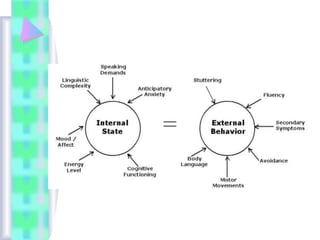
The document discusses language-based dysfluency and stuttering in children. It defines stuttering and describes common types of disruptions in speech. Normal childhood dysfluencies are distinguished from stuttering, which may require intervention. Assessment of potential stuttering involves case history and analyzing speech samples. Treatment aims to help children feel comfortable talking and make speech easier through techniques like modifying rate and tension. Treatment involves both direct methods, like speech modification, and indirect family counseling. The goals are to facilitate fluency and successful communication development.