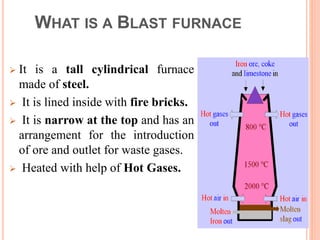
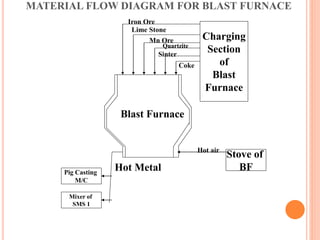
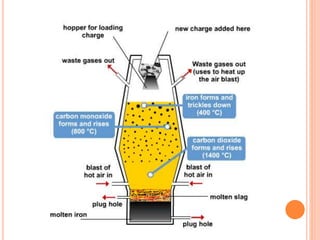
The document discusses the function and structure of a blast furnace, which reduces iron oxides into liquid iron through a process involving iron ore, coke, and limestone. It outlines the operation steps and by-products, including molten iron and slag, with additional details about the furnace’s design and material flow. The presentation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing process in a blast furnace.