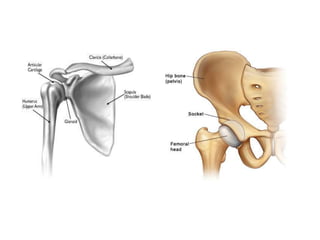
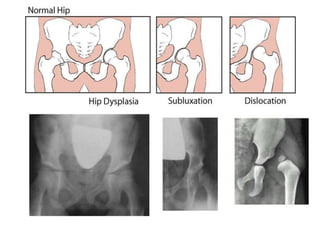
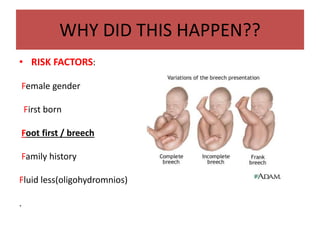
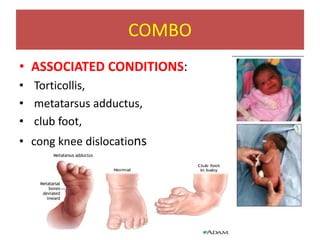
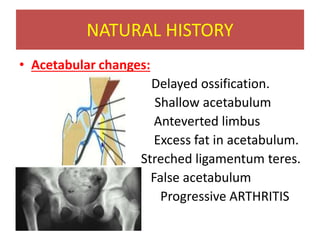
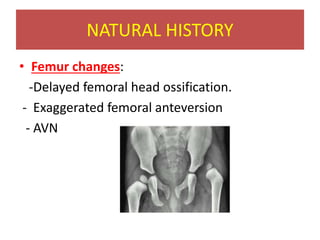
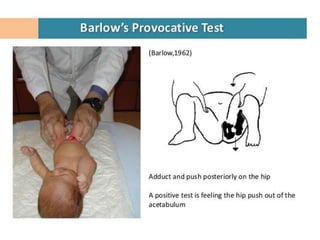
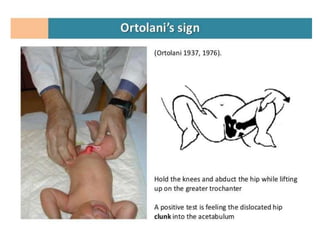
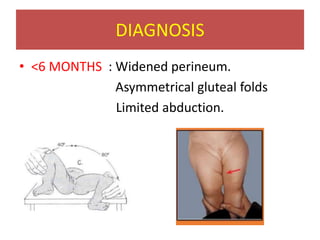
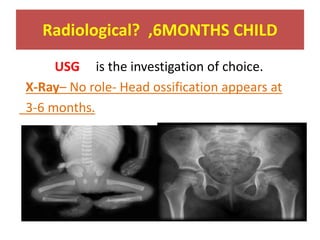
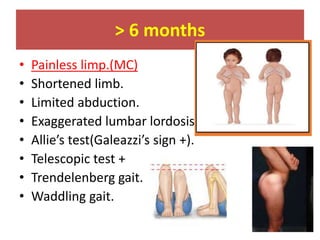
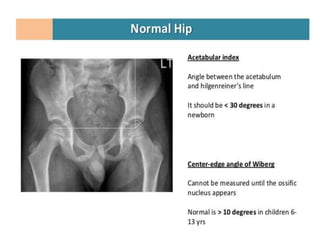
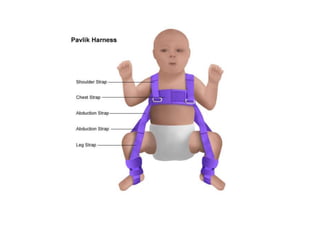
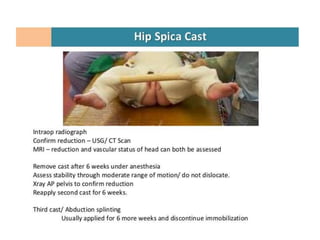
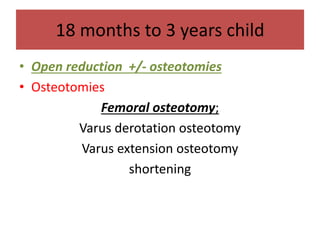
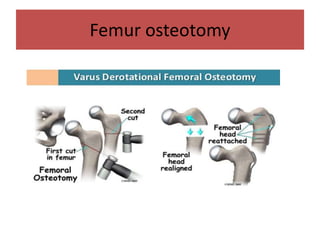
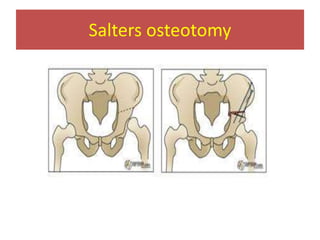
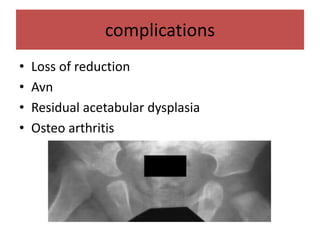
This document discusses hip instability in newborns, which can result in subluxation or dislocation of the femoral head. It outlines risk factors like female gender and breech birth position. For diagnosis, tests like Barlow's and Ortolani's are used in newborns, while ultrasound is preferred over X-ray for babies under 6 months. Treatment for those under 6 months involves closed reduction and immobilization with a Pavlik harness. For older children, open reduction and hip spica casting is often used, and may require femoral or pelvic osteotomies. Complications can include loss of reduction, avascular necrosis, residual dysplasia, and osteoarthritis.