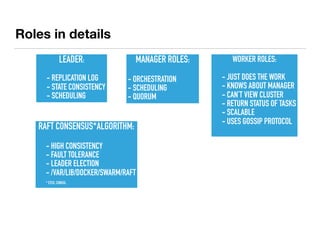
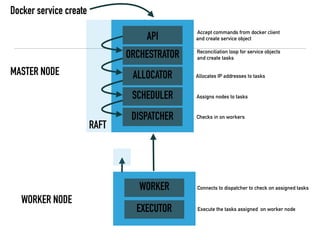
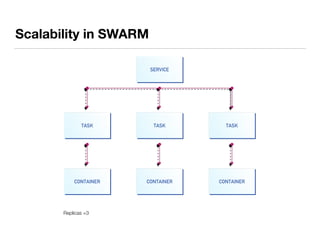
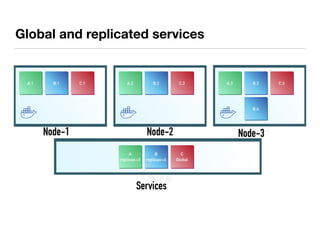
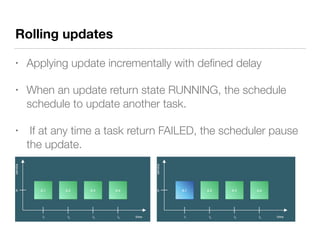
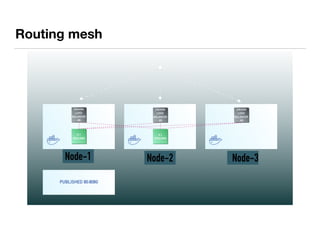
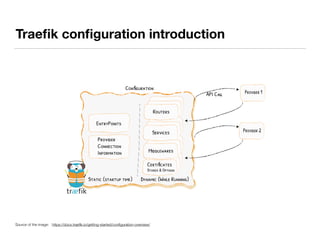
The document presents an overview of container orchestration using Docker Swarm and Traefik, emphasizing their features and benefits in implementing a DevOps culture. It includes a demonstration of a multi-tier application stack deployed on a Docker Swarm cluster, detailing the roles of managers and workers and how services can be scaled and updated. Additionally, it covers the management of sensitive data with Docker Secrets and the seamless integration of Traefik for load balancing and reverse proxying services.