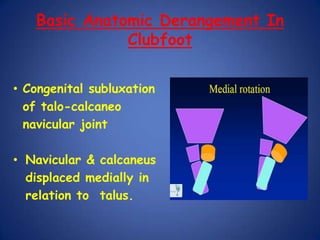
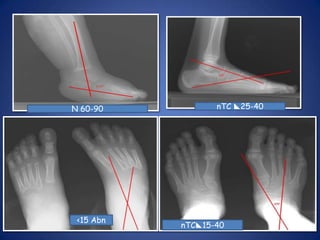
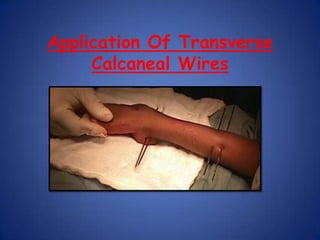
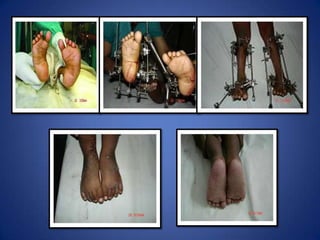
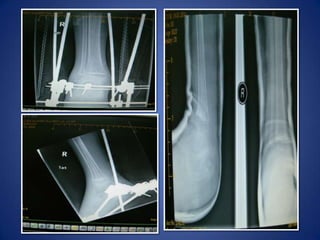
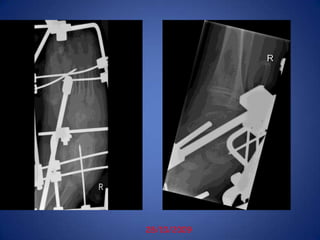
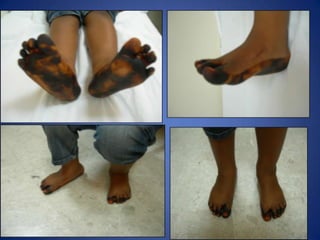
This document discusses Dr. B.B. Joshi's External Stabilization System (JESS) for treating clubfoot, also known as congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV). It provides details on the causes of clubfoot relapse, assessment methods, the basic anatomy derangements in clubfoot, and the principles and components of the JESS fixator system. The JESS system uses gradual distraction with differential rates to correct the deformity while preventing tissue damage. It has advantages over surgery or other external fixators in allowing correction without shortening and minimizing scarring.