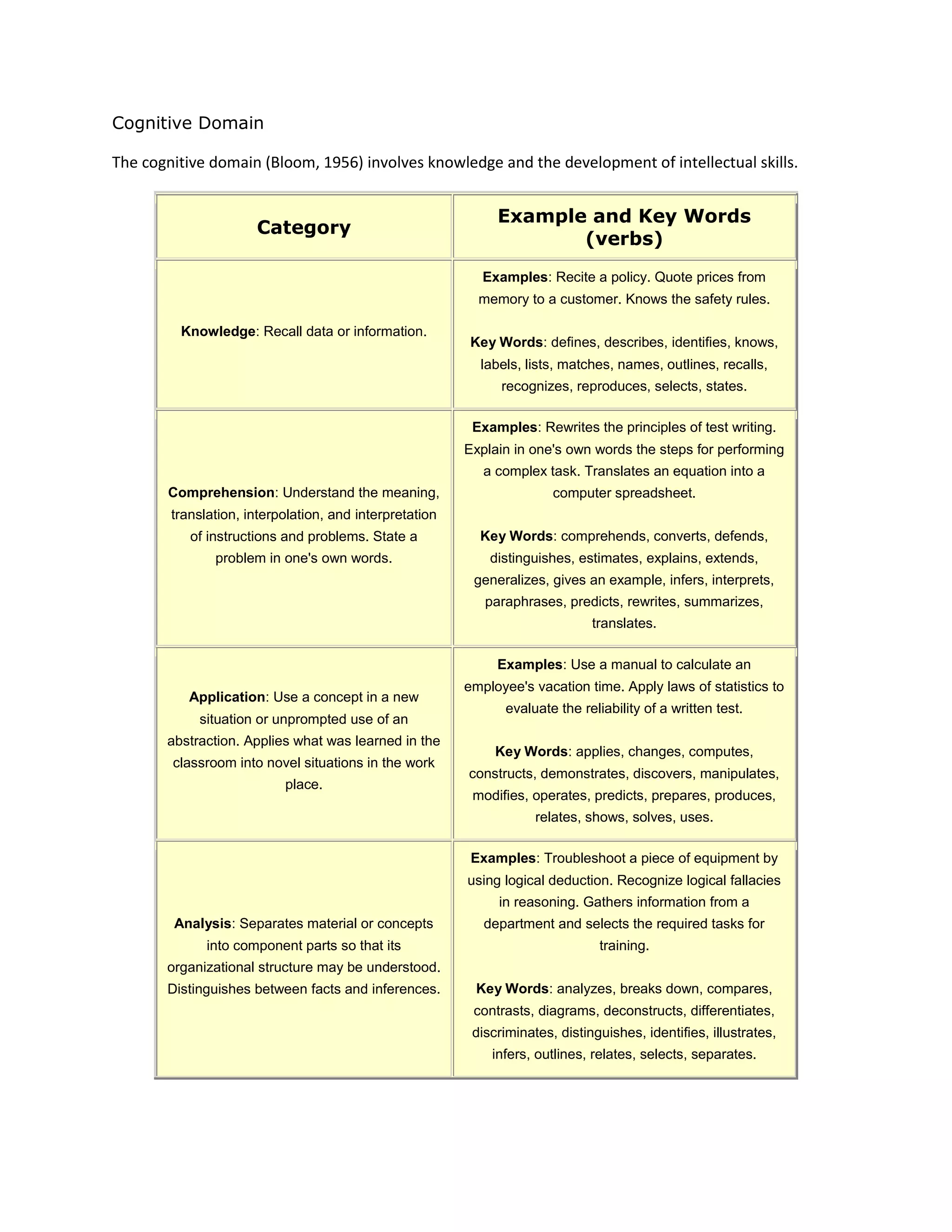
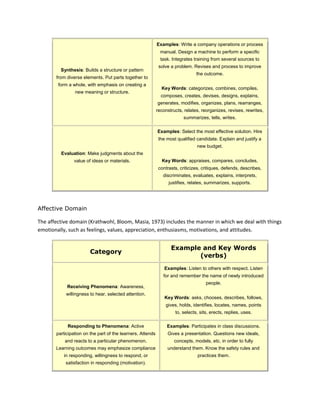
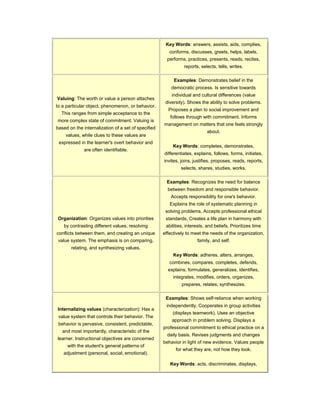
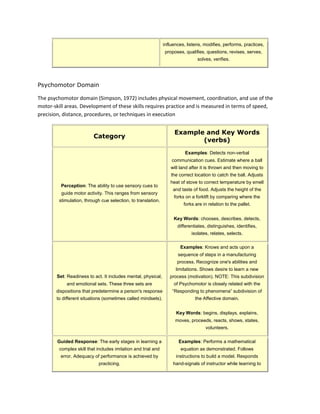
The cognitive domain involves the development of intellectual skills like knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. The affective domain includes how people deal with things emotionally and includes constructs like receiving phenomena, responding to phenomena, and valuing. Both domains describe classifications of learning objectives and outcomes.