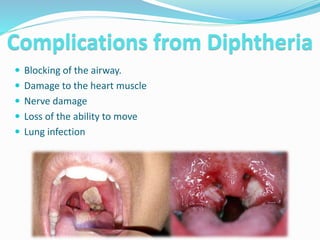
Diphtheria is a contagious bacterial infection of the nose and throat caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. It is spread through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing. Symptoms include a thick gray membrane in the throat, sore throat, difficulty breathing, and fever. Complications can include heart damage, nerve damage, kidney problems, and trouble breathing if the membrane blocks the airway. Diphtheria is preventable through vaccination and treated with antitoxin to neutralize the toxin and antibiotics to kill the bacteria.