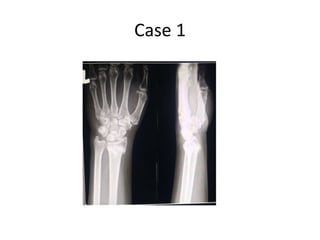
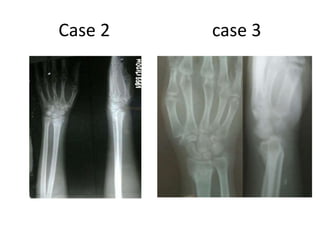
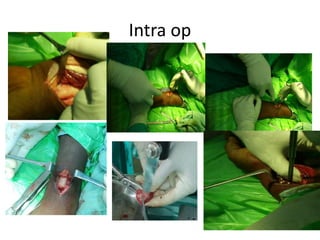
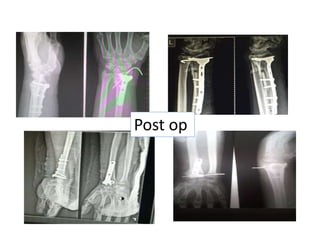
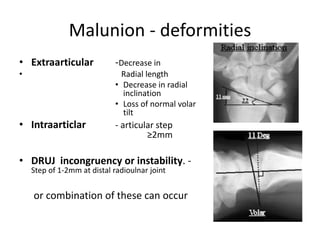
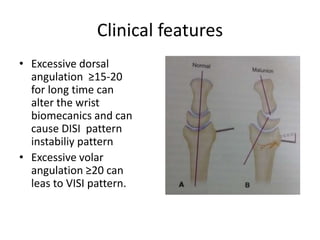
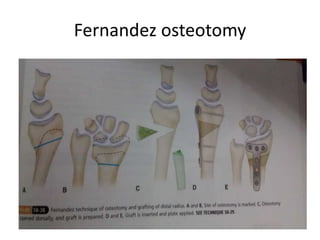
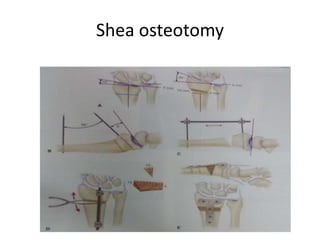
This document describes the management of distal radius malunion through corrective osteotomy and bone grafting with definitive fixation. It discusses the clinical features and radiographic evaluation of distal radius malunion. It also outlines the indications and contraindications for surgical treatment, as well as strategies for treating extra-articular and intra-articular malunion. Specific procedures described for correcting deformities include Fernandez and Shea osteotomies, as well as procedures for addressing distal radioulnar joint incongruencies such as ulnar shortening osteotomy or Darrach's procedure. Post-operative protocols including immobilization and restricted activities are also summarized.