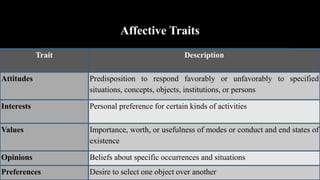
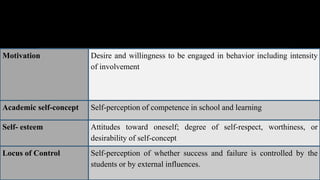
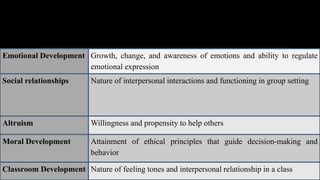
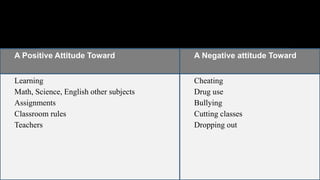
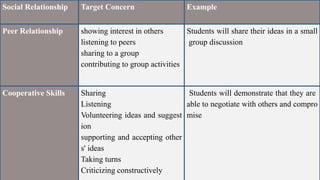
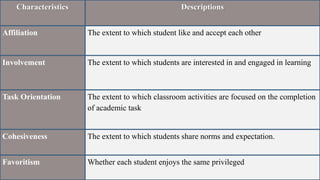
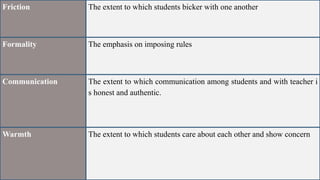
1. The document discusses assessing affective learning outcomes, which relate to non-cognitive variables like attitudes, interests, and values.
2. It defines key affective concepts like the affective domain, levels of affective learning, and methods of assessing affective outcomes.
3. The importance of assessing the affective domain is explained, such as its ability to predict future behavior and help teachers teach more effectively.