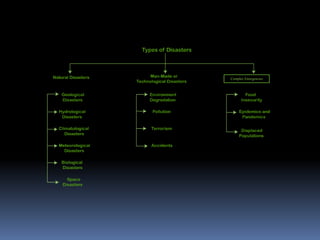
The document discusses different types of disasters, including natural disasters caused by geological, hydrological, climatological, meteorological, biological, and space events; human-made or technological disasters resulting from environmental degradation, pollution, terrorism, and accidents; and complex emergencies involving food insecurity, epidemics and pandemics, and displaced populations impacted by multiple disasters. Natural disasters are broadly classified according to their origin or cause, while human-made disasters typically involve human activity or negligence and can exacerbate the impacts of natural disasters. Complex emergencies incorporate elements of both natural and human-made disasters that overwhelm local capabilities.