Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times


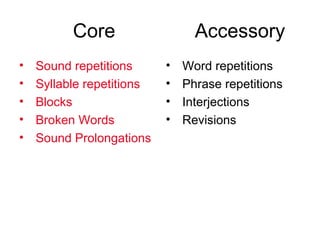





The document discusses different types of disfluencies in speech, categorizing them as either core or accessory disfluencies. It notes there are nine main types of disfluencies that can be further broken down into subcategories like sound or syllable repetitions. The document also examines different schemes for categorizing disfluencies and discusses using person-first respectful terminology when referring to individuals.






