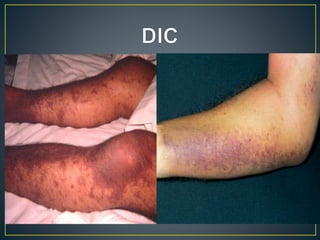
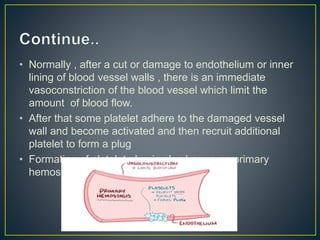
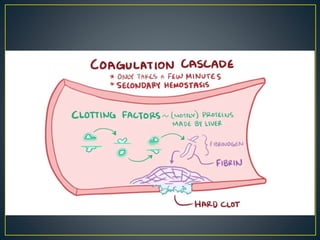
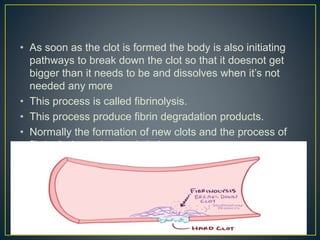
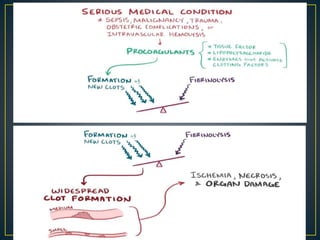
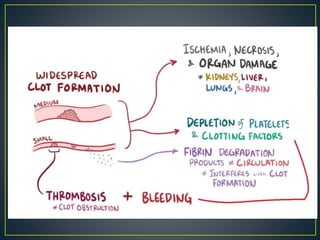
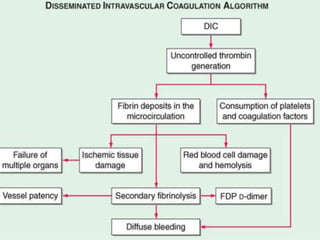
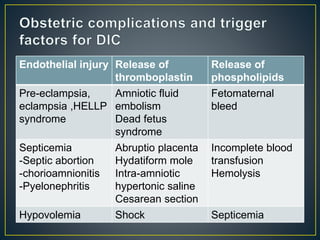
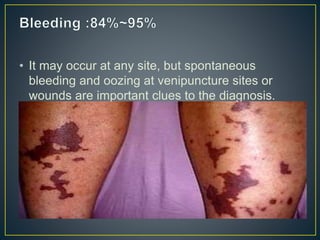
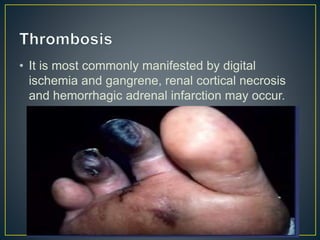
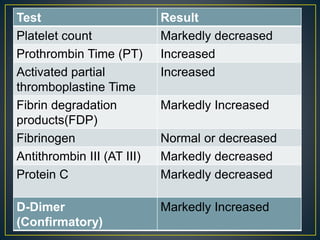
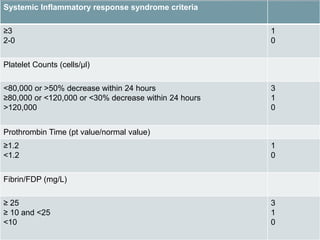
This document discusses disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), providing definitions, mechanisms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment approaches. DIC is described as a thrombo-hemorrhagic disorder caused by excessive activation of coagulation and consumption of clotting factors. It can be triggered by infections, cancers, trauma, and obstetric complications. The diagnostic approach involves checking platelet count, prothrombin time, fibrin degradation products and D-dimer levels. Treatment focuses on treating the underlying condition while replacing clotting factors and platelets as needed to manage bleeding or thrombosis.