The document summarizes three domains of learning: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.
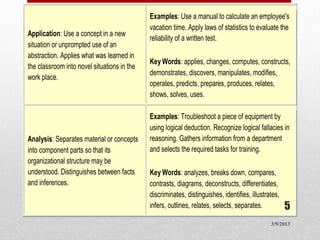
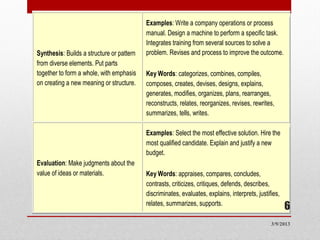
1) The cognitive domain involves mental skills like knowledge, comprehension, and application. It has six categories ranging from remembering to evaluating.
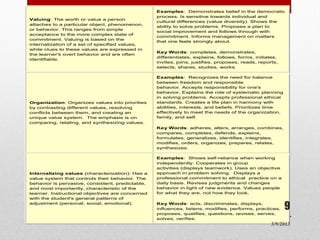
2) The affective domain deals with emotions, values, and attitudes. It has five categories from receiving phenomena to internalizing values.
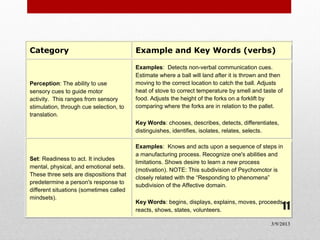
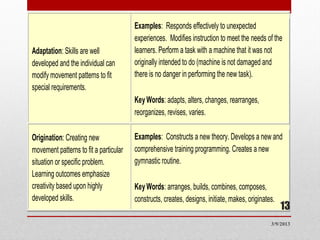
3) The psychomotor domain includes physical skills and movement. It has seven categories from perception to origination.