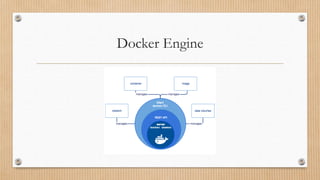
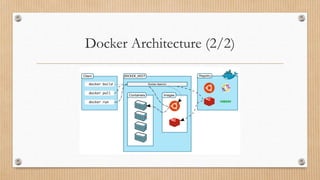
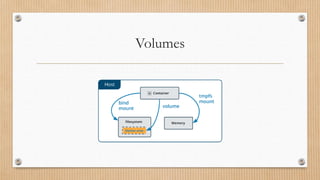
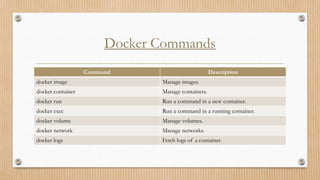
Docker provides tools for building and running containerized applications. The Docker Engine manages Docker objects like images, containers, networks and volumes. Docker Desktop is for Mac/Windows and includes Docker Engine and other tools. Docker Compose defines multi-container apps. Docker Hub is a public registry and Docker Swarm manages clusters of Docker Engines.












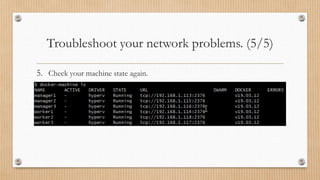
![Docker Machine Installation
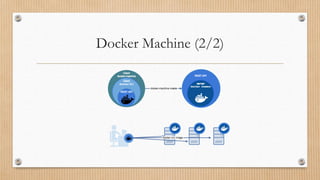
1. Run the command below with Git Bash program.
$ if [[ ! -d "$HOME/bin" ]]; then mkdir -p "$HOME/bin"; fi
&& base=https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.16.2
&& curl -L $base/docker-machine-Windows-x86_64.exe > "$HOME/bin/docker-machine.exe"
&& chmod +x "$HOME/bin/docker-machine.exe"
2. Check the installation by displaying the Docker Machine version.
$ docker-machine version](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docker-200831054228/85/Docker-19-320.jpg)












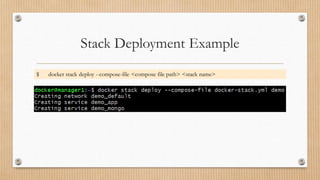
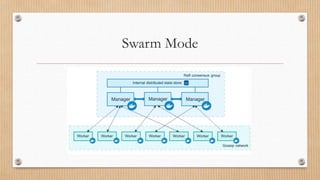
![Deploy a service in the swarm.
$ docker service create --name <service name> <image name> [command] [arguments…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docker-200831054228/85/Docker-34-320.jpg)