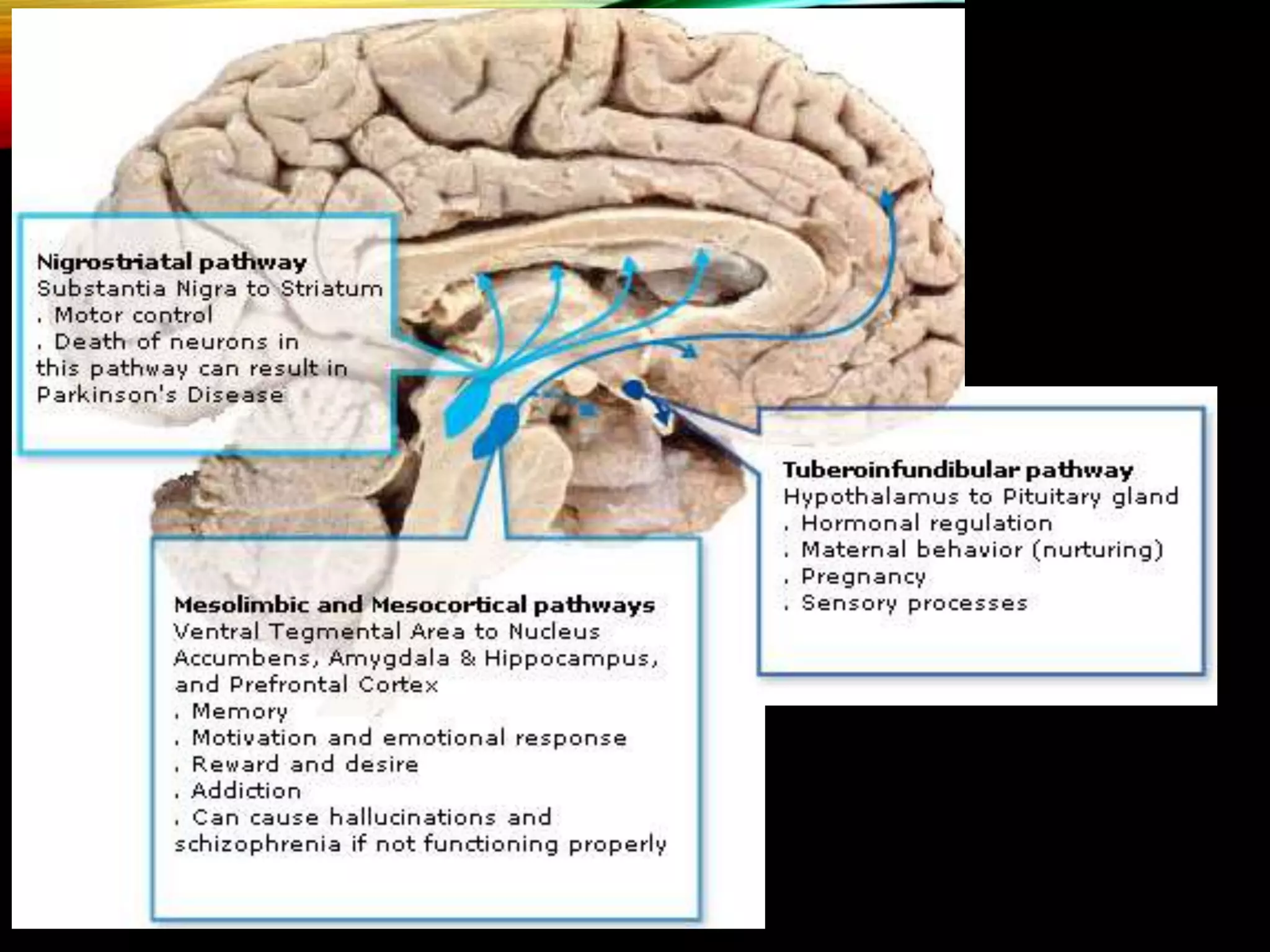
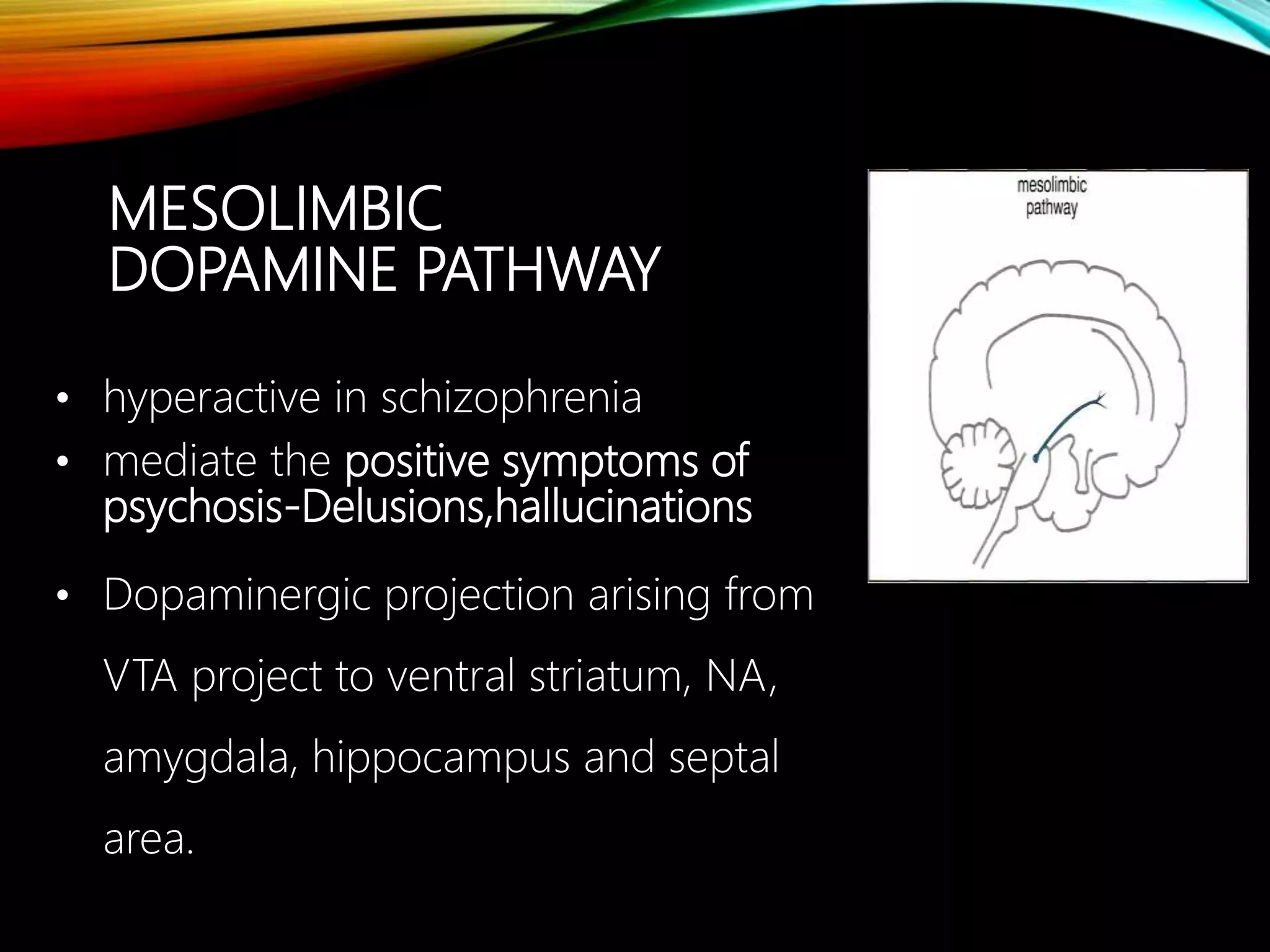
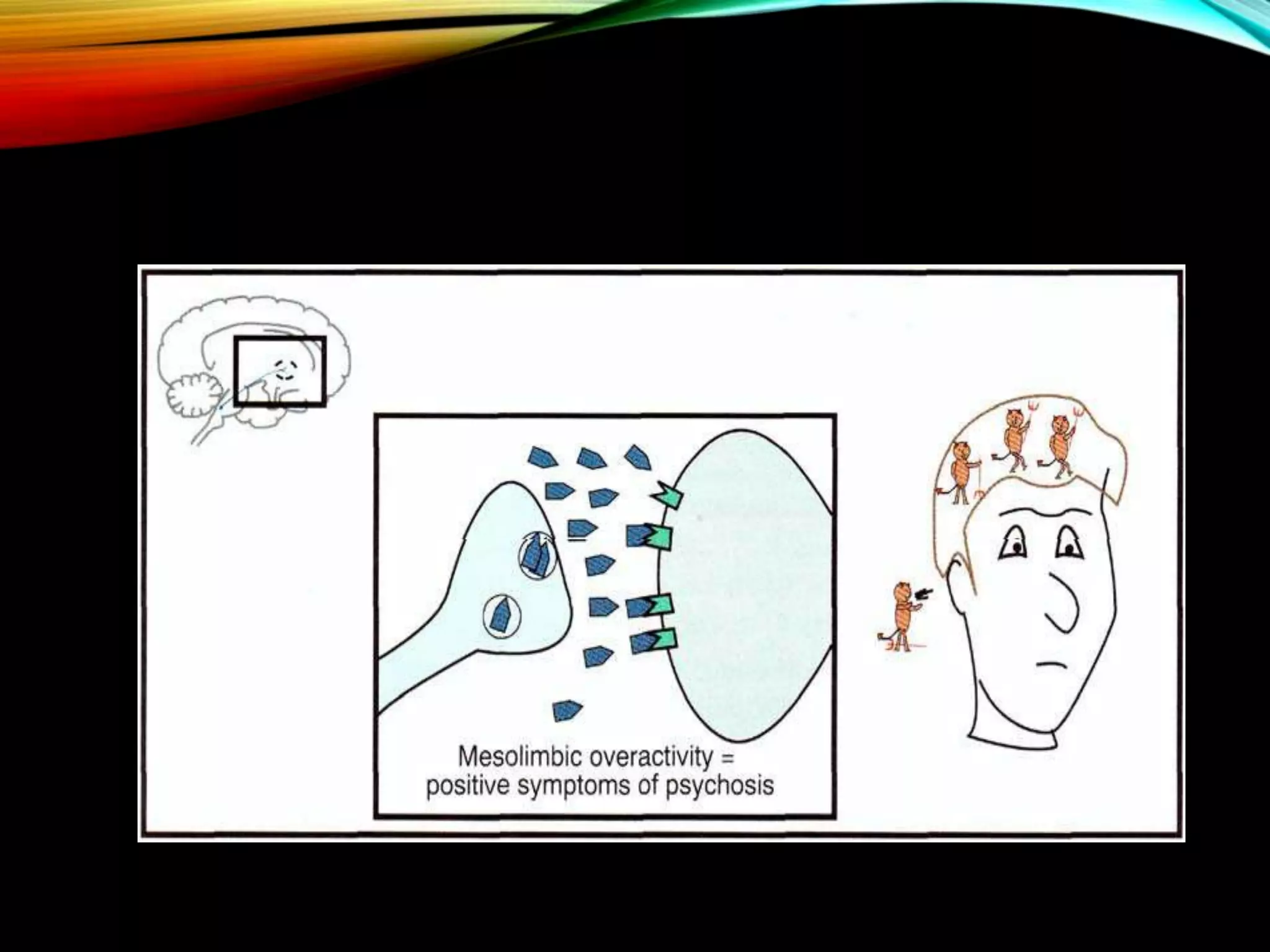
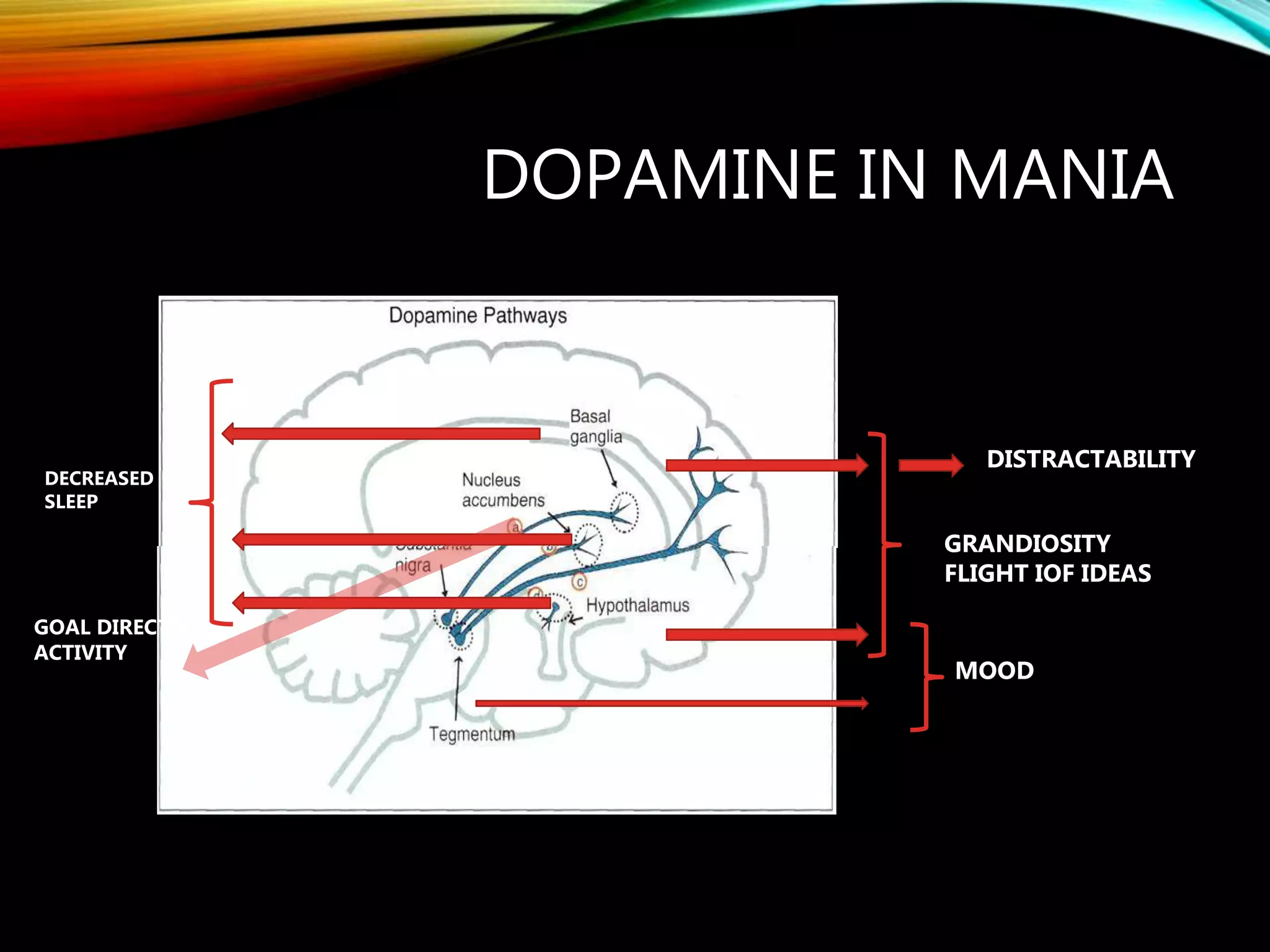
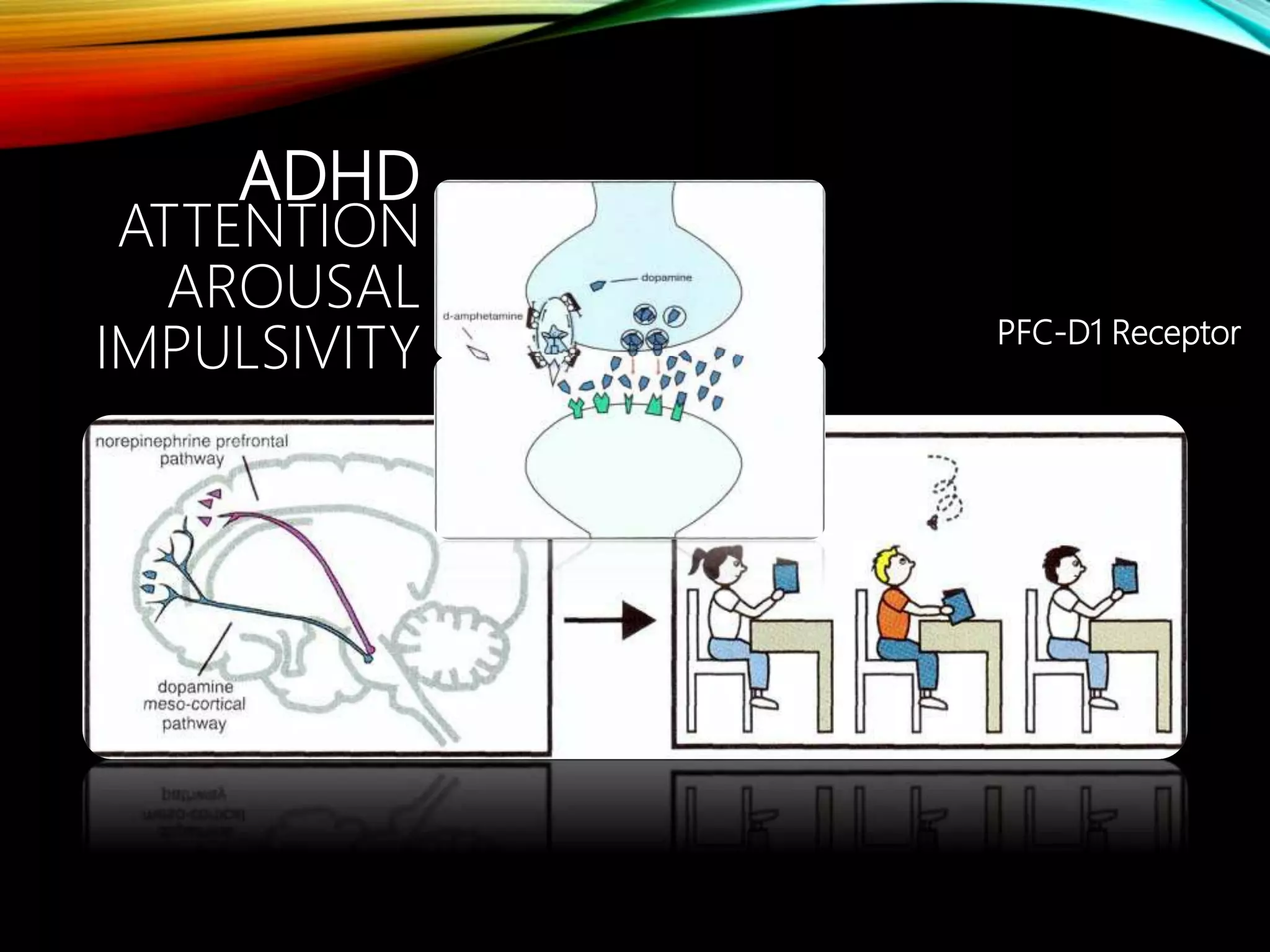
- Major dopaminergic pathways include the mesocortical, mesolimbic, nigrostriatal, and tuberoinfundibular pathways which are involved in cognition, reward, movement, and prolactin regulation respectively.
- Dopamine plays a role in schizophrenia, mood disorders, attention deficit disorders, substance abuse, and movement disorders like Parkinson's disease























![NMS
Acute dopamine antagonism (of
hypothalamo spinal tracts) by anti
psychotics may alter sympathetic
nervous system function
Manifestations include increased
muscle metabolism and tone (due to
increased intracellular [Ca2+]), which
elevate creatine phosphokinase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dopamine-161117180920/75/Dopamine-36-2048.jpg)










