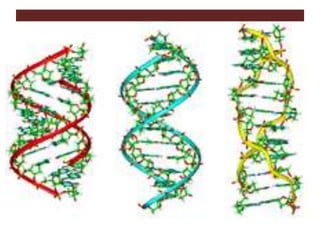
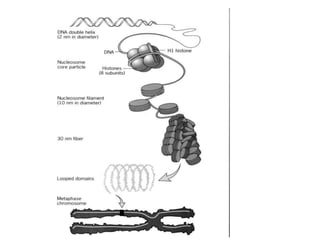
The document discusses the tertiary structure of DNA. It explains that DNA folds into specific 3D shapes, including B-DNA, A-DNA, and Z-DNA. B-DNA is the most common form found in vivo, forming a narrow, elongated double helix. A-DNA is shorter and wider, while Z-DNA has a left-handed helix. The document also describes how DNA is packaged in the cell nucleus through association with histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which coil the DNA into higher-order chromatin structures in the chromosome.