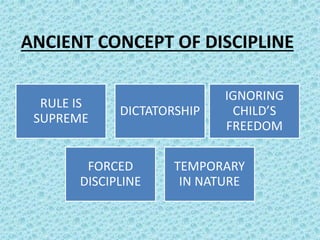
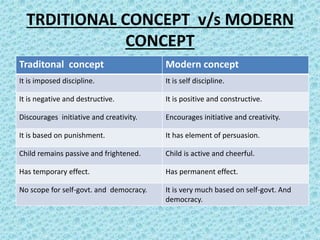
The document discusses the concepts of discipline in traditional and modern contexts. Traditionally, discipline was imposed from external forces and focused on obedience, punishment, and temporary behavioral changes. Modern discipline concepts emphasize voluntary, internal control through positive reinforcement, democratic principles, and fostering initiative and creativity to enable permanent behavioral adaptation. Effective discipline in schools requires a balance of order and student freedom, with discipline arising from students internalizing rules rather than external enforcement alone.