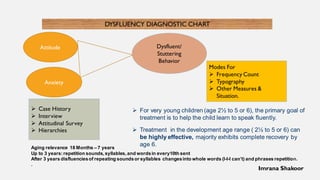
This document discusses disfluency, its types and management. It defines disfluency as errors that disrupt speech flow, such as fillers, repetitions and restarts. The main types are normal developmental disfluency common in young children, stuttering, neurogenic dysfunction, psychogenic dysfunction and language delay. Treatment approaches include fluency shaping, modification therapy and home strategies like maintaining eye contact and responding acceptingly. The document provides details on evaluating and assessing disfluency severity.