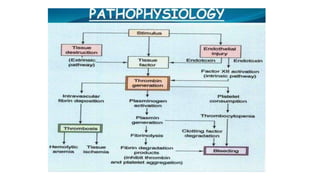
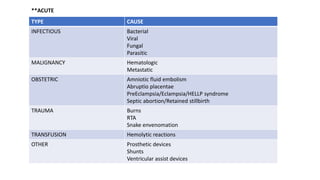
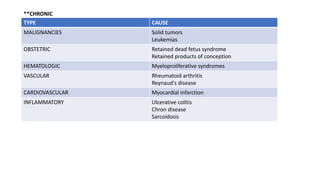
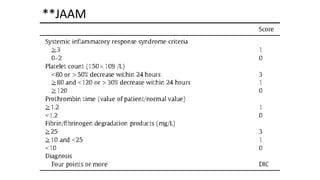
This document discusses disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC), an acquired syndrome characterized by widespread blood clotting. It can be acute or chronic. Acute DIC develops rapidly from sudden exposure to clotting factors, while chronic DIC reflects slower, continuous exposure. Signs include bleeding and organ dysfunction. Diagnosis is based on clinical evaluation and lab tests of clotting factors and platelets. Treatment focuses on the underlying cause, with replacement of platelets or clotting factors for severe bleeding.