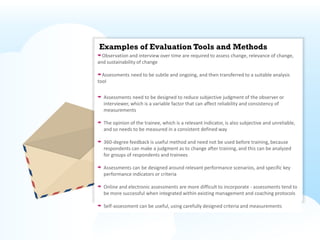
The document provides an overview of instructional design theories covered in a session on instructional design, including:
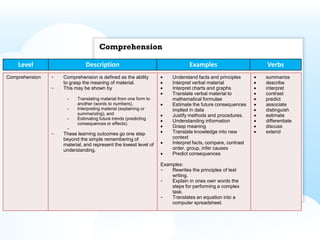
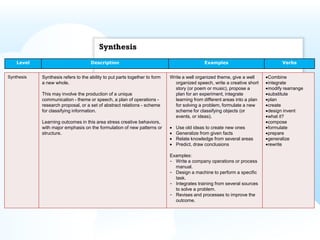
- Bloom's Taxonomy, which categorizes learning objectives from simplest to most complex.
- Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction, which outlines steps for effective instruction including gaining attention, informing objectives, and eliciting performance.
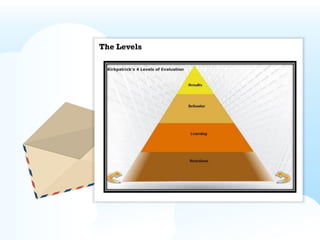
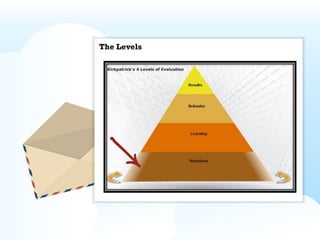
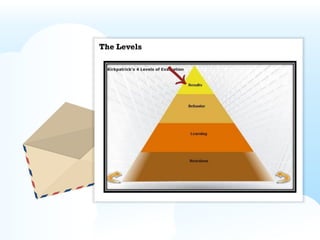
- Kirkpatrick's Four Levels of Training Evaluation, which measures the effectiveness of training through reaction, learning, behavior change, and results.