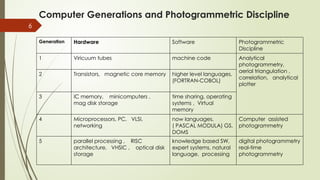
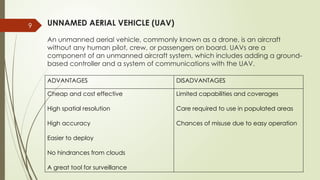
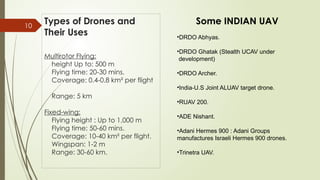
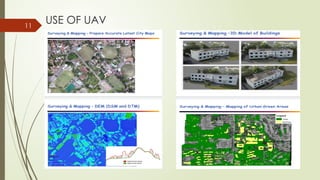
The document discusses the role of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in digital photogrammetry, detailing the basics of photogrammetry, data acquisition methods, hardware and software requirements, as well as the types of drones and their applications. It highlights the importance of UAVs in various sectors such as agriculture, infrastructure planning, and wildlife monitoring, emphasizing their capabilities and advancements in technology. The conclusion reflects on how drones have revolutionized data collection and decision-making processes, aided by improvements in storage and analysis techniques.