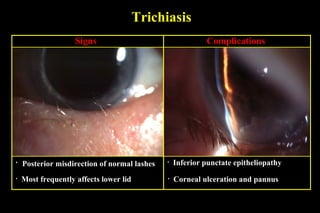
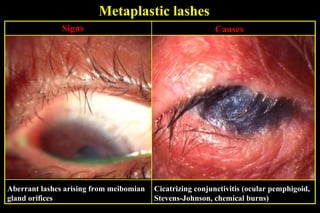
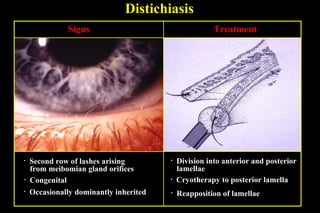
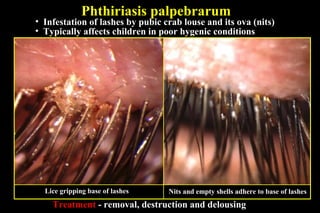
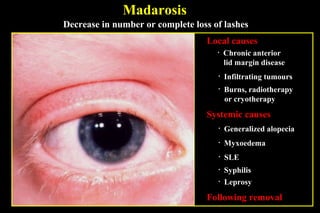
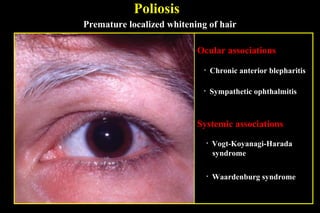
This document summarizes several disorders of the eyelashes including trichiasis, metaplastic lashes, distichiasis, phthiriasis palpebrarum, madarosis, and poliosis. Trichiasis involves the misdirection of normal lashes toward the eye and can cause punctate epitheliopathy and corneal issues. Metaplastic lashes arise from meibomian gland orifices due to conditions like cicatrizing conjunctivitis. Distichiasis has a second row of lashes from the meibomian glands that may be treated by cryotherapy or surgery. Phthiriasis palpebrarum is an infestation by crab lice.