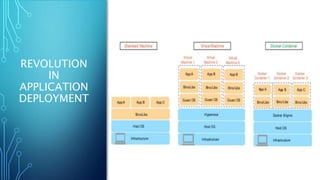
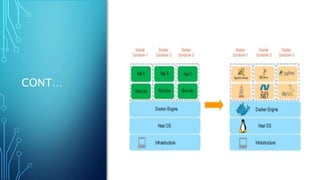
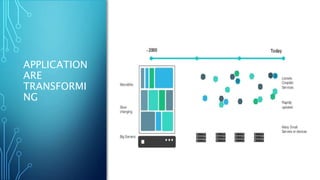
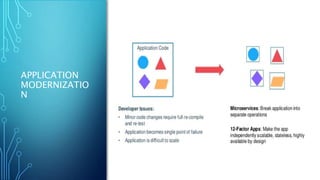
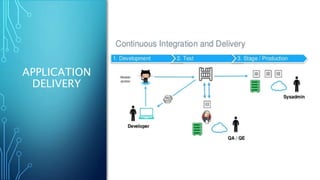
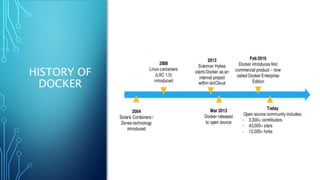
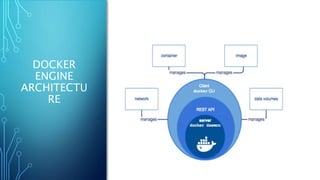
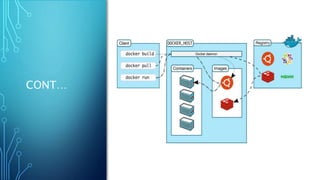
Docker is a platform for developing and running applications within containers. Containers allow applications to be packaged with all their dependencies and run consistently across different computing environments. The Docker platform includes Docker Engine for running containers, Docker images which are templates for containers, and Docker registries for storing images. When running, a container is isolated from other containers and the host machine. Docker uses a client-server architecture with Docker Engine running as a daemon process and CLI client for interacting with it.