This document provides an overview of Docker Swarm 1.12, including:
- Docker Swarm allows clustering of Docker engines into a single virtual engine for orchestrating services across nodes.
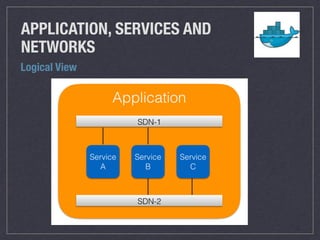
- In Swarm, an application consists of one or more services running on software defined networks, and each service can connect to multiple networks.
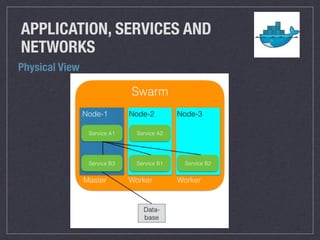
- Swarm has manager nodes that orchestrate tasks and worker nodes that execute tasks, and services are scaled through replicated or global tasks distributed across nodes.
- Key Swarm features include load balancing, high scalability, failover/availability, and flexible container scheduling policies.
- The document concludes with an example Swarm demo of creating a cluster and deploying/managing services.