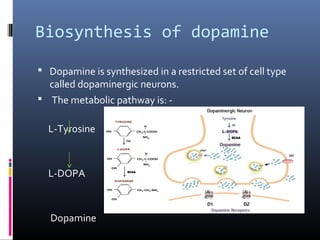
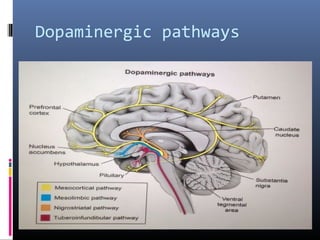
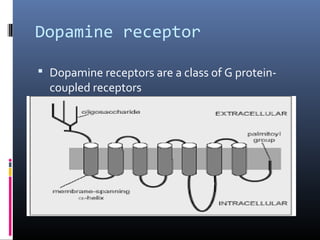
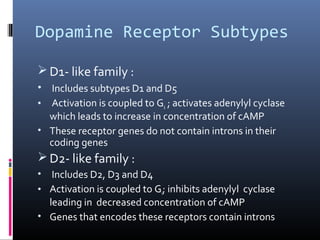
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that binds to dopamine receptors and influences movement, memory, reward, behavior and other functions. It is synthesized from tyrosine and transported through dopaminergic pathways in the brain. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D1-like and D2-like, which are G protein-coupled receptors that either activate or inhibit the enzyme adenylyl cyclase. Dopamine receptor dysfunction is implicated in diseases like Parkinson's, schizophrenia and addiction. Dopamine agonists mimic dopamine while antagonists block dopamine receptors.